Abstract
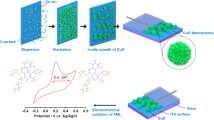
We report here the highly sensitive and selective electrochemical determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), one of the dopamine metabolites in the presence of important interferents ascorbic acid (AA) and uric acid (UA) using an ultrathin electropolymerized film of 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol (p-ATT) modified glassy carbon (GC) electrode in 0.20M phosphate buffer solution (pH5.0). The bare GC electrode fails to resolve the oxidation peaks of AA, DOPAC and UA in a mixture. Further, the oxidation peak potentials of them were shifted to more positive potential with decreased peak currents in the subsequent cycles. On the other hand, the p-ATT modified electrode not only separated the voltammetric signals of AA, DOPAC and UA but also enhanced their peak currents. The amperometric current response was increased linearly with increasing DOPAC concentration in the range of 4.0×10 − 8 to 1.0×10 − 5 M and the detection limit was found to be 150pM (S/N = 3).

5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol was electropolymerized on glassy carbon electrode and utilised for selective determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in the presence of important interferents ascorbic and uric acids. The modified electrode showed excellent selectivity towards 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid even in the presence of 50-folds excess of ascorbic and uric acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson G M, Riddle M A, Hoder E L, Feibel F C, Shaywitz B A, Cohen D J 1988 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 51 1100
Thiffault C, Langston J W and Monte D A D 2003 Exp. Neuro. 18 173
D’Angio M and Scatton B 1989 Neurosci. Lett. 96 223
Chase T N 1980 Neurochemical alterations in Parkinson’s disease (ed) J H Wood, Neurobiology of cerebrospinal fluid (New York: Plenum), pp. 207
LeWitt P A 1993 Adv. Neurol. 60 544
Thogi H, Abe T, Saheki M, Yamazaki K and Murata T 1997 J. Neural. Transm. 104 441
Wightman R M, May L J and Michael A C 1988 Anal. Chem. 60 769A
Stamford J A, Palij P, Davidson C and Trout S J 1995 Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 38 289
Valentini F, Orlanducci S, Terranova M L, Amine A and Palleschi G 2004 Sens. Actuators B 100 117
Salimi A, MamKhezri H and Hallaj R 2006 Talanta 70 823
Roy P R, Saha M S, Okajima T, Park S G, Fujishima A and Ohsaka T 2004 Electroanalysis 16 1777
Raj C R and Ohsaka T 2002 Electroanalysis 14 679
Raj C R and Behera S 2005 J. Electroanal. Chem. 581 61
Raj C R and Ohsaka T 2001 Chem. Lett. 30 670
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2008 J. Electroanal. Chem. 617 164
Maldonado S, Morin S, and Stevenson K J 2006 Analyst 131 262
Wang J, Li M, Shi Z, Li N and Gu Z 2001 Electrochim. Acta 47 651
Liu A, Honma I and Zhou H 2005 Electrochem. Commun. 7 233
Curulli A, Valentini F, Padeletti G, Viticoli M, Caschera D and Palleschi G 2005 Sens. Actuators B 111–112 441
Yeung P K F, Buckley S J, Pedder S C J and Dingemanse J 1996 J. Pharm. Sci. 85 451
Adcock J L, Barnett N W, Costin J W, Francis P S, and Lewis S W 2005 Talanta 67 585
Drujan B D, Alvarez N and Borges J M D 1966 Anal. Biochem. 15 8
Weisel F A 1975 Neurosci. Lett. 1 219
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2009 Electrochem. Commun. 11 367
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2009 Bioelectrochemistry 77 13
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2009 Biosens. Bioelectron. 24 3575
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2009 Anal. Chim. Acta 647 97
Kalimuthu P and John S A 2009 Electrochem. Commun. 11 1065
Giz M J, Duong B and Tao N J 1999 J. Electroanal. Chem. 465 72
Zhao H, Zhang Y and Yuan Z 2001 Anal. Chim. Acta 441 117
Crespi F, Martin K F and Marsden C A 1988 Neuroscience 27 885
Liu A, Honma I and Zhou H 2005 Biosens. Bioelectron. 21 809
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KALIMUTHU, P., JOHN, S.A. Selective determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in the presence of ascorbic and uric acids using polymer film modified electrode. J Chem Sci 123, 349–355 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-011-0086-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-011-0086-3