Abstract
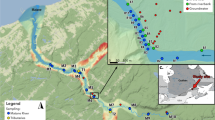
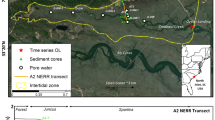
Groundwater may be highly enriched in dissolved carbon species, but its role as a source of carbon to coastal waters is still poorly constrained. Exports of deep and shallow groundwater-derived dissolved carbon species from a small subtropical estuary (Korogoro Creek, Australia, latitude −31.0478°, longitude 153.0649°) were quantified using a radium isotope mass balance model (233Ra and 224Ra, natural groundwater tracers) under two hydrological conditions. In addition, air-water exchange of carbon dioxide and methane in the estuary was estimated. The highest carbon inputs to the estuary were from deep fresh groundwater in the wet season. Most of the dissolved carbon delivered by groundwater and exported from the estuary to the coastal ocean was in the form of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC; 687 mmol m−2 estuary day−1; 20 mmol m−2 catchment day−1, respectively), with a large export of alkalinity (23 mmol m−2 catchment day−1). Average water to air flux of CO2 (869 mmol m−2 day−1) and CH4 (26 mmol m−2 day−1) were 5- and 43-fold higher, respectively, than the average global evasion in estuaries due to the large input of CO2- and CH4-enriched groundwater. The groundwater discharge contribution to carbon exports from the estuary for DIC, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), alkalinity, CO2, and CH4 was 22, 41, 3, 75, and 100 %, respectively. The results show that CO2 and CH4 evasion rates from small subtropical estuaries surrounded by wetlands can be extremely high and that groundwater discharge had a major role in carbon export and evasion from the estuary and therefore should be accounted for in coastal carbon budgets.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abril, G., and N. Iversen. 2002. Methane dynamics in a shallow non-tidal estuary (Randers Fjord, Denmark). Marine Ecology: Progress Series 230: 171–181.
Abril, G., S. Bouillon, F. Darchambeau, C.R. Teodoru, T.R. Marwick, F. Tamooh, F. Ochieng Omengo, N. Geeraert, L. Deirmendjian, P. Polsenaere, and A.V. Borges. 2015. Technical note: large overestimation of pCO2 calculated from pH and alkalinity in acidic, organic-rich freshwaters. Biogeosciences 12(1): 67–78.
Adame, M.F., and C.E. Lovelock. 2011. Carbon and nutrient exchange of mangrove forests with the coastal ocean. Hydrobiologia 663: 23–50.
Atkins, M.L., I.R. Santos, S. Ruiz-Halpern, and D.T. Maher. 2013. Carbon dioxide dynamics driven by groundwater discharge in a coastal floodplain creek. Journal of Hydrology 493: 30–42.
Bauer, J., and T. Bianchi. 2011. Dissolved organic carbon cycling and transformation. Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science 5: 7–67.
Bergamaschi, B.A., D.P. Krabbenhoft, G.R. Aiken, E. Patino, D.G. Rumbold, and W.H. Orem. 2012. Tidally driven export of dissolved organic carbon, total mercury, and methylmercury from a mangrove-dominated estuary. Environmental Science and Technology 46: 1371–1378.
Bianchi, T.S. 2007. Biogeochemistry of estuaries. New York: Oxford University Press.
Borges, A.V., and G. Abril. 2011. Carbon dioxide and methane dynamics in estuaries. In Treatise on estuarine and coastal science, vol. 5, ed. E. Wolanski and D.S. McLusky, 119–161. Waltham: Academic.
Borges, A., B. Delille, L.-S. Schiettecatte, F. Gazeau, G. Abril, and M. Frankignoulle. 2004. Gas transfer velocities of CO2 in three European estuaries (Randers Fjord, Scheldt and Thames). Limnology and Oceanography 49: 1630–1641.
Bouillon, S., et al. 2007. Importance of intertidal sediment processes and porewater exchange on the water column biogeochemistry in a pristine mangrove creek (Ras Dege, Tanzania). Biogeosciences Discussions 4: 317–348.
