Abstract
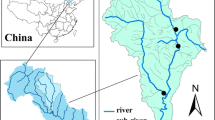
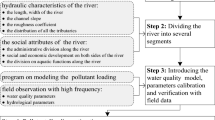
Individual participation of pollutants in the pollution load should be estimated even if roughly for the appropriate environmental management of a river basin. It is difficult to identify the sources and to quantify the load, especially in modeling nonpoint source. In this study a revised model was established by integrating point and nonpoint sources into one-dimensional Streeter-Phelps (S-P) model on the basis of real-time hydrologic data and surface water quality monitoring data in the Jilin Reach of the Songhua River Basin. Chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) loads were estimated. Results showed that COD loads of point source and nonpoint source were 134 958 t/yr and 86 209 t/yr, accounting for 61.02% and 38.98% of total loads, respectively. NH3-N loads of point source and nonpoint source were 16 739 t/yr and 14 272 t/yr, accounting for 53.98% and 46.02%, respectively. Point source pollution was stronger than nonpoint source pollution in the study area at present. The water quality of upstream was better than that of downstream of the rivers and cities. It is indispensable to treat industrial wastewater and municipal sewage out of point sources, to adopt the best management practices to control diffuse pollutants from agricultural land and urban surface runoff in improving water quality of the Songhua River Basin. The revised S-P model can be successfully used to identify pollution source and quantify point source and nonpoint source loads by calibrating and validating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Zeid M A, 1998. Water and sustainable development: The vision for world water, life and the environment. Water Policy, 1: 9–19. DOI: 10.1016/s1366-7017(98)00002-6
Belic S S, Belic A V, 1996. Water quality changes in a small plain agricultural catchment area. Water Science and Technology, 33(4–5): 205–210. DOI: 10.1016/s0273-1223(96)00232-6
Chen Youyuan, Hui Erqing, Jin Chunji et al.2003. A hydrological method for estimation of nonpoint source pollution loads and its application. Research of Environmental Sciences, 16(1): 10–13. (in Chinese)
Drolc A, Koncan J Z, Tisler T, 2007. Evaluation of point and diffuse sources of nutrients in a river basin on base of monitoring data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129: 461–470. DOI: 10.1007/s10661-006-9376-5
Enger E D, Smith B F, 2006. Environmental Science: A Study of Interrelationships (11th edition). New York: McGraw-Hill Press, 347–349.
European Environment Agency, 1999. Environment in the European Union at the turn of the century. In: Environmental Assessment Report No.2, 446.
Hong Xiaokang, Li Huaien, 2000. Correlation method of water quality and quantity and its application to load estimation of nonpoint source pollution. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 16(4): 384–386. (in Chinese)
Ichiki A, Yamada K, Ohnishi T, 1996. Prediction of runoff pollutant load considering characteristics of river basin. Water Science & Technology, 33(4–5): 117–126. DOI: 10.1016/s027-3-1223(96)00221-1
Knisel W G, 1982. Systems for evaluating nonpoint source pollution: an overview. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 24: 173–184. DOI: 10.1016/s0378-4754(82)90099-4
Leon L F, Lam D C, Swayne D A et al.2000. Integration of a nonpoint source pollution model with a decision support system. Environmental Modelling & Software, 15(3): 249–255. DOI: 10.1016/s1364-8152(00)00011-6
Leon L F, Soulis E D, Kouwen N et al.2001. Nonpoint source pollution: a distributed water quality modeling approach. Water Research, 35(4): 997–1007. DOI: 10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00-336-5
Li Huaien, 2000. Mean concentration method for estimation of nonpoint source load and its application. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20(4): 397–400. (in Chinese)
Luo B, Li J B, Huang G H et al.2006. A simulation-based interval two-stage stochastic model for agricultural nonpoint source pollution control through land retirement. Science of the Total Environment, 361(1–3): 38–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.053
Qian Yi, Zhang Jie, Li Guibai, 2007. Study on Water Pollution and Control Strategy in Northeast China. Beijing: Science Press, 135–138. (in Chinese)
Taebi A, Droste R L, 2004. Pollution loads in urban runoff and sanitary wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 327(1–3): 175–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.11.015
Torrecilla N J, Galve J P, Zaera L G et al.2005. Nutrient sources and dynamics in a Mediterranean fluvial regime (Ebro river, NE Spain) and their implications for water management. Journal of Hydrology, 304(1–4): 166–182. DOI:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.07.029
USEPA, 2006. Need for Watershed Approaches. http://www.epa.gov/owow/watershedframework/ch4.html.
Withers P J A, Lord E I, 2002. Agricultural nutrient inputs to rivers and groundwaters in the UK: Policy, environmental management and research needs. Science of the Total Environment, 282–283: 9–24. DOI: 10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00935-4
Yang Yuhong, Yan Baixing, Shen Bo et al.2009. Study on load of nonpoint source pollution in the Second Songhua River Basin. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(1): 161–165. (in Chinese)
Yue Yong, Cheng Hongguang, Yang Shengtian et al.2007. Integrated assessment of non-point source pollution in Songhuajiang River Basin. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 27(2): 231–236. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2004CB418502, No. 2007CB407205) and the Knowledge Innovation Programs of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KSCX1-YW-09-13)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yan, B. & Shen, W. Assessment of point and nonpoint sources pollution in Songhua River Basin, Northeast China by using revised water quality model. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 20, 30–36 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-010-0030-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-010-0030-3