Abstract
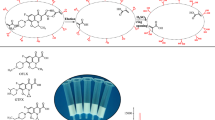
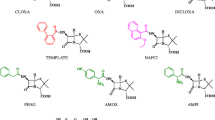
A series of novel ofloxacin-imprinted polymers have been prepared using poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-ethylenedimethacrylate) (PGMA/EDMA) particles as a support and their recognition abilities evaluated. Several factors that are known to influence the rebinding of the imprinted polymers were investigated, including the pH and water content of the adsorbed solutions. The binding capabilities of the materials were also evaluated. The resulting PGMA/EDMA molecularly imprinted polymers were used as selective solid phase extraction sorbents for the simultaneous determination of three different quinolones in milk, with the results revealing high levels of selectivity. The use of 10 % methanol–water as washing solution together with 2 % trifluoroacetic acid–acetonitrile as an elution solution allowed for the three different quinolones to be selectively extracted from the milk samples. Furthermore, all of the matrix interference factors were eliminated simultaneously, whereas the enrichment factors were >234. The quantification limit was determined to be 1.00 ng/mL using an ultraviolet detector, and the recovery was in the range of 81.8–102.0 % with a relative deviation of <9.6 %.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al–Almad A, Daschner FD, Kummerer K (1999) Biodegradability of cefotiam, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, penicillin G, and sulfamethoxazole and inhibition of wastewater bacteria. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:158–163
Blasco C, Picó Y (2007) Progress in analysis of residual antibacterials in food. Trends Anal Chem 26(9):895–913
Fang GZ, Tan J, Yan XP (2005) An ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique combined with a sol–gel process for selective solid-phase extraction of cadmium(II). Anal Chem 77(6):1734–1739
García–Galán MJ, Díaz–Cruz MS, Barceló D (2010) Determination of triazines and their metabolites in environmental samples using molecularly imprinted polymer extraction, pressurized liquid extraction and LC–tandem mass spectrometry. J Hydrol 383(1–2):30–38
He CY, Long YY, Pan JL, Li K, Liu F (2007) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:133–150
Huang HC, Lin CI, Joseph AK, Lee YD (2004) Photo-lithographically impregnated and molecularly imprinted polymer thin film for biosensor applications. J Chromatogr A 1027(1–2):263–268
Huang BY, Chen YC, Wang GR, Liu CY (2011) Preparation and evaluation of a monolithic molecularly imprinted polymer for the chiral separation of neurotransmitters and their analogues by capillary electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(6):849–855
Ingerslev F, Halling–Sørensen B (2000) Biodegradability properties of sulfonamides in activated sludge. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(10):2467–2473
Kümmerer K, Al-Almad A, Mersch-Sundermann V (2000) Biodegradability of some antibiotics, elimination of the genotoxicity and affection of wastewater bacteria in a simple test. Chemosphere 40(7):701–710
Li Y, Li X, Dong CK, Li YQ, Jin PF, Qi JY (2009) Selective recognition and removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution usin molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Biosens Bioelectron 25(2):306–312
Li YB, Zhang ZJ, Li JS, Li HG, Chen Y, Liu ZH (2011) Simple, stable and sensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence detector for high-performance liquid chromatography and its application in direct determination of multiple fluoroquinolone residues in milk. Talanta 84(3):690–695
Lin HY, Hsu CY, Thomas JL, Wang SE, Chen HC, Chou TC (2006) The microcontact imprinting of proteins: The effect of cross-linking monomers for lysozyme, ribonuclease A and myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 22(4):534–543
Liu XJ, Chen ZY, Zhao R, Shangguan DH, Liu GQ, Chen Y (2007) Uniform-sized molecularly imprinted polymer for metsulfuron-methyl by one-step swelling and polymerization method. Talanta 71(3):1205–1210
Liu HM, Liu CH, Yang XJ, Zeng SJ, Xiong YQ, Xu WJ (2008) Solid-phase extraction of ursolic acid from herb using β-cyclodextrin-based molecularly imprinted microspheres. J Sep Sci 31(20):3573–3580
Lok KP, Ober CK (1985) Particle size control in dispersion polymerization of polystyrene. Can J Chem 63(1):209–216
Lombardo-Agüí M, Gámiz-Gracia L, Cruces-Blanco C, García-Campaña AM (2011) Comparison of different sample treatments for the analysis of quinolones in milk by capillary-liquid chromatography with laser induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1218(30):4966–4971
