Abstract
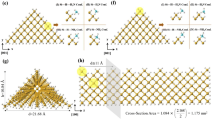
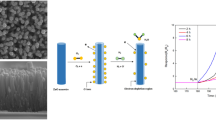
ZnO nanowires (NWs) were deposited on a glass substrate by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method (SILAR). Sensing response of ZnO NWs towards reducing vapours was tested at ambient temperature \(({\sim }32{^{\circ }}\hbox {C})\) by the chemiresistor method. The vapour response was found to be 80.2, 1.6, 1.1 and 1.1 for \(\hbox {NH}_{3}, \hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {O}, (\hbox {CH}_{3})_{2}\hbox {CO}\) and \(\hbox {C}_{2}\hbox {H}_{5}\hbox {OH}\), respectively. Also, density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed to understand the charge transfer and electronic property change during adsorption of molecules over ZnO NW. The band of the Zn 3d state was altered after adsorption and no significant changes were observed in the O 2p state. Higher binding energy (14.6 eV) with significant charge transfer (\(0.04{\vert }e{\vert }\)) was observed in the ammonia-adsorbed ZnO NW. On comparing response obtained through experimental and computational studies, almost a similar trend of response was observed except for the \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {O}\)–\(\hbox {ZnO}\) system. This was due to lack of dispersion interaction and steric effect influence in the DFT calculation with the chosen computational methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lexi Z, Jianghong Z, Haiqiang L, Liming G, Li L, Jianfeng Z et al 2011 Sens. Actuators B 160 364
Mohini D, Jitendra B, Ashok S, Vimal V and Golla E 2014 IEEE Sens. J. 14 1577
Samarasekara P, Yapa N U S, Kumara N T R N and Perera M V K 2007 Bull. Mater. Sci. 30 113
Shudi P, Gaolin W, Wei S and Qian W 2013 J. Nanomater. 2013 1
Rajesh K, Al-Dossary O, Girish K and Ahmad U 2015 Nano-Micro Lett. 7 97
Kalyamwar V S, Raghuwanshi F C, Narayan L J and Anil J G 2013 J. Sens. Technol. 3 31
Akash K, Sun-Woo C, Hyoun W K and Sang S K 2015 J. Hazard. Mater. 286 229
Wagh M S, Jain G H, Patil D R, Patil S A and Patil L A 2006 Sens. Actuators B 115 128
Bhooloka Rao B 2000 Mater. Chem. Phys. 64 62
Hsueh H T, Hsueh T J, Chang S J, Hung F Y, Hsu C L, Dai B T et al 2012 IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11 520
Martins J B L, Longo E, Salmon O D R, Espinoza V A A and Taft C A 2004 Chem. Phys. Lett. 400 481
Prades J D, Cirera A and Morante J R 2009 Sens. Actuators B 142 179
Meyer B and Marx D 2003 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15 89
Noei H, Gallino F, Jin L, Zhao J, Valentin C D and Wang Y 2013 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 1977
Morimoto T, Yanal H and Nagao M 1976 J. Phys. Chem. 80 471
Ozawa K, Hasegawa T, Edamoto K, Takahashi K and Kamada M 2002 J. Phys. Chem. B 106 9380
Yuan Q, Zhao Y P, Li L and Wang T 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 6107
Virtual Nanolab version 2016.0 QuantumWise A/S (www.quantumwise.com)
Brandbyge M, Mozos J L, Ordejon P, Taylor J and Stokbro K 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 165401
Soler J M, Artacho E, Gale J D, García A, Junquera J, Ordejón P et al 2002 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14 2745
Perdew J P, Burke K and Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
Mulliken R S 1955 J. Chem. Phys. 23 1833
Amalraj A S and Senguttuvan G 2014 J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25 2035
Pandeeswari R and Jeyaprakash B G 2014 Sens. Actuators B 195 206
Mohammadi A S, Mahdy Baizaee S and Salehi H 2011 World Appl. Sci. J. 14 1530
Charifi Z, Baaziz H and Reshak A H 2007 Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 244 3154
Agapito L A, Curtarolo S and Nardelli M B 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 011006
Arockia J K, Jonnala R R, Parthasarathy S, Babu K J, Ganesh K M, Prabakaran S et al 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 688A 422
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), India, under ER & IPR Project (ERIPR/ER/1003908/M/01/1541). We thank Dr Arkaprava Bhattacharyya, SASTRA University, for providing ATK QuantumWise software to carry out the DFT studies. We also thank SASTRA University for providing the infrastructural facility to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anasthasiya, A.N.A., Ramya, S., Balamurugan, D. et al. Adsorption property of volatile molecules on ZnO nanowires: computational and experimental approach. Bull Mater Sci 41, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1538-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1538-2