Abstract
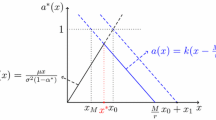
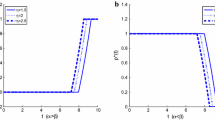
In this paper we consider a diffusion approximation to a classical risk process, where the claims are reinsured by some reinsurance with deductible b ∈ [0,b̃], where b = b̃ means “no reinsurance” and b = 0 means “full reinsurance”. The cedent can choose an adapted reinsurance strategy (b t ) t ≥0, i. e. the deductible can be changed continuously. In addition, the cedent has to inject fresh capital in order to keep the surplus positive. The problem is to minimise the expected discounted cost over all admissible reinsurance strategies. We find an explicit expression for the value function and the optimal strategy using the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman approach. Some examples illustrate the method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asmussen S (2000) Ruin Probabilities. World Scientific, Singapore
Azcue P, Muler N (2005) Optimal reinsurance and dividend distribution policies in the Cramér–Lundberg model. Math Finance 15:261–308
de Finetti B (1957) Su un’impostazione alternativa della teoria collettiva del rischio. Trans XVth Int Congr Actuar 2:433–443
Gerber HU (1969) Entscheidungskriterien für den zusammengesetzten Poisson-Prozess. Schweiz Verein Versicherungsmath Mitt 69:185–228
Gerber HU (1979) An Introduction to Mathematical Risk Theory. Huebner Foundation Monographs, Philadelphia
Grandell J (1991) Aspects of Risk Theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Hipp C (2003) Optimal dividend payment under a ruin constraint: Discrete time and state space. DGVFM 26:255–264
Kulenko N, Schmidli H (2008) Optimal dividend strategies in a Cramér–Lundberg model with capital injections. Insur Math Econ 43:270–278
Rogers LCG, Williams D (2000) Diffusions, Markov processes and martingales, vol 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rolski T, Schmidli H, Schmidt V, Teugels J (1999) Stochastic Processes for Insurance and Finance. Wiley, Chichester
Schmidli H (2001) Optimal proportional reinsurance policies in a dynamic setting. Scand Actuar J 55–68
Schmidli H (2008) Stochastic Control in Insurance. Springer-Verlag, London
Shreve SE, Lehoczky JP, Gaver DP (1984) Optimal consumption for general diffusions with absorbing and reflecting barriers. SIAM J Control Optim 22:55–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eisenberg, J., Schmidli, H. Optimal control of capital injections by reinsurance in a diffusion approximation . Blätter DGVFM 30, 1–13 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11857-009-0066-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11857-009-0066-6