Abstract
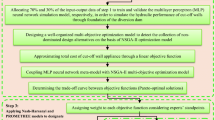
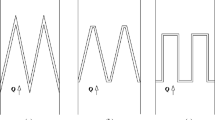
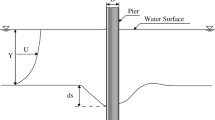
The labyrinth spillway continues to be a popular type of the control structures. The focus of the present study is that on the optimization of the shape of the labyrinth spillway through the minimization of the construction costs because the use of it is a suitable solution in the rehabilitation process of existing reservoirs. An Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) model was developed to determine the discharge coefficient of the labyrinth spillway as a function of the angle between alignment of the crest and direction of flow, the relative depth of flow over spillway and its crest height. Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm and Genetic Algorithm (GA) were adopted to minimize the spillway cost as the objective function by considering certain hydraulic conditions as the constraints of the optimization procedure. The results indicated that DE and GA can respectively reduce 19.3% and 16.6% the construction cost of a real benchmark design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amanian, N. (1995). Performance and design of labyrinth spillway, Utah State University, Logan, Utah.
Aydin, M. C. (2012). “CFD simulation of free-surface flow over triangular labyrinth side weir.” Advances in Engineering Software, Vol. 45, No. 1, pp. 159–166, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.09.006.
Aydin, M. C. and Emiroglu, M. E. (2013). “Determination of capacity of labyrinth side weir by CFD.” Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, Vol. 29, pp. 1–8, DOI: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2012.09.008.
Azamathulla, H. (2014). “Discussion of “Orifice spillway aerator: Hydraulic design” by V. V. Bhosekar, V. Jothiprakash, and P. B. Deolalikar.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 141, No. 1, 07014016-1, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000932.
Azamathulla, H. M. and Ahmad, Z. (2013). “Estimation of critical velocity for slurry transport through pipeline using adaptive neurofuzzy interference system and gene-expression programming.” Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 131–137, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)PS.1949-1204.0000123.
Azamathulla, H. and Ahmad, Z. (2014). “Closure to “Estimation of critical velocity for slurry transport through pipeline using adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system and gene-expression programming” by H. Md. Azamathulla and Z. Ahmad.” Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)PS.1949-1204.0000192 (In press).
Azamathulla, H. M., Deo, M. C., and Deolalikar, P. B. (2005). “Neural networks for estimation of scour downstream of a ski-jump bucket.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 131, No. 10, pp. 898–908, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:10(898).
Azamathulla, H. M. D., Deo, M. C., and Deolalikar, P. B. (2006). “Estimation of scour below spillways using neural networks.” Journal of Hydraulic Research, Vol. 44, No. 1, pp. 61–69, DOI: 10.1080/00221686.2006.9521661.
Azamathulla, H. M., Deo, M. C., and Deolalikar, P. B. (2008). “Alternative neural networks to estimate the scour below spillways.” Advances in Engineering Software, Vol. 39, No. 8, pp. 689–698, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2007.07.004.
Azamathulla, H. M., Deo, M. C., Bhajantri, M. R., and Deolalikar, P. B. (2004). “Scour at the base of flip-bucket spillways.” ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 121–129, DOI: 10.1080/09715010.2004.10514759.
Barati, R. (2011). “Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm.” Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 946–954, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000379.
Barati, R. (2013). “Application of excel solver for parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum models.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1139–1148, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-0037-2.
Barati, R., Salehi Neyshabouri, S. A. A., and Ahmadi, G. (2014a). “Development of empirical models with high accuracy for estimation of drag coefficient of flow around a smooth sphere: An evolutionary approach.” Powder Technology, Vol. 257, May 2014, pp. 11–19, DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.045.
Barati, R., Salehi Neyshabouri, S. A. A., and Ahmadi, G. (2014b). “Sphere drag revisited using shuffled complex evolution algorithm.” River Flow 2014 — the 7th International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics — at EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Bilhan, O., Emiroglu, M. E., and Kisi, O. (2011). “Use of artificial neural networks for prediction of discharge coefficient of triangular labyrinth side weir in curved channels.” Advances in Engineering Software, Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 208–214, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.02.006.
