Abstract
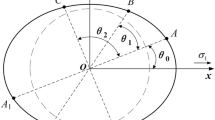
In order to obtain the distribution rules of in situ stress and mining-induced stress of Beiminghe Iron Mine, the stress relief method by overcoring was used to measure the in situ stress, and the MC type bore-hole stress gauge was adopted to measure the mining-induced stress. In the in situ stress measuring, the technique of improved hollow inclusion cells was adopted, which can realize complete temperature compensation. Based on the measuring results, the distribution model of in situ stress was established and analyzed. The in situ stress measuring result shows that the maximum horizontal stress is 1.75–2.45 times of vertical stress and almost 1.83 times of the minimum horizontal stress in this mineral field. And the mining-induced stress measuring result shows that, according to the magnitude of front abutment pressure the stress region can be separated into stress-relaxed area, stress-concentrated area and initial stress area. At the −50 m mining level of this mine, the range of stress-relaxed area is 0–3 m before mining face; the range of stress-concentrated area is 3–55 m before mining face, and the maximum mining-induced stress is 16.5–17.5 MPa, which is 15–20 m from the mining face. The coefficient of stress concentration is 1.85.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ZHAO J, HEFNY A M, ZHOU Y X. Hydrofracturing in situ stress measurements in Singapore granite [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2005, 42: 577–583.
SHIN K, SUGAWARA K, OKUBO S. Application of Weibull’s theory to estimating in situ maximum stress σH by hydrofracturing [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2001, 38: 413–420.
CAI M F, YU B, QIAO L, CHEN G, LI C. Experience of in situ stress measurement with hydrofracturing and overcoring techniques in Ekou mine, China [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1997, 34(2): 299–302.
CHARSLEY A D, MARTIN C D, MCCREATH D R. Sleeve-fracturing limitations for measuring in situ stress in an anisotropic stress environment [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2003, 40: 127–136.
BECKER A. In situ stress data from the Jura Mountains—New results and interpretation [J]. Terra Nova, 1999, 11(1): 9–15.
SINGH D P, SINGH P K. An experimental approach for developing an alternative method for determining in situ stress using acoustic emission technique [J]. Indian Journal of Engineering and Materials Sciences, 1998, 5(3): 106–110.
HOLCOMB D J. Observations of the Kaiser effect under multiaxial stress states-Implications for its use in determining in-situ stress [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1993, 20(19): 2119–2122.
HUANG Song-ling, LI Lu-ming, SHI Ke-ren, WANG Xiao-feng. Magnetic field properties caused by stress concentration [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2004, 11(1): 23–26.
OUYANG Zhen-hua, CAI Mei-feng, LI Chang-hong, XIE Mo-wen. Seepage effects of groundwater and its make-up water on triggering ground subsidence [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2006, 13(1): 11–15.
DING De-xin, ZHANG Zhi-jun, BI Zhong-wei. A new approach to predicting mining induced surface subsidence [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(4): 438–444.
DENG Jian, BIAN Li, LI Xi-bing. Analysis of factors and countermeasures of mining subsidence in Kaiyang Phosphorus Mine [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(6):733–737.
CAI Mei-feng, QIAO Lan, YU Bo, WANG Shuang-hong. Stress measurement with an improved hollow inclusion technique In Jinchuan Nickel Mine [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2000, 7(3): 157–160.
CAI M F, QIAO L, LI C, YU J, YU B, CHEN G. Application of an improved hollow inclusion technique for in situ stress measurement in Xincheng gold mine [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1995, 32(7): 735–739.
CAI M F, JI H G, WANG J A. Study of the time-space-strength relation for mining seismicity at Laohutai coal mine and its prediction [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2005, 42: 145–151.
WU Man-lu, ZHANG Chun-shan, LIAO Chun-ting, MA Yin-sheng, OU Ming-yi. The recent state of stress in the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau according to in-situ stress measurements [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(2): 327–332. (in Chinese)
LI F Q. In situ stress state in Mainland China [J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1995, 145: 775–787.
CAI M F, QIAO L, LI C, YU B, WANG S H. Results of in situ stress measurement and their application to mining design at five Chinese metal mines [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2000, 37: 509–515.
CAI Mei-feng. Measuring theory and technique of in situ stress [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
OUYANG Zhen-hua. Study on the coupling effect of seepage and stress on failure of mining rock mass [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2006. (in Chinese)
QIAO Lan, OUYANG Zhen-hua, LAI Xing-ping, MIAO Sheng-jun. In situ stress measuring and its result analysis in Sanshandao gold mine of China [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2004, 26(6): 569–571. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(10702072, 10632100) supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, Zh., Li, Ch., Xu, Wc. et al. Measurements of in situ stress and mining-induced stress in Beiminghe Iron Mine of China. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 16, 85–90 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0014-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0014-6