Bouillon, S. et al. 2008. Mangrove production and carbon sinks: a revision of global budget estimates. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 22. doi: 10.1029/2007GB003052
Burnett, W.C., et al. 2006. Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. The Science of the Total Environment 367: 498–543.
Burnett, W.C., R.N. Peterson, I.R. Santos, and R.W. Hicks. 2010. Use of automated radon measurements for rapid assessment of groundwater flow into Florida streams. Journal of Hydrology 380: 298–304.
Cable, J.E., G.C. Bugna, W.C. Burnett, and J.P. Chanton. 1996. Application of 222Rn and CH4 for assessment of groundwater discharge to the coastal ocean. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1347–1353.
Cai, W.J. 2003. The geochemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon in a surficial groundwater aquifer in North Inlet, South Carolina, and the carbon fluxes to the coastal ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 67: 631–637.
Cai, W.-J. 2011. Estuarine and coastal ocean carbon paradox: CO2 sinks or sites of terrestrial carbon incineration? Annual Review of Marine Science 3: 123–145.
Cai, Y., L. Guo, and T.A. Douglas. 2008. Temporal variations in organic carbon species and fluxes from the Chena River, Alaska. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 1408–1419.
Call, M., et al. 2015. Spatial and temporal variability of carbon dioxide and methane fluxes over semi-diurnal and spring-neap-spring timescales in a mangrove creek. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 150: 211–225.
Chapagain, S.K., V.P. Pandey, S. Shrestha, T. Nakamura, and F. Kazama. 2010. Assessment of deep groundwater quality in Kathmandu valley using multivariate statistical techniques. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 210: 277–288.
Charette, M.A., and M.C. Allen. 2006. Precision ground water sampling in coastal aquifers using a direct‐push, Shielded‐Screen Well‐Point System. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation 26: 87–93.
Chen, C.-T.A., T.-H. Huang, Y.-C. Chen, Y. Bai, X. He, and Y. Kang. 2012. Air–sea exchanges of CO2 in the world’s coastal seas. Biogeosciences 10: 6509–6544.
Constantz, J., C.L. Thomas, and G. Zellweger. 1994. Influence of diurnal variations in stream temperature on streamflow loss and groundwater recharge. Water Resources Research 30: 3253–3264.
Cyronak, T., I. R. Santos, A. McMahon, and B. D. Eyre. 2013. Carbon cycling hysteresis in permeable carbonate sands over a diel cycle: Implications for ocean acidification. Limnology & Oceanography, 58(1): 131–143.
Cyronak, T., I.R. Santos, D.V. Erler, D.T. Maher, and B.D. Eyre. 2014. Drivers of pCO2 variability in two contrasting coral reef lagoons: the influence of submarine groundwater discharge. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 28: 398–414.
De La Paz, M., A. Gómez-Parra, and J. Forja. 2007. Inorganic carbon dynamic and air–water CO2 exchange in the Guadalquivir Estuary (SW Iberian Peninsula). Journal of Marine Systems 68: 265–277.
de Sieyes, N.R., K.M. Yamahara, B.A. Layton, E.H. Joyce, and A.B. Boehm. 2008. Submarine discharge of nutrient-enriched fresh groundwater at Stinson Beach, California is enhanced during neap tides. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 1434–1445.
Dhar, R.K., Y. Zhenga, A. van Geen, Z. Cheng, M. Shanewaz, M. Shamsudduha, M.A. Hoque, M.W. Rahman, and K.M. Ahmed. 2008. Temporal variability of groundwater chemistry in shallow and deep aquifers of Araihazar, Bangladesh. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 99: 97–111.
Dickson, A.G. 1990. Standard potential of the reaction: AgCl (s)+ 12H2 (g) = Ag (s)+ HCl (aq), and the standard acidity constant of the ion HSO4 − in synthetic sea water from 273.15 to 318.15 K. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics 22: 113–127.
Dixon, J.L., J.R. Helms, R.J. Kieber, and G.B. Avery. 2014. Biogeochemical alteration of dissolved organic material in the Cape Fear River Estuary as a function of freshwater discharge. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 149: 273–282.
