Abstract
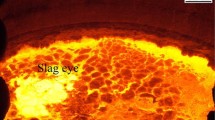
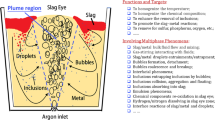
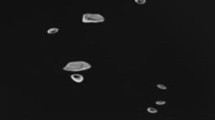
In ladle metallurgy, bubble–liquid interaction leads to complex phase structures. Gas bubble behavior, as well as the induced slag layer behavior, plays a significant role in the refining process and the steel quality. In the present work, a mathematical model using the large eddy simulation (LES) is developed to investigate the bubble transport and slag layer behavior in a water model of an argon-stirred ladle. The Eulerian volume of fluid model is adopted to track the liquid steel–slag–air free surfaces while the Lagrangian discrete phase model is used for tracking and handling the dynamics of discrete bubbles. The bubble coalescence is considered using O’Rourke’s algorithm to solve the bubble diameter redistribution and bubbles are removed after leaving the air–liquid interface. The turbulent liquid flow that is induced by bubble–liquid interaction is solved by LES. The slag layer fluactuation, slag droplet entrainment and spout eye open–close phenomenon are well revealed. The bubble diameter distribution and the spout eye size are compared with the experiment. The results show that the hybrid Eulerian–Lagrangian–LES model provides a valid modeling framework to predict the unsteady gas bubble–slag layer coupled behaviors.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b cri :
-
Criteria impact parameter (m)
- C D :
-
Drag force coefficient
- C VM :
-
Virtual mass force coefficient
- C L :
-
Lift force coefficient
- C S :
-
Smagorinsky constant
- d :
-
Distance to the closest wall (m)
- d pi :
-
Initial bubble diameter (m)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{VM}} \) :
-
Virtual mass force (m/s2)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{L}} \) :
-
Lift force (m/s2)
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{PG}} \) :
-
Pressure gradient force (m/s2)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m/s2)
- n :
-
Number of bubbles
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Q :
-
Gas flow rate (m3/s)
- r :
-
Bubble radii (m)
- Re :
-
Relative Reynolds Number
- S :
-
Rate-of-strain tensor (s−1)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- u :
-
Velocity (m/s)
- V :
-
Cell volume (m3)
- We :
-
Collisional Weber number
- α :
-
Volume fraction
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- σ :
-
Stress tensor (N/m2)
- τ :
-
Subgrid-scale stress (N/m2)
- μ :
-
Viscosity (kg/m/s)
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity (kg/m/s)
- κ :
-
Von Kármán constant
- δ ij :
-
Dirac function
References
L. Nastac, JOM 56, 43 (2004).
Q. Zheng and A. Yu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 068001 (2014).
L. Zhang, Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 8, 463 (2000).
A. Mukhopadhyay, E.W. Grald, K. Dhanasekharan, S. Sarkar, and J. Sanyal, Steel Res. Int. 76, 22 (2005).
B. Li, H. Yin, C. Zhou, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 48, 1704 (2008).
N. Kochi, Y. Ueda, T. Uemura, T. Ishii, and M. Iguchi, ISIJ Int. 51, 1011 (2011).
L. Li, Z. Liu, B. Li, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 55, 1337 (2015).
Z. Liu, L. Li, F. Qi, B. Li, M. Jiang, and F. Tsukihashi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46B, 406 (2015).
S.T. Johansen and F. Boysan, Metall. Trans. B 19B, 755 (1988).
D. Guo and G.A. Irons, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31B, 1457 (2000).
H. Liu, Z. Qi, and M. Xu, Steel Res. Int. 82, 440 (2011).
L. Zhang, J. Aoki, and B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 37B, 361 (2006).
S.M. Cho, S.H. Kim, and B.G. Thomas, ISIJ Int. 54, 845 (2014).
K. Jin, B.G. Thomas, R. Liu, S.P. Vanka, and X.M. Ruan, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 84, 012095 (2015).
L. Li, Z. Liu, M. Cao, and B. Li, JOM 67, 1459 (2015).
J. Klostermann, K. Schaake, and R. Schwarze, Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 71, 960 (2013).
C.W. Hirt and B.D. Nichols, J. Comput. Phys. 39, 201 (1981).
L. Zhang, JOM 64, 1059 (2012).
Y.M. Lau, W. Bai, N.G. Deenn, and J.A.M. Kuipers, Chem. Eng. Sci. 108, 9 (2014).
D. Jain, J.A.M. Kuipers, and N.G. Deen, Chem. Eng. Sci. 119, 134 (2014).
T. Zhang, Z.G. Luo, C.L. Liu, H. Zhou, and Z.S. Zou, Powder Technol. 273, 154 (2015).
Z. Liu, B. Li, M. Jiang, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 53, 484 (2013).
M. van Sint Annaland, N.G. Deen, and J.A.M. Kuipers, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60, 2999 (2005).
J. Smagorinsky, Month. Weather Rev. 91, 99 (1963).
S.A. Morsi and A.J. Alexander, J. Fluid Mech. 55, 193 (1972).
A. Tomiyama, H. Tamai, I. Zun, and S. Hosokawa, Chem. Eng. Sci. 57, 1849 (2002).
D. Darmana, R.L.B. Henket, N.G. Deen, and J.A.M. Kuipers, Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 2556 (2007).
P.J. O’Rourke, Collective drop effects on vaporizing liquid sprays, Ph.D Thesis, Princeton University, 1981.
A.A. Amsden, P.J. O’Rourke, and T.D. Butler, NASA Sti/Recon Technical Report No. 89, 1989.
X. Gu, S. Basu, and R. Kumar, Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 55, 5322 (2012).
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China for support of this research, Grant No. 51574068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Li, B. Investigation of Bubble-Slag Layer Behaviors with Hybrid Eulerian–Lagrangian Modeling and Large Eddy Simulation. JOM 68, 2160–2169 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1849-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1849-6