Abstract
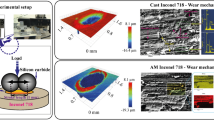
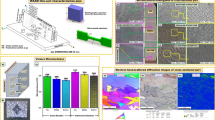
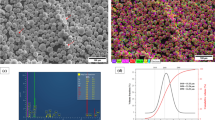
Pearlitic ductile irons (PDIs) are used in transportation and nuclear energy industries. In heavy loading situation, the service life of PDI is affected by numerous tribo aspects. In this study, surface of the PDI is alloyed with WC-12%Co powder using a high power fibre laser. The wear properties of the base material and laser alloying samples were investigated by tribometer with various parameters, i.e., temperature, load and sliding speed. Based on experimental test, the load has maximum percentage of contribution and followed by sliding speed and working temperature. The optimized tribological parameters by Grey relational analysis (GRA) were established and those values are closely matched with predicted values. Besides, base material and laser alloying surfaces were examined through Vickers hardness machine, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and roughness tester. The laser altered specimen shows no defects and improves the wear properties than substrates. The identified optimal tribological parameters are load of 30 N, speed of 0.5 m/s and working temperature of 300 °C, and load of 30 N, speed of 0.5 m/s and working temperature of 200 °C for base metal and laser alloying samples, respectively.
摘要
珠光体球墨铸铁(PDIs)应用于运输和核能工业。在重载情况下, PDI的使用寿命受到多方面的 影响。在本研究中, 采用高功率光纤激光器使用WC-12%Co粉末对PDI表面进行合金化。在各种实 验参数下, 包括温度、载荷和滑动速度, 使用摩擦计研究了基材和激光合金化试样的磨损性能。实验 结果表明, 负载具有最大贡献百分比, 其次是滑动速度和工作温度。通过灰色关联分析(GRA)建立了 优化的摩擦学参数, 与预测值匹配。此外, 还通过维氏硬度机、扫描电镜(SEM)和粗糙度测试仪对基 材和激光合金表面进行了研究。激光处理没有使试样产生缺陷, 还改善了其磨损性能。母材和激光合 金化试样的最佳摩擦学参数分别为载荷30 N, 速度0.5 m/s及工作温度300 °C和载荷30N, 速度0.5 m/s 及工作温度200 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- L :
-
Load
- SV:
-
Sliding velocity
- T :
-
Temperature
- GRA:
-
Grey relational analyses
- GRC:
-
Grey relational coefficient
- Lv:
-
Volume loss
- CoF:
-
Coefficient of friction
- R w :
-
Wear rate
- DF:
-
Degree of freedom
- SS:
-
Sum of squares
- V:
-
Variance
- P :
-
Percentage of contribution
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
WILK-KOLODZIEJCZYK D, REGULSKI K, GUMIENNY G. Comparative analysis of the properties of the nodular cast iron with carbides and the austempered ductile iron with use of the machine learning and the support vector machine [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 87: 1077–1093. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-016-8510-y.
HUTTER G, ZYBELL L, KUNA M. Micro mechanisms of fracture in nodular cast iron: From experimental findings towards modeling strategies-A review [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2015, 144: 118–141. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.06.042.
JEYAPRAKASH N, SIVASANKARAN S, PRABU G, YANG C H, ALABOODI A S. Enhancing the tribological properties of nodular cast iron using multi wall carbon nano-tubes (MWCNTs) as lubricant additives [J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6: 045038. DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aafce9.
CESCHINI L, CAMPANA G, PAGANO N, ANGELINI V. Effect of laser surface treatment on the dry sliding behaviour of the EN-GJS400-12 ductile cast iron [J]. Tribology International, 2016, 104: 342–351. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.09.018.
PODGORNIK B, VIZINTIN J, THORBJORNSSON I, JOHANNESSON B, THORGRIMSSON J T, MARTINEZ CELIS M, VALLE N. Improvement of ductile iron wear resistance through local surface reinforcement [J]. Wear, 2012, 274–275: 267-273. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.09.005.
QI X, ZHU S, DING H, ZHU Z, HAN Z. Microstructure and wear behaviors of WC-12%Co coating deposited on ductile iron by electric contact surface strengthening, [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 282: 672–679. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.06.032.
JEYAPRAKASH N, YANG Che-hua, MUTHUKANNAN DURAISELVAM, PRABU G. Microstructure and tribological evolution during laser alloying WC- 12%Co and CnC2-25%NiCr powders on nodular iron surface, [J]. Results in Physics, 2019, 12: 1610–1620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.01.069.
BENYOUNIS K Y, FAKRON OMA, ABBOUD A G, OLABI A G, HASHMI M J S. Surface melting of nodular cast iron by Nd-YAG laser and TIG [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2005, 170: 127–132. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.04.108.
VILAR R. Laser powder deposition [J]. Comprehensive Materials Processing, 2014, 10: 163–216.
WANG Zhong-qi, ZHANG Jian-long, ZHANG Peng, ZHOU Hong, ZHOU Ti. Effect of the 75 ferrosilicon on the laser cladding on gray cast iron [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2019, 113: 64–71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.12.013.
NABHANI M, RAZAVI R S, BAREKAT M. Corrosion study of laser cladded Ti-6A1-4V alloy in different corrosive environments [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 97: 234–241. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.01.023.
LI Yong-jian, DONG Shi-yun, HE Peng, YAN Shi-xing, LI En-zhong, LIU Xiao-ting, XU Bin-shi. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of new-type FeNiCr laser cladding alloy coating on nodular cast iron [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 269: 163–171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019. 02.010.
RAMESH B N, SURESHA B. Optimization of tribological parameters in abrasive wear mode of carbon-epoxy hybrid composites [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 59: 38–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.023.
ALAJMI M, SHALWAN A. Correlation between mechanical properties with specific wear rate and the coefficient of friction of graphite/epoxy composites [J]. Materials, 2015, 8: 4162–4175. DOI: 10.3390/ma8074162.
JEYAPRAKASH N, YANG C H, TSENG S P. Wear tribo-performances of laser cladding colmonoy-6 and stellite-6 micron layers on stainless steel 304 using Yb:YAG disk laser [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2020. DOI: 10.1007/sl2540-019-00526-6.
AXEN N, JACOBSON S. A model for abrasive wear resistance of multiphase materials [J]. Wear, 1994, 174: 187–199.
JEYAPRAKASH N, YANG Che-hua, SIVASANKARAN S. Laser cladding process of cobalt and nickel based hard-micron-layers on 316L-stainless-steel-substrate [J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 35: 142–151. DOI: 10.1080/10426914.2019.1692354.
LEE G Y, DHARAN C K H, RITCHIE R O. A physically-based abrasive wear model for composite materials [J]. Wear, 2002, 252: 322–331. DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00896-1.
YEN B, DHARAN C K H. A model for the abrasive wear of fiber-reinforced polymer composites [J]. Wear, 1996, 195: 123–127.
BIJWE J, RAJESH J J, JEYAKUMAR A, GHOSH A, TEWARI U S. Influence of solid lubricants and fibre reinforcement on wear behaviour of polyethersulphone [J]. Tribology International, 2000, 33: 697–706. DOI: 10.1016/ 0043-1648(95)06804-X
PATNAIK A, SATAPATHY A, BISWAS S. Investigations on three-body abrasive wear and mechanical properties of particulate filled glass epoxy composites [J]. Malayan Polymer Journal, 2010, 5: 37–48.
SURESHA B, CHANDRAMOHAN G, MOHANRAM P V. Role of fillers on three-body abrasive wear of glass fabric reinforced epoxy composites [J]. Polymer Composite, 2009, 30: 1106–1113. DOI: 10.1002/pc.20662.
SURESHA B, KISHORE S, SEETHARAMU S, KUMARAN S S. Investigations on the influence of graphite filler on dry sliding wear and abrasive wear behaviour of carbon fabric reinforced epoxy composites [J]. Wear, 2009, 267: 1405–1414. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009. 01.026.
JEYAPRAKASH N, YANG Che-hua, MUTHUKANNAN DURAISELVAM, PRABU G, TSENG S P, KUMAR D R. Investigation of high temperature wear performance on laser processed nodular iron using optimization technique, [J]. Results in Physics, 2019, 15: 102585. DOI: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102585.
CHANG C Y, HUANG R, LEE P C, WENG T L. Application of A weighted Grey-Taguchi method for optimizing recycled aggregate concrete mixtures [J]. Cement and Concreate Composites, 2011, 33: 1038–1049. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.06.005.
PHADKE S M. Quality engineering using robust design [M]. Englewood Cliffs (NJ): Prentice-Hall, 1989.
TARNG Y S, JUANG S C, CHANG C H. The use of Grey based Taguchi methods to determine submerged arc welding process parameters in hardfacing [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2012, 28: 1–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01261-4.
KOPAC J, KRAJNIK P. Robust design of flank milling parameters on Grey-Taguchi method [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2007, 191: 400–403. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.03.051.
RAJMOHAN T, PALANIKUMAR K, KARTHIVEL K. Optimization of machining parameters in drilling hybrid aluminum metal matrix composites [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1286–1297. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61317-4.
TZENG C, LIN Y, YANG Y, JENG M. Optimization of turning operations with multiple performance characteristics using the Taguchi method and Grey relational analysis [J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 2753–2759. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.06.046.
PAN L K, WANG C C, HSIAO Y C, HAASO K C. Optimization of Nd: YAG laser welding onto magnesium alloy via taguchi analysis [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2004, 37: 33–42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2004.02.007.
CAYDAS U, HASCALIK A. Use of the Grey relational analysis to determine optimum laser cutting parameters with multi-performance characteristics [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2008, 40: 987–994. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2008.01.004.
TSAO C C. Grey-Taguchi method to optimize the milling parameters of aluminum alloy [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 40: 41–48. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-007-1314-3.
ASTM Standard, G: 99-05. Standard test method for wear testing with A pin-on-disk apparatus [S].
ESSAM R I M, MAHMOUD F, El-LABBAN H F. Microstructure and wear behavior of tic coating deposited on spheroidized graphite cast iron using laser surfacing [J]. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 2014, 4: 696–701.
ZAFAR S, SHARMA A K. Microstructure and wear performance of heat treated WC-12Co microwave clad [J]. Vacuum, 2016, 131: 213–222. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2016. 06.021.
SAMPEDRO J, PEREZ I, CARCEL B, RAMOS J A, AMIGO V. Laser cladding of TiC for better titanium components [J]. Physics Procedia, 2011, 12-A: 313322. DOI: 10.1016/j.phpro.2011.03.040.
CHEHRGHANI A, TORKAMANY M J, HAMEDI M J, SABBAGHZADEH J. Numerical modeling and experimental investigation of TiC formation on titanium surface pre-coated by graphite under pulsed laser irradiation [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258: 2068–2076. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.04.064.
MONFARED A, KOKABIA H, ASGARI S. Microstructural studies and wear assessments of Ti/TiC surface composite coatings on commercial pure Ti produced by titanium cored wires and TIG process [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 137: 959–966. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012. 11.009.
MAHAMOOD R M, AKINLABI E T, SHUKLA M, PITYANA S. Scanning velocity influence on microstructure, microhardness and wear resistance performance of laser deposited TiöAUV/TiC composite [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 50: 656–666. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.049.
YAN H, WANG A, XIONG Z, XU K, HUANG Z. Microstructure and wear resistance of composite layers on A ductile iron with multicarbide by laser surface alloying [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256: 7001–7009. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.05.015.
CHEN Y, GAN C H, WANG L X, YU G, KAPLAN A. Laser surface modified ductile iron by pulsed Nd: YAG laser beam with two-dimensional array distribution [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 245: 316–321. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2004.10.030.
ZENG D W, XIE C S, YUNG K C. Investigation of laser surface alloying of copper on high nickel austenitic ductile iron [J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 2002, 333: 223–231. PII: S0921-5093(01)01841-X.
GULZAR A, AKHTER J I, AHMAD M, ALI G, MAHMOOD M, AJMAL M. Microstructure evolution during surface alloying of ductile iron and austempered ductile iron by electron beam melting [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255: 8527–8532. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc. 2009.06.011.
BALLA V K, BOSE S, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Microstructure and wear properties of laser deposited WC-12%Co composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 6677–6682. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea. 2010.07.006.
ROY K R. A premier on Taguchi method [M]. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1990.
SUGISHITA J, FUJIYOSHI S. The effect of cast iron graphites on friction and wear performance II: Variables influencing graphite film formation [J]. Wear, 1981, 68: 7–20. DOI: 10.1016/0043-1648(81)90015-6.
GADAG S P, SRINIVASAN M N. Dry sliding wear and friction: Laser-treated ductile iron [J]. Wear, 1994, 173: 21–29. DOI: 10.1016/0043-1648(94)90253-4.
JEYAPRAKASH N, DURAISELVAM M, ADITYA S V Numerical modelling of WC-12% Co laser alloyed cast iron in high temperature sliding wear condition using response surface methodology [J]. Surface Review and Letters, 2019, 26: 1950009. DOI: 10.1142/S0218625X 19500094.
JEYAPRAKASH N, DURAISELVAM M, RAJU R. Modelling of Cr3C2-25% NiCr laser alloyed cast iron in high temperature sliding wear condition using response surface methodology [J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 2018, 63(3): 1303–1315. DOI: 10.24425/123805.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank National Taipei University of Technology, Taiwan, China for all support required to carry out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeyaprakash, N., Yang, Ch. & Tseng, Sp. Optimization of tribological parameters over WC-12%Co laser alloyed pearlitic ductile iron using Taguchi based Grey relational analysis. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 736–751 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4327-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4327-9
Keywords
- WC-12%Co
- laser alloying
- microstructure
- wear resistance
- Grey technique
- analysis of variance
- optimization
- roughness