Dorsett, A., A. Jennifer Cherrier, J.B. Martin, and J.E. Cable. 2011. Assessing hydrologic and biogeochemical controls on pore-water dissolved inorganic carbon cycling in a subterranean estuary: A 14C and 13C mass balance approach. Marine Chemistry 127: 76–89.
Dürr, H.H., G.G. Laruelle, C.M. Van Kempen, C.P. Slomp, M. Meybeck, and H. Middelkoop. 2011. Worldwide typology of nearshore coastal systems: defining the estuarine filter of river inputs to the oceans. Estuaries and Coasts 34: 441–458.
Faber, P.A., V. Evrard, R.J. Woodland, I.C. Cartwright, and P.L. Cook. 2014. Pore-water exchange driven by tidal pumping causes alkalinity export in two intertidal inlets. Limnology and Oceanography 59: 1749–1763.
Ferrón, S., T. Ortega, A. Gómez-Parra, and J. Forja. 2007. Seasonal study of dissolved CH4, CO2and N2O in a shallow tidal system of the bay of Cádiz (SW Spain). Journal of Marine Systems 66: 244–257.
Frankignoulle, M., I. Bourge, and R. Wollast. 1996. Atmospheric CO2 fluxes in a highly polluted estuary (the Scheldt). Limnology and Oceanography 41: 365–369.
Frankignoulle, M., et al. 1998. Carbon dioxide emission from European estuaries. Science 282: 434–436.
Gagan, M.K., L.K. Ayliffe, B.N. Opdyke, D. Hopley, H. Scott‐Gagan, and J. Cowley. 2002. Coral oxygen isotope evidence for recent groundwater fluxes to the Australian Great Barrier Reef. Geophysical Research Letters 29: 43-1–43-4.
Gatland, J.R., I.R. Santos, D.T. Maher, T. Duncan, and D.V. Erler. 2014. Carbon dioxide and methane emissions from an artificially drained coastal wetland during a flood: Implications for wetland global warming potential. Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 119: 1698–1716.
Gazeau, F., et al. 2005. Planktonic and whole system metabolism in a nutrient-rich estuary (the Scheldt estuary). Estuaries and Coasts 28: 868–883.
Gleeson, J., I.R. Santos, D.T. Maher, and L. Golsby-Smith. 2013. Groundwater–surface water exchange in a mangrove tidal creek: evidence from natural geochemical tracers and implications for nutrient budgets. Marine Chemistry 156: 27–37.
Goñi, M.A., and I.R. Gardner. 2003. Seasonal dynamics in dissolved organic carbon concentrations in a coastal water-table aquifer at the forest-marsh interface. Aquatic Geochemistry 9: 209–232.
Hunt, C.W., J.E. Salisbury, and D. Vandermark. 2011. Contribution of non-carbonate anions to total alkalinity and overestimation of pCO2 in New England and New Brunswick rivers. Biogeosciences 8: 3069–3076.
Kim, G., J.-S. Kim, and D.-W. Hwang. 2011. Submarine groundwater discharge from oceanic islands standing in oligotrophic oceans: Implications for global biological production and organic carbon fluxes. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 673–682.
Lee, J.-M., and G. Kim. 2006. A simple and rapid method for analyzing radon in coastal and ground waters using a radon-in-air monitor. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 89: 219–228.
Linto, N., J. Barnes, R. Ramachandran, J. Divia, P. Ramachandran, and R. Upstill-Goddard. 2014. Carbon dioxide and methane emissions from mangrove-associated waters of the Andaman Islands, Bay of Bengal. Estuaries and Coasts 37: 381–398.
Liu, Q., et al. 2012. How significant is submarine groundwater discharge and its associated dissolved inorganic carbon in a river-dominated shelf system? Biogeosciences 9: 1777–1795.
Liu, Q., M.A. Charette, P.B. Henderson, D.C. Mccorkle, W. Martin, and M. Dai. 2014. Effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the coastal ocean inorganic carbon cycle. Limnology and Oceanography 59: 1529–1554.
