Abstract
Identifying a good site for groundwater exploration in hard rock terrain is a challenging task. In hard rocks, groundwater occurs in secondary porosity developed due to weathering, fracturing, faulting, etc., which is highly variable within short distance and contributing to near-surface inhomogeneity. In such situations topographic, hydrogeological and geomorphological features provide useful clues for the selection of suitable sites.
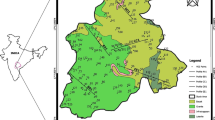
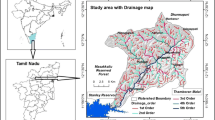
Initially, based on satellite imagery, topographical, geomorphological and hydrogeological features, an area of about 149 km2 was demarcated as a promising zone for groundwater exploration in the hard rock tract of Seethanagaram Mandal, Vizianagaram District, Andhra Pradesh, India. A total of 50 Vertical Electrical Soundings (VES) were carried out using Wenner electrode configuration. An interactive interpretation of the VES data sharpened the information inferred from geomorphological and hydrogeological reconnaissance. Ten sites were recommended for drilling. Drilling with Down-The-Hole Hammer (DTH) was carried out at the recommended sites down to 50 to 70 m depths. The interpreted VES results matched well with the drilled bore well lithologs. The yields of bore wells vary from 900 to 9000 liters per hour (lph).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker R, Rao T V and Thangarajan M 2001 Delineation of contaminant zone through electrical imaging technique; Curr. Sci. 81(3) 277–283.
Compagnie General de Geophysique 1963 Master curves for electrical soundings; 2nd edn; European Association of exploration Geophysicists, The Hague, pp. 49.
Ghosh D P 1971 Inverse filter coefficients for computation of apparent resistivity standard curves for a horizontally stratified earth; Geophysical Prospecting 19 769–775.
Hummel J N 1931 A theoretical study of apparent resistivity in surface potential methods; AIME Tech. Publn. No. 418.
Jacob C E 1947 Draw down test to determine effective radius of artesian well; Trans. Amer. Soc. of Civil Engrs. 112, paper 2321, 1047–1064.
Mabee S B, Curry P J and Hardcastle K C 2002 Correlation of lineaments to ground water inflows in bedrock tunnel; Ground Water 40(1) 37–43.
Mabee S B, Hardcastle K C and Wise D U 1994 A method of collecting and analyzing lineaments for regional scale fractured-bedrock aquifer studies; Ground Water 32(4) 884–894.
Magowe M and Carr J R 1999 Relationship between lineaments and ground water occurrence in western Botswana; Ground Water 37(2) 282–286.
Mooney H M and Wetzel W W 1956 The potentials about a point electrode and apparent resistivity curves for a two-three and four layered earth; Minneapolis, University of Minnesota Press, pp. 146.
Moore R W 1945 An empirical method of interpretation of earth resistivity measurements; AIME Tech. Publ. No. 1743.
Narayan P V S and Ramanujachary K R 1967 An inverse slope method determining absolute resistivity; Jr. Geophysics 32 1036–1040.
Orellana E and Mooney H M 1966 Master tables and curves of vertical electrical sounding over layered structures; Interciencia, Madrid, pp. 193.
Patra H P and Nath S K 1999 Schlumberger geoelectrical sounding in groundwater: principles, interpretation and application; A A Balkema, Rotterdam; and Oxford & IHB Publishing Company Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, pp. 153.
Raju K C B, Rao G V K and Kumar B J 1989 Analytical aspects of remote sensing techniques for groundwater prospecting in hard rocks; Proc. of the 6th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, pp. 127–132.
Rangarajan R and Athavale R N 2000 Annual replenishable groundwater potential of India — an estimate based on injected tritium studies; J. Hydrol. 234 38–53.
Roman I 1934 Some interpretation of earth resistivity data; AIME Trans. 110 183.
Rorabaugh M J 1953 Graphical and theoretical analysis of step-drawdown test of artesian well; Proc. Amer. Soc. Civil Engrs., vol. 79, separate no. 362, 23 pp.
Sander P, Minor T M and Chesley M M 1997 Groundwater Exploration based on lineament analysis and reproductivity tests; Ground Water 35(5) 888–894.
State Ground Water Department (SGWB) 2005 District report, Vizianagaram; p.87.
Tagg G F 1934 Interpretation of resistivity measurements; AIME. Trans. 110 135.
Van Dam J C 1967 Mathematical denotation of standard-graphs for resistivity prospecting in view of their calculation by means of a digital computer; Geophysical Prospecting 15 pp. 57–70.
Yin Z Y and Brook G A 1992 The topographic approach to locating high yield wells in crystalline rocks: Does it work?; Ground Water 30(1) 96–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, N.C., Das, S.N. & Singh, V.S. Integrated approach for identification of potential groundwater zones in Seethanagaram Mandal of Vizianagaram District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Earth Syst Sci 117, 133–144 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0004-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0004-3