Chang, F. J. and Chang, Y. T. (2006). “Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for prediction of water level in reservoir.” Advances in Water Resources, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 1–10, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2011.02.006.
Crookston, B. M. (2010). Labyrinth weirs, PhD Thesis, Utah State University.
Crookston, B. M. and Tullis, B. P. (2012). “Labyrinth weirs: Nappe interference and local submergence.” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Vol. 138, No. 8, pp. 757–765, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000466.
Crookston, B. M. and Tullis, B. P. (2013). “Hydraulic design and analysis of labyrinth weirs. I: Discharge relationships.” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Vol. 139, No. 5, pp. 363–370, DOI:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000558.
Dabling, M. R., Tullis, B. P., and Crookston, B. M. (2013). “Staged labyrinth weir hydraulics.” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Vol. 139, No. 11, pp. 955–960, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000558.
Darvas, L. A. (1971). “Discussion of Performance and design of labyrinth weirs.” Journal of the Hydraulics Division, Vol. 97, No. 8, pp. 1246–1251.
Emiroglu, M. E. and Kisi, O. (2013). “Prediction of discharge coefficient for trapezoidal labyrinth side weir using a neuro-fuzzy approach.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 27, No. 5, pp. 1473–1488, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-012-0249-0.
Emiroglu, M. E., Bilhan, O., and Kisi, O. (2011). “Neural networks for estimation of discharge capacity of triangular labyrinth side-weir located on a straight channel.” Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 38, No. 1, pp. 867–874, DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.07.058.
Emiroglu, M. E., Cihan Aydin, M., and Kaya, N. (2014). “Discharge characteristics of a trapezoidal labyrinth side weir with one and two cycles in subcritical flow.” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, Vol. 140, No. 5, 04014007-1-04014007-13, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000709.
Emiroglu, M. E., Kisi, O., and Bilhan, O. (2010). “Predicting discharge capacity of triangular labyrinth side weir located on a straight channel by using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy technique.” Advances in Engineering Software, Vol. 41, No. 2, pp. 154–160, DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2009.09.006.
Falvay, H. (2003). Hydraulic design of labyrinth weirs, ASCE Press Pub., Virginia, USA.
Falvey, H. and Treille, P. (1995). “Hydraulics and design of fusegates.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 121, No. 7, pp. 512–518, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1995)121:7(512).
Ghare, A. D., Mhaisalkar, V. A., and Porey, P. D. (2008). “An approach to optimal design of trapezoidal labyrinth weirs.” World Applied Sciences Journal, Vol. 3, No. 6, pp. 934–938.
Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning, Addison Wesley, Reading.
Haddad, O. B., Mirmomeni, M., and Mariño, M. A. (2010). “Optimal design of stepped spillways using the HBMO algorithm.” Civil Engineering and Environmental Systems, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 81–94, DOI: 10.1080/10286600802542465.
Hay, N. and Taylor, G. (1970). “Performance and design of labyrinth weirs.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 96, No. 11, pp. 2337–2357.
Holland, J. H. (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: An introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence, U. Michigan Press.
Houston, K. L. (1982). Hydraulic model study of Ute dam labyrinth spillway, Bureau of Reclamation Division of Research Hydraulics Branch, Denver.
Indlekofer, H. and Rouve, G. (1975). “Discharge over polygonal weirs.” Journal of the Hydraulics Division, Vol. 101(HY3), pp. 385–401.
Jang, J. S. R. (1993). “ANFIS: Adaptive network based fuzzy inference system.” IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 665–683, DOI: 10.1109/21.256541.
Jang, J. S. R., Sun, C. T., and Mizutani, E. (1997). Neuro-fuzzy and soft Computing: A computational approach to learning and machine intelligence, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, USA.
Kabiri-Samani, A. (2010). “Analytical approach for flow over an oblique weir.” Transaction A: Civil Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 107–117.