Macklin, P.A., D.T. Maher, and I.R. Santos. 2014. Estuarine canal estate waters: hotspots of CO2 outgassing driven by enhanced groundwater discharge? Marine Chemistry 167: 82–92.
Maher, D.T., and B.D. Eyre. 2010. Benthic fluxes of dissolved organic carbon in three temperate Australian estuaries: Implications for global estimates of benthic DOC fluxes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences (2005–2012) 115, G04039. doi:10.1029/2010JG001433.
Maher, D., and B.D. Eyre. 2011. Insights into estuarine benthic dissolved organic carbon (DOC) dynamics using δ13C-DOC values, phospholipid fatty acids and dissolved organic nutrient fluxes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75: 1889–1902.
Maher, D and B.D. Eyre 2012. Carbon budgets for three autotrophic Australian estuaries: Implications for global estimates of the coastal air‐water CO2 flux. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 26. doi: 10.1029/2011GB004075.
Maher, D.T., I.R. Santos, L. Golsby-Smith, J. Gleeson, and B.D. Eyre. 2013a. Groundwater-derived dissolved inorganic and organic carbon exports from a mangrove tidal creek: The missing mangrove carbon sink? Limnology and Oceanography 58: 475–488.
Maher, D.T., et al. 2013b. Novel use of cavity ring-down spectroscopy to investigate aquatic carbon cycling from microbial to ecosystem scales. Environmental Science and Technology 47: 12938–12945.
Maher, D.T., K. Cowley, I.R. Santos, P. Macklin, and B.D. Eyre. 2015. Methane and carbon dioxide dynamics in a subtropical estuary over a diel cycle: insights from automated in situ radioactive and stable isotope measurements. Marine Chemistry 168: 69–79.
Millero, F.J., T.B. Graham, F. Huang, H. Bustos-Serrano, and D. Pierrot. 2006. Dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater as a function of salinity and temperature. Marine Chemistry 100: 80–94.
Miyajima, T., Y. Tsuboi, Y. Tanaka, and I. Koike. 2009. Export of inorganic carbon from two Southeast Asian mangrove forests to adjacent estuaries as estimated by the stable isotope composition of dissolved inorganic carbon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences. (2005–2012) 114. doi: 10.1029/2008JG000861
Moore, W.S. 2010. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean. Annual Review of Marine Science 2: 59–88.
Moore, W.S., and R. Arnold. 1996. Measurement of 223Ra and 224Ra in coastal waters using a delayed coincidence counter. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012) 101: 1321–1329.
Moore, W.S., Blanton J.O., and Joye S.B. 2006. Estimates of flushing times, submarine groundwater discharge, and nutrient fluxes to Okatee Estuary, South Carolina. Journal Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012) 111. doi: 10.1029/2005JC003041.
Neubauer, S.C., and J.P. Megonigal. 2015. Moving beyond global warming potentials to quantify the climatic role of ecosystems. Ecosystems 18(6): 1000–1013.
Nirmal Rajkumar, A., J. Barnes, R. Ramesh, R. Purvaja, and R. Upstill-Goddard. 2008. Methane and nitrous oxide fluxes in the polluted Adyar River and estuary, SE India. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 2043–2051.
Noriega, C., and M. Araujo. 2014. Carbon dioxide emissions from estuaries of northern and northeastern Brazil. Scientific Reports 4: 6164.
O’Reilly, C., I.R. Santos, T. Cyronak, A. McMahon and D.T. Maher. 2015. Nitrous oxide and methane dynamics in a coral reef lagoon driven by porewater exchange: Insights from automated high frequency observations. Geophysical Research Letters. 42(8), doi: 10.1002/2015GL063126.
Panneer Selvam, B., S. Natchimuthu, L. Arunachalam, and D. Bastviken. 2014. Methane and carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters in India—implications for large scale greenhouse gas balances. Global Change Biology 20: 3397–3407.
