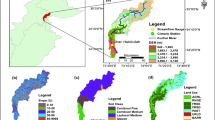
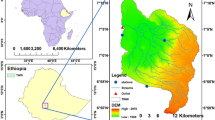
Abstract
The impacts of future climate change on streamflow of the Dongliao River Watershed located in Jilin Province, China have been evaluated quantitatively by using a general circulation model (HadCM3) coupled with the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) hydrological model. The model was calibrated and validated against the historical monitored data from 2005 to 2009. The streamflow was estimated by downscaling HadCM3 outputs to the daily mean temperature and precipitation series, derived for three 30-year time slices, 2020s, 2050s and 2080s. Results suggest that daily mean temperature increases with a changing rate of 0.435°C per decade, and precipitation decreases with a changing rate of 0.761 mm per decade. Compared with other seasons, the precipitation in summer shows significant downward trend, while a significant upward trend in autumn. The annual streamflow demonstrates a general downward trend with a decreasing rate of 0.405 m3/s per decade. The streamflow shows significant downward and upward trends in summer and in autumn, respectively. The decreasing rate of streamflow in summer reaches 1.97 m3/s per decade, which contributes primarily to the decrease of streamflow. The results of this work would be of great benifit to the design of economic and social development planning in the study area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold J G, Fohrer N, 2005. SWAT2000: Current capabilities and research opportunities in applied watershed modelling. Hydrological Processes, 19(3): 563–572. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5611
Arnold J G, Srinivasan R, Muttiah R S et al., 1998. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 34(1): 73–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Chen Xiaofeng, 2009. Simulation study on runoff in Bailian River Basin based on SWAT model. International Journal Hydroelectric Energy, 27(1): 21–24. (in Chinese)
Collins M, Tett S F B, Cooper C, 2001. The internal cliamte variability of HadCM3, a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments. Cliamte Dynamics, 17: 61–81. doi: 10.1007/s003820000094
Dibike Y B, Coulibaly P, 2005. Hydrologic impact of cliamte change in the Saguenay watershed: Comparision of downscaling methods and hydrologic models. Journal of hydrology, 307(1–4): 145–163. doi: 10.1016/j.hydrol.2004.10.012
Fan L L, Shen Z Y, Liu R M et al., 2008. Spatial distribution of non-point source pollution in Daninghe Watershed based on SWAT model. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(4): 133–137. (in Chinese)
Gao Yang, Zhu Bo, Zhou Pei et al., 2008. Study on the application AnnAGNPS and SWAT to non-point resource pollution research: A case of Yanting agro-ecological experimental station, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Agricultural Science), 26(6): 567–574. (in Chinese)
Gassman P W, Reyes M R, Green C H et al., 2007. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications, and future research directions. Transactions of the Asabe, 50(4): 1211–1250.
Hu Lianwen, Wang Xuejun, Luo Dinggui et al., 2007. Effect of sub-watershed partitioning on flow, sediment and nutrient predictions. Advances in Water Science, 18(2): 235–240. (in Chinese)
Jha M, Pan Z, Takle E S et al., 2004. Impacts of climate change on streamflow in the upper Mississippi River Basin: A regional climate model perspective. Journal of Geophysical Research-atmosphere, 109(D9): 1–12. doi: 10.1029/2003JD003686
Jiang T, 2005. Monthly Water Balance Modeling for Hydrological Impact Assessment of Climate Change in the Dongjiang (East River) Basin, South China. Hong Kong: The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Kumar S, Merwade V, Kam J et al., 2009. Streamflow trends in Indiana: Effects of long term persistence, precipitation and subsurface drains. Journal of Hydrology, 374(1–2): 171–183. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.012
Li Di, 2011. Simulation of Agriculture Non-point Source Pollution in Dongliaohe Watershed Based on SWAT Model. Changchun: Jilin University. (in Chinese)
Moriasi D, Arnold J, Van Liew M et al., 2007. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 50(3): 885–900.
Muleta M K, Nicklow J W, 2005. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis coupled with automatic calibration for a distributed watershed model. Journal of Hydrology, 306(1–4): 127–145. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.09.005
Nasha J E, Sutcliffea J V, 1970. River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part I-A discussion of principles. Journal of Hydrology, 10(3): 282–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(70)-90255-6
Neitsch S L, Arnold J G, Kiniry J R et al., 2005. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2005. Temple Texas: Grassland, Soil And Water Research Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service and Blackland Research Center, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station.
Qin Yaomin, Xu Yanling, Li Huaien, 2009. SWAT model of non-point source pollution under different land use scenarios in the Heihe river basin. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 29(2): 440–448. (in Chinese)
Risbey J S, Stone P H, 1996. A case study of the adequacy of GCM simulations for input to regional climate change. Journal of Climate, 9(7): 1441–1467.
Santhi G, Arnold J G, Williams J R et al., 2001. Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 37(6): 1169–1188. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03630.x
Sun Wei, 2011. Study on Surface Water Quality Assessment of Liao River Source Region Based on GIS. Changchun: Jilin University. (in Chinese)
Wigley T M L, Jones P D, Briffa K R et al., 1990. Obtaining sub-grid-scale information from coarse-resolution general circulation model output. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95(D25): 1943–1953. doi: 10.1029/JD095iD02p01943
Wilby R L, Dawson C W, Barrow E M, 2002. SDSM—A decision support tool for the assessment of regional climate change impacts. Environmental Modelling & Software, 17(2): 147–159.
Wood A W, Leung L R, Sridhar V et al., 2004. Hydrologic implications of dynamical and statistical approaches to downscaling climate model outputs. Climatic Change, 62(1–3): 189–216. doi: 10.1023/B:CLIM.0000013685.99609.9e
Xu C Y, 1999a. Climate change and hydrologic models: A review of existing gaps and recent research developments. Water Resources Management, 13(5): 369–382. doi: 10.1023/A:1008 190900459
Xu C Y, 1999b. From GCMs to river flow: A review of downscaling methods and hydrologic modelling approaches. Progress in Physical Geography, 2(23): 229–249. doi: 10.1177/030913339902300204
Zhang Xiang, Yang Qingchun, Chen Yanfei, 2011. Coupling of hydrological and ecological process: An approach to implement the sustainable water resources management in Hanjiang watershed. 2011 International Symposium on Water Resource and Environmental Protection (ISWREP), 2: 1078–1083. doi: 10.1109/ISWREP.2011.5893201
Zhao Fangfang, Xu Zongxue, 2009. Hydrological response to climate change in headwater catchment of the Yellow River Basin. Resources Science, 31(5): 722–730. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (No. 2009ZX07526-006-04-01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Lu, W., Yang, Q. et al. Hydrological impacts of climate change on streamflow of Dongliao River watershed in Jilin Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 22, 522–530 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0559-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0559-4