Khatsuria, R. M. (2004). Hydraulics of spillways and energy dissipators, CRC Press.
Khatsuria, R., Deolalikar, P., and Bhosekar, V. (1988). Design of duckbill spillway and reversed sloping curved stilling basin, Salauli Project, 54th R&D Session, CBI&P, Ranchi, India.
Khode, B. V. and Tembhurkar, A. R. (2010). “Evaluation and analysis of crest coefficient for labyrinth weir.” World Applied Sciences Journal, Vol. 11, No. 7, pp. 835–839.
Laugier, F. (2007). “Design and construction of the first Piano Key Weir (PKW) spillwayat the goulours dam.” Hydropower & Dams, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 94–101.
Lux, F. L. and Hinchliff, D. (1985). “Design and construction of labyrinth spillways.” Proc. 15 th International Congress on Large Dams, Paris, France, Vol. 4, No. 59, pp. 249–274.
Nayak, P., Sudheer, K., Rangan, D., and Ramasa, K. (2004). “A neurofuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series.” Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 291, No. 1, pp. 52–66, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.12.010.
Noori, B. and Chilmeran, T. (2005). “Characteristics of flow over normal and oblique weirs with semicircular crest.” Al-Rafidain Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 49–61.
Ouamane, A. and Lempérière, F. (2006). “Design of a new economic shape of weir.” Proceedings of the International Symposium on Dams in the Societies of the 21st Century, Vol. 18, pp. 463–470.
Paxson, G., Campbell, D., and Monroe, J. (2011). “Evolving design approaches and considerations for labyrinth spillways.” USSD Conference, U.S. Society on Dams, San Diego, pp. 1645–1666.
Price, K., Storn, R. M., and Lampinen, J. A. (2006). Differential evolution: A practical approach to global optimization, Springer.
Ribeiro, M., Boillat, J., Schleiss, A., Laugier, F., and Albalat, C. (2007). “Rehabilitation of St-Marc dam. Experimental optimization of a piano key weir.” Proc. of the 32ndCongress of IAHR, Venice, Italy.
Robertson, G. K. (2014). Labyrinth weir hydraulics: Validation of CFD modelling, MSc Thesis, Stellenbosch University.
Savage, B. M. and Brenchley, S. (2013). “Fish passage using broadcrested labyrinth weirs for low-head dams.” International Journal of River Basin Management, Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 277–286, DOI: 10.1080/15715124.2013.811417.
Seamons, T. R. (2014). Labyrinth weirs: A look into geometric variation and its effect on efficiency and design method predictions, MSc Thesis, Utah State University.
Shahheydari, H., Jafari Nodoshan, E., Barati, R., and Azhdary Moghadam, M. (2014). “Discharge coefficient and energy dissipation over stepped spillway under skimming flow regime.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-0749-3.
Sharma, R. K. and Sharma, T. K. (1992). Textbook of irrigation engineering Volume II: Dam Engineering (including Water Power Engineering), s.l.:Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.
Storn, R. and Price, K. (1997). “Differential evolution-A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces.” Journal of Global Optimization, Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 341–359, DOI: 10.1023/A:1008202821328.
Taylor, G. (1968). The performance of labyrinth weirs, PhD Thesis, University of Nottingham, U.K.
Tullis, J. P., Amanian, N., and Waldron, D. (1995). “Design of labyrinth spillways.” Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 121, No. 3, pp. 247–255, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1995)121:3(247).
Vermeyen, T. (1991). Hydraulic model study of Ritschard dam spillways, Bureau of Reclamation, Denver.
Wormleaton, P. R. and Tsang, C. C. (2000). “Aeration performance of rectangular planform labyrinth weirs.” Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 126, No. 5, pp. 456–465, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2000)126:5(456).
Zounemat-Kermani, M. and Teshnehlab, M. (2008). “Using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for hydrological time series prediction.” Applied Soft Computing, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 928–936, DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2007.07.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, K., Nodoushan, E.J., Barati, R. et al. Optimal design of labyrinth spillways using meta-heuristic algorithms. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 468–477 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0462-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0462-5