Pelletier, G., E. Lewis, and D. Wallace. 2007. CO 2 Sys. xls: a calculator for the CO 2 system in seawater for Microsoft Excel/VBA. Olympia: Washington State Department of Ecology/Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Peterson, R.N., W.C. Burnett, N. Dimova, and I.R. Santos. 2009. Comparison of measurement methods for radium-226 on manganese-fiber. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 7: 196–205.
Porubsky, W.P., N.B. Weston, W.S. Mooreb, C. Ruppel, and S.B. Joye. 2014. Dynamics of submarine groundwater discharge and associated fluxes of dissolved nutrients, carbon, and trace gases to the coastal zone (Okatee River estuary, South Carolina). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 131: 81–97.
Raymond, P.A., J.E. Bauer, and J.J. Cole. 2000. Atmospheric CO2 evasion, dissolved inorganic carbon production, and net heterotrophy in the York River estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1707–1717.
Rodríguez-Murillo, J., J. Zobrist, and M. Filella. 2015. Temporal trends in organic carbon content in the main Swiss rivers, 1974–2010. The Science of the Total Environment 502: 206–217.
Ruprecht, J.E., and W.A. Timms. 2010. Hat Head Effluent Disposal Scheme – Ongoing Monitoring Results to September 2010. WRL Technical Report.
Sadat-Noori, M., I. Santos, D. Maher, C. Sanders, and L. Sanders. 2015. Groundwater discharge into an estuary using spatially distributed radon time series and radium isotopes. Journal of Hydrology 528: 703–719.
Sanders, C.J., I.R. Santos, D.T. Maher, M. Sadat-Noori, B. Schnetger, and H.-J. Brumsack. 2015. Dissolved iron exports from an estuary surrounded by coastal wetlands: can small estuaries be a significant source of Fe to the ocean? Marine Chemistry 176: 75–82.
Santos, I.R., W.C. Burnett, T. Dittmar, I.G.N.A. Suryaputra, and J. Chanton. 2009. Tidal pumping drives nutrient and dissolved organic matter dynamics in a Gulf of Mexico subterranean estuary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73: 1325–1339.
Santos, I.R., D.T. Maher, and B.D. Eyre. 2012a. Coupling automated radon and carbon dioxide measurements in coastal waters. Environmental Science and Technology 46: 7685–7691.
Santos, I.R., P.L.M. Cook, L. Rogers, J. De Weys, and B.D. Eyre. 2012b. The “salt wedge pump”: convection-driven pore-water exchange as a source of dissolved organic and inorganic carbon and nitrogen to an estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 1415–1426.
Santos, I.R., et al. 2015. Porewater exchange as a driver of carbon dynamics across a terrestrial-marine transect: insights from coupled 222Rn and pCO2 observations in the German Wadden Sea. Marine Chemistry 171: 10–20.
Seitzinger, S., J. Harrison, E. Dumont, A.H. Beusen, and A. Bouwman. 2005. Sources and delivery of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus to the coastal zone: An overview of Global Nutrient Export from Watersheds (NEWS) models and their application. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 19. doi: 10.1029/2005GB002606.
Stewart, B.T., I.R. Santos, D.R. Tait, P.A. Macklin, and D.T. Maher. 2015. Submarine groundwater discharge and associated fluxes of alkalinity and dissolved carbon into Moreton Bay (Australia) estimated via radium isotopes. Marine Chemistry 174(20): 1–12.
St‐Jean, G. 2003. Automated quantitative and isotopic (13C) analysis of dissolved inorganic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in continuous‐flow using a total organic carbon analyser. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 17: 419–428.
Striegl, R.G., M.M. Dornblaser, G.R. Aiken, K.P. Wickland, and P.A. Raymond. 2007. Carbon export and cycling by the Yukon, Tanana, and Porcupine rivers, Alaska, 2001–2005. Water Resources Research. 43. doi: 10.1029/2006WR005201.
Tamše, S., N. Ogrinc, L.M. Walter, D. Turk, and J. Faganeli. 2014. River sources of dissolved inorganic carbