Abstract
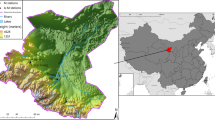
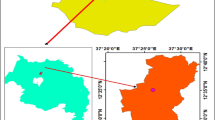
Due to the over use of available water resources, it has become very important to define appropriate strategies for planning and management of irrigated farmland. In this paper, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (Jing-Jin-Ji) region was chosen as the case study area for its special political and economic status and its severe water problem. To achieve effective planning, the information about crop water requirements, irrigation withdrawals, soil types and climatic conditions were obtained in the study area. In the meantime, a GIS method was adopted, which extends the capabilities of the crop models to a regional level. The main objectives of the study are: 1) to estimate the spatial distribution of the evapotranspiration of spring maize; 2) to estimate climatic water deficit; 3) to estimate the yield reduction of spring maize under different rainfed and irrigated conditions. Based on the water deficit analysis, recommended supplemental irrigation schedule was developed using CropWat model. Compared to the rainfed control, the two or three times of supplemental water irrigated to spring maize at the right time reduced the loss of yield, under different scenarios.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R G, Pereira L A, Raes D et al., 1998. Crop evapotranspiration. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. Rome: FAO, 293.
Chen Zhikai, 2000. Sustainable development and utilization of China’s water resources in 21st century. Engineering Sciences in China, 2(3), 7–11. (in Chinese)
Clarke D, Smith M, El-Askari K, 1998. CropWat for Windows: User Guide. Southampton: University of Southampton, 1–43.
Dechmi F, Playan E, Faci J M et al., 2003, Analysis of an irrigation district in northeastern Spain II. Irrigation evaluation, simulation and scheduling. Agricultural Water Management, 61: 93–109.
Doorenbos J, Kassam A H, 1979. Yield response to water. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 33. Rome: FAO, 193.
Doorenbos J, Pruitt W O, 1977. Crop water requirements. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 24. Rome: FAO, 144.
FAO, 1979. Yield response to water. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 33. Rome: FAO, 112–113.
FAO, 1992. CROPWAT A computer program for irrigation planning and management. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 46. Rome: FAO, 126.
Gouranga Kar, Verma H N, 2005. Climatic water balance, probable rainfall, rice crop water requirements and cold period in AER 12.0 in India. Agricultural Water Management, 72: 15–32.
Han Shumin, Cheng Yisong, Hu Chunsheng, 2005. Relationship between crop coefficient and precipitation pattern in the piedmont of Mt. Taihang. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 23(5): 152–158. (in Chinese)
Jensen M E, Burman R D, Allen R G, 1990, Evapotranspiration and irrigation water requirements. In: Manual and Reports on Engineering Practice. New York: American Society of Civil Engineers, 15–41.
Martyniak L, Dabrowska-Zielinska K, Szymczyk R et al., 2006. Validation of satellite-derived soil-vegetation indices for prognosis of spring cereals yield reduction under drought conditions—Case study from central-western Poland. Advances in Space Research, 8: 1–6.
Smith M, 1992. CROPWAT, A computer program for irrigation planning and management. In: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 46. Rome: FAO. 1–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. SU210200)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Liu, D. & Zhang, Y. Water requirements and irrigation scheduling of spring maize using GIS and CropWat model in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Chin. Geograph.Sc. 17, 56–63 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-007-0056-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-007-0056-3