Abstract
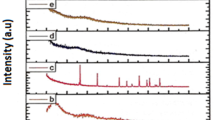
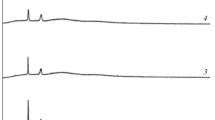
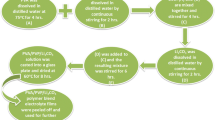
Lithium ion conducting polymer blend electrolyte films based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) with different Mwt% of lithium nitrate (LiNO3) salt, using a solution cast technique, have been prepared. The polymer blend electrolyte has been characterized by XRD, FTIR, DSC and impedance analyses. The XRD study reveals the amorphous nature of the polymer electrolyte. The FTIR study confirms the complex formation between the polymer and salt. The shifts in T g values of 70 PVA–30 PVP blend and 70 PVA–30 PVP with different Mwt% of LiNO3 electrolytes shown by DSC thermograms indicate an interaction between the polymer and the salt. The dependence of T g and conductivity upon salt concentration has been discussed. The ion conductivity of the prepared polymer electrolyte has been found by a.c. impedance spectroscopic analysis. The PVA–PVP blend system with a composition of 70 wt% PVA: 30 wt% PVP exhibits the highest conductivity of 1·58 × 10 − 6 Scm − 1 at room temperature. Polymer samples of 70 wt% PVA–30 wt% PVP blend with different molecular weight percentage of lithium nitrate with DMSO as solvent have been prepared and studied. High conductivity of 6·828 × 10 − 4 Scm − 1 has been observed for the composition of 70 PVA:30 PVP:25 Mwt% of LiNO3 with low activation energy 0·2673 eV. The conductivity is found to increase with increase in temperature. The temperature dependent conductivity of the polymer electrolyte follows the Arrhenius relationship which shows hopping of ions in the polymer matrix. The relaxation parameters (ω) and (τ) of the complexes have been calculated by using loss tangent spectra. The mechanical properties of polymer blend electrolyte such as tensile strength, elongation and degree of swelling have been measured and the results are presented.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amatucci G and Tarascon J M 2002 J. Electrochem. Soc. 149 K31
Archer W L and Armstrong R D 1995 Electrochim. Acta 991 40
Armand M, Gorecki W and Andreani R 1990 in Second int. symp. polymer electrolytes (ed.) B Scrosati (London: Elsevier) p. 91
Benrabah D, Bard D, Sanchez J Y, Armand M and Gard G G 1993 J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 355 89
Boukamp B A 1986 Solid State Ionics 20 301
Cherng J Y, Munshi M Z A, Owens B B and Smyrl W H 1988 Solid State Ionics 857 28
Covpuano F, Croce F and Scrosati B 1991 J. Electrochem. Soc. 1918 138
Dieterich W and Maass P 2002 Chem. Phys. 284 439
Hodge R M, Edward G H and Simon G P 1996 Polymer 1371 37
Jonscher A K 1977 Nature 267 673
Rajeswari N, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Prabu M, Hirankumar G, Nithya H and Sanjeeviraja C 2011 J. Non-Crystal. Solids 3751 357
Ramya C S, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T, Hirankumar G and Angelo P C 2006 Eur. Polym. J. 42 2672
Ramya C S, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T and Hirankumar G 2007 Physica B 393 11
Todd Alam M, Joshua Otaigbe U, Dave Rhoades, Gregory P Holland, Brian R Cherry and Paul G Kotula 2005 Polymer 46 12468
Utracki L A 1990 Polymer alloys and blends (Munich: Hanser)
Vasile Cristian Grigoras and Virgil Barboiu 2008 Revue Roumanine de Chimie 53(2) 127
Wen Z, Itoh T, Uno T, Kubo M and Yamamoto O 2003 Solid State Ionics 160 141
Wieczorek W and Stevens J R 1997 J. Phys. Chem. Solids B1529 101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RAJESWARI, N., SELVASEKARAPANDIAN, S., PRABU, M. et al. Lithium ion conducting solid polymer blend electrolyte based on bio-degradable polymers. Bull Mater Sci 36, 333–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-013-0463-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-013-0463-2