Abstract
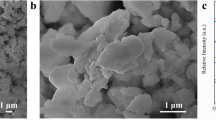
The effects of SiO2 (amorphous) and TiO2 (crystalline, rutile) fillers on softening point (T s), glass transition temperature (T g), coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and dielectric constant (ɛ) of zinc bismuth borate, ZnO-Bi2O3-B2O3 (ZBIB) glass microcomposites have been investigated with a view to its use as the white back (rear glass dielectric layer) of plasma display panels (PDPs). The experimentally measured properties have also been compared with those of theoretically predicted values. Both the experimental and theoretical trends of these properties with added filler contents correlate very well. The interaction of fillers with glass which occurred during sintering at 560°C has also been monitored by XRD and FTIR spectroscopic analyses. The microstructures and distribution of fillers in the glass matrix have been analyzed by SEM images. It is observed that the fillers have partially dissolved in the glass at the firing temperature leaving some unreacted filler as residue which results in ceramic-glass microcomposites. In consideration of the desired properties of white back of PDPs, the addition of TiO2 filler to ZBIB glass is found to be more preferable than SiO2 filler. The addition of 10 wt% TiO2 filler yielded T s, T g, CTE and ɛ values of 560°C, 480°C, 82 × 10−7/K and 14·6 which are found to meet the desired values of <580°C, <500°C, <83 × 10−7/K and <15, respectively with respect to use of PD200 glass as substrate in PDP technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baia L, Stefan R, Popp J, Sinon S and Keifer W 2003 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 324 109
Chang M S, Pae B J, Lee Y K, Ryu B G and Pork M H 2001 J. Inf. Display 2 39
Dakin T K 1993 Insulating materials-general properties, in standard handbook for electrical engineers (eds) D G Fink and H W Beaty (New York: McGraw-Hill) 13th edn, pp 4–117
Fuxi G 1992 Optical and spectroscopic properties of glass (Berlin: Springer-Verlag)
Hiromitsu W, Hiroyuki O, Masahiko O and Kazuo H 2000 US patent 6010973
Hwang G -H, Kim W -Y, Jeon H -J and Kim Y -S 2002 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85 2961
Kamitsos E I, Karakassides A M and Chryssikos D G 1987 Phys. Chem. Glasses 91 1073
Kharlamov A A, Almeida R M and Heo J 1996 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 202 233
Kim S G, Shin H, Park J S, Hong K S and Kim H 2005 J. Electroceram. 15 129
Kim S -G, Park J -S, An J -S, Hong K S, Shin H and Kim H 2006 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89 902
Kim T Y and Sunnoo J H 2000 US patent 6097151
Last J T 1957 Phys. Rev. 105 1740
Lim E -S, Kim B -S, Lee J -H and Kim J -J 2006 J. Electroceram. 17 359
Masahi A and Shinji K 1999 US patent 5977708
Motke S G, Yowale S P and Yawale S S 2002 Bull. Mater. Sci. 25 75
Naoya H and Kazuhiro N 1999 JP patent 11246233
Priven A I 1998 Glass Phys. & Chem. 24 67
Priven A I 2004 Glass Technol. 45 244
Priven A I and Mazunin O V 2003 Glass Technol. 44 156
Rao C N R 1963 Chemical application of infrared spectroscopy (New York: Academic Press)
Scholze H 1991 Glass, nature, structure and properties (New York: Springer) 3rd ed.
SciGlass (Glass Properties Information System), Version 6.7
Shin H, Kim S -G, Park J -S, An J -S, Hong K S and Kim H 2006a J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89 3258
Shin H, Kim S -G, Park J -S, Jung H S, Hong K S and Kim H 2006b J. Mater. Res. 21 1753
Shinoda T, Wakitani M, Nanto T, Awaji N and Kanagu S 2000 IEEE Trans. Electrons. Electron Dev. 47 77
Shiro T, Hideaki M, Tadahiko U and Koji K 1998 JP patent 10338547
Song J -Y and Choi S -Y 2006 Display 27 112
Song J -Y, Park T -J and Choi S -Y 2006 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 352 5403
Uma T and Nogami M 2007 J. Phys. Chem. C111 16635
Vernacotola D E 1994 Key Engg. Mater. 94–95 379
Vernacotola D E and Shelby J E 1993 Ceram. Trans. 29 215
Volf M B 1984 Chemical approach to glass (Amsterdam: Elsevier)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.P., Pal, K., Tarafder, A. et al. Effects of SiO2 and TiO2 fillers on thermal and dielectric properties of eco-friendly bismuth glass microcomposites of plasma display panels. Bull Mater Sci 33, 33–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0005-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0005-0