Abstract
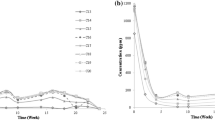
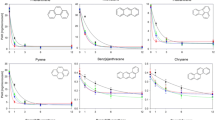
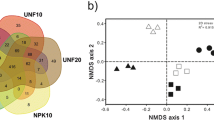
A real-time PCR quantification method for indigenous hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria (HDB) carrying the alkB gene in the soil environment was developed to investigate their distribution in soil. The detection limit of indigenous HDB by the method was 1 × 106 cells/g-soil. The indigenous HDB were widely distributed throughout the soil environment and ranged from 3.7 × 107 to 5.0 × 108 cells/g-soil, and the ratio to total bacteria was 0.1–4.3 %. The dynamics of total bacteria, indigenous HDB, and Rhodococcus erythropolis NDKK6 (carrying alkB R2) during bioremediation were analyzed. During bioremediation with an inorganic nutrient treatment, the numbers of these bacteria were slightly increased. The numbers of HDB (both indigenous bacteria and strain NDKK6) were gradually decreased from the middle stage of bioremediation. Meanwhile, the numbers of these bacteria were highly increased and were maintained during bioremediation with an organic nutrient. The organic treatment led to activation of not only the soil bacteria but also the HDB, so an efficient bioremediation was carried out.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wuxing, L., Yongming, L., Ying, T., Zhengao, L., & Lena, Q. M. (2010). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32, 23–29.
Hejazi, R. F., Husain, T., & Khan, F. I. (2003). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 99, 287–302.
Margesin, R., & Schinner, F. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 3127–3133.
Fujii, T., Narikawa, T., Takeda, K., & Kato, J. (2004). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 68, 2171–2177.
Quatrini, P., Scaglione, G., Pasquale, C. D., Riela, S., & Puglia, A. M. (2007). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 104, 251–259.
Piccolo, L. L., Pasquale, C. D., Fodale, R., Puglia, A. M., & Quatrini, P. (2011). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 1204–1213.
Kirkwood, K. M., Chernik, P., Foght, J. M., & Gray, M. R. (2008). Biodegradation, 19, 785–794.
Mao, D., Lookman, R., Diels, L., Weghe, H. V. D., Vanermen, G., Brucker, N. D., et al. (2009). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1216, 1524–1527.
Kubota, K., Koma, D., Matsumiya, Y., Chung, S. Y., & Kubo, M. (2008). Biodegradation, 19, 749–757.
Geissdörfer, W., Frosch, S. C., Haspel, G., Ehrt, S., & Hillen, W. (1995). Microbiology, 141, 1425–1432.
van Beilen, J. B., Panke, S., Lucchini, S., Franchini, A. G., Röthlisberger, M., & Witholt, B. (2001). Microbiology, 147, 1621–1630.
Wentzel, A., Ellingsen, T. E., Kotlar, H. K., Zotchev, S. B., & Throne-Holst, M. (2007). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 1209–1221.
Rojo, F. (2009). Environmental Microbiology, 11, 2477–2490.
Dutta, T. K., & Harayama, S. (2001). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 1970–1974.
Koma, D., Sakashita, Y., Kubota, K., Fujii, Y., Hasumi, F., Chung, S. Y., et al. (2003). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 67, 1590–1593.
Hatayama, K., Sakihama, Y., Matsumiya, Y., & Kubo, M. (2008). In J. B. Dominguez (Ed.) Soil contamination research trends. Nova Science, Hauppauge, 143–160.
Blattner, F. R., Plunkett, G., Bloch, C. A., Perna, N. T., Burland, V., Riley, M., et al. (1997). Science, 277, 1453–62.
Aoshima, H., Kimura, A., Shibutani, A., Okada, C., Matsumiya, Y., & Kubo, M. (2006). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 71, 875–880.
Harayama, S., Kasai, Y., & Hara, A. (2004). Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 15, 205–214.
Okano, Y., Hristova, K. R., Leutenegger, C. M., Jackson, L. E., Denison, R. F., Gebreyesus, B., et al. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 1008–1016.
Maeda, K., Toyoda, S., Shimojima, R., Osada, T., Hanajima, D., Morioka, R., et al. (2010). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 1555–1562.
Long, X., Chen, C., Xu, Z., Oren, R., & He, J. (2012). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 46, 163–171.
Haasea, S., Philippotb, L., Neumannc, G., Marhana, S., & Kandelera, E. (2008). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40, 1225–1234.
Chapuis-Lardy, L., Brauman, A., Bernard, L., Pablo, A. L., Toucet, J., Mano, M. J., et al. (2010). Applied Soil Ecology, 45, 201–208.
Chen, Z., Liu, J., Wu, M., Xie, X., Wu, J., & Wei, W. (2012). Microbial Ecology, 63, 446–459.
Post-Beittenmiller, D. (1996). Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 47, 405–430.
Schulz, S., Giebler, J., Chatzinotas, A., Wick, L. Y., Fetzer, I., Welzl, G., et al. (2012). The ISME Journal, 17, 1–12.
Filler, D. M., Lindstrom, J. E., Braddock, J. F., Johnson, R. A., & Nickalaski, R. (2001). Cold Regions Science and Technology, 32, 143–156.
Agarry, S. E., Owabor, C. N., & Yusuf, R. O. (2010). Bioremediation Journal, 14, 189–195.
Hamdi, H., Benzarti, S., Manusadžianas, L., Aoyama, I., & Jedidi, N. (2007). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 1926–1935.
Yakubu, B. M., Ma, H., & Zhang, C. (2009). International Journal of Environmental Pollution, 36, 400–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuhara, Y., Horii, S., Matsuno, T. et al. Distribution of Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria in the Soil Environment and Their Contribution to Bioremediation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 329–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0170-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0170-x