Lucci P, Núñez O, Galceran MT (2011) Solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of natural and synthetic estrogens from aqueous samples.J. Chromatogr A 1218:4828–4833
Okuno H, Kitano T, Yakabe H, Kishimoto M, Deore BA, Siigi H, Nagaoka T (2002) Characterization of overoxidized polypyrrole colloids imprinted with L-lactate and their application to enantioseparation of amino acids. Anal Chem 74(16):4184–4190
Pan XD, Wu PG, Yang DJ, Wang LY, Shen XH, Zhu CY (2013) Simultaneous determination of melamine and cyanuric acid in dairy products by mixed–mode solid phase extraction and GC–MS. Food Control 30(2):545–548
Porobić I, Kontrec D, Šoškić M (2013) Molecular recognition of indole derivatives by polymers imprinted with indole-3-acetic acid: a QSPR study. Bioorg Med Chem 21(3):653–659
Rambla-Alegre M, Collado-Sánchez MA, Esteve-Romero J, Carda-Broch S (2011) Quinolones control in milk and eggs samples by liquid chromatography using a surfactant-mediated mobile phase. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:1303–1313
Seifrtová M, Nováková L, Lino C, Pena A, Solich P (2009) An overview of analytical methodologies for the determination of antibiotics in environmental waters. Anal Chim Acta 649(2):158–179
Tan CJ, Tong YW (2007) Molecularly imprinted beads by surface imprinting. Anal Bioanal Chem 389(2):369–376
Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A, Tadeo JL (2007) Molecular imprinting-based separation methods for selective analysis of fluoroquinolones in soils. J Chromatogr A 1172(2):97–104
Wang S, Li Y, Wu XL, Ding MJ, Yuan LH, Wang RY, Wen TT, Zhang J, Chen LN, Zhou XM, Li F (2011) Construction of uniformly sized pseudo template imprinted polymers coupled with HPLC-UV for the selective extraction and determination of trace estrogens in chicken tissue samples. J Hazard Mater 186(2–3):1513–1519
Yokotaa A, Kubota H, Komiya S, Sato K, Akiyama H, Koshiishi I (2012) Sensitive and simple determination of bromate in foods disinfected with hypochlorite reagents using high performance liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization. J Chromatogr A 1262:219–222
Yoshida M, Hatate Y, Uezu K, Goto M, Furusaki S (2000) Chiral-recognition polymer prepared by surface molecular imprinting technique. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 169(1–3):259–269
Zheng MM, Gong R, Zhao X, Feng YQ (2010) Selective sample pretreatment by molecularly imprinted polymer monolith for the analysis of fluoroquinolones from milk samples. J Chromatogr A 1217(14):2075–2081
Zhou YX, Yu B, Shiu E, Levon K (2004) Potentiometric sensing of chemical warfare agents: surface imprinted polymer integrated with an indium iin oxide electrode. Anal Chem 76(10):2689–2693
Zhu XL, Yang J, Su QD, Cai JB, Gao Y (2005) Selective solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for the analysis of polar organophosphorus pesticides in water and soil samples. J Chromatogr A 1092:161–169
Zhu QJ, Wang LP, Wu SF, Joseph W, Gu XH, Tang J (2009) Selectivity of molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction for sterol compounds. Food Chem 113(2):608–615
Zorita S, Larsson L, Mathiasson L (2008) Comparison of solid-phase sorbents for the determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in wastewater. J Sep Sci 31:3117–3121
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for financially supporting this research (grant no. 81173025).
Conflict of Interest
Jing Zhang has no conflict of interest. Ling-Ling Wang has no conflict of interest. Jin-Qin Ma has no conflict of interest. Yan-Li Wang has no conflict of interest. The institutes where the authors work also agree to the submission of this paper to the journal. Jing Zhang has received research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China. All authors have read and approved this version of the article, and due care has been taken to ensure the integrity of the work. More importantly, this article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects. The institutes where the authors work also agree to the submission of this paper to the journal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, LL., Ma, JQ. et al. Preparation of Ofloxacin Poly(Glycidyl Methacrylate-Co-Ethylenedimethacrylate) (PGMA/EDMA) Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres and Their Application to the Analysis of Quinolones in Milk. Food Anal. Methods 7, 721–729 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9754-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9754-x