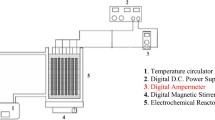
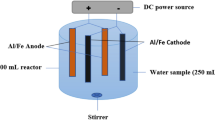
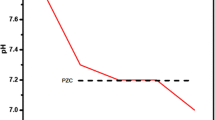
Abstract
The present study provides an electrocoagulation process for the removal of iron from drinking water with aluminum alloy as the anode and stainless steel as the cathode. The studies were carried out as a function of pH, temperature and current density. The adsorption capacity was evaluated with both the Langmuir and the Freundlich isotherm models. The results showed that the maximum removal efficiency of 98.8% was achieved at a current density of 0.06 A dm−2, at a pH of 6.5. The adsorption of iron preferably fitting the Langmuir adsorption isotherm suggests monolayer coverage of adsorbed molecules. The adsorption process follows second-order kinetics. Temperature studies showed that adsorption was endothermic and spontaneous in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Das, J. Talukdar, S. Sarma, B. Gohain, R. K. Dutta and A. C. Das, Curr. Sci., 85, 657 (2003).
D. B. Mahanta, N. N. Das and R. K. Dutta, Indian J. Environ. Prot., 24, 654 (2004).
R. Sharma, S. Shah and C. Mahanta, Asain J. Water Environ. Pollut., 2, 47 (2005).
N. Subba Rao, Environ. Monit. Assess., 136, 437 (2007).
WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Health criteria and other supporting information, 2nd edition (2), WHO, Geneva (1996).
Council directive 98/83/EC on the quality of water intended for human consumption, L330/32-L330/50, Official Journal of the European Communities (1998).
Central pollution control board, Ministry of Environment and Forests, http://www.cpcb.nic.in Government of India, Delhi.
K. Vaaramaa and H. J. Lehto, Desalination, 155, 157 (2003).
R. Munter, H. Ojaste and J. Sutt, J. Environ. Eng., 131, 1014 (2005).
W. C. Andersen and T. J. Bruno, Anal. Chim. Acta, 485, 1 (2003).
P. Berbenni, A. Pollice, R. Canziani, L. Stabile and F. Nobili, Bioresour. Technol., 74, 109 (2000).
H. A. Aziz, M. S. Yusoff, M. N. Adlan, N. H. Adnan and S. Alias, Water Manage., 24, 353 (2004).
D. Ellis, C. Bouchard and G. Lantagne, Desalination, 130, 255 (2000).
B. Das, P. Hazarika, G. Saikia, H. Kalita, D. C. Goswami, H. B. Das, S. N. Dube and R. K. Dutta, J. Hazard. Mater., 141, 834 (2007).
B. Y. Cho, Process Biochem., 40, 3314 (2005).
D.W. Miwa, G. R. P. Malpass, S. A. S. Machado and A. J. Motheo, Water Res., 40, 3281 (2006).
E. Onder, A. S. Koparal and U. B. Ogutveren, Sep. Purif. Technol., 52, 527 (2007).
M. Ikematsu, K. Kaneda, M. Iseki and M. Yasuda, Sci. Total Environ., 382, 159 (2007).
C. Carlesi Jara, D. Fino, V. Specchia, G. Saracco and P. Spinelli, Appl. Catals. B, 70, 479 (2007).
P. A. Christensen, T. A. Egerton, W. F. Lin, P. Meynet, Z.G. Shaoa and N. G. Wright, Chem. Commun., 38, 4022 (2006).
A. Carlos, M. Huitle and S. Ferro, Chem. Soc. Rev., 35, 1324 (2006).
C. Gabrielli, G. Maurin, H. Francy-Chausson, P. Thery, T. T. M. Tran and M. Tlili, Desalination, 201, 150 (2006).
X. Chen, G. Chen and P. L. Yue, Chem. Eng. Sci., 57, 2449 (2002).
G. Chen, Sep. Purif. Technol., 38, 11 (2004).
N. Adhoum and L. Monser, Chem. Eng. Process, 43, 1281 (2004).
M. Kobya, O. T. Can and M. Bayramoglu, J. Hazard. Mater., B100, 163 (2003).
C. Namasivayam and K. Prathap, J. Hazard. Mater., 123B, 127 (2005).
G. Mckay and Y. S. Ho, Water Res., 33, 578 (1999).
C. Namasivayam and S. Senthil Kumar, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 37, 4816 (1998).
F. H. Uber, Z. Phys. Chem., 57, 387 (1985).
I. Langmuir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 40, 1361 (1918).
L. D. Michelson, P. G. Gideon, E. G. Pace and L. H. Kutal, US Department Industry, Office of Water Research and Technology Bulletin (1975).
W. Nigussie, F. Zewgeb and B. S. Chandravanshi, J. Hazard. Mater., 147, 954 (2007).
S. Nayak Preeti and B. K. Singh, Res. J. Chem. Environ., 11, 23 (2007).
X.Y. Yang and A. D. Bushra, Chemical Engineering Journal, 83, 15 (2001).
A. K. Golder, A.N. Samantha and S. Ray, Sep. Purif. Technol., 52, 102 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasudevan, S., Jayaraj, J., Lakshmi, J. et al. Removal of iron from drinking water by electrocoagulation: Adsorption and kinetics studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26, 1058–1064 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0176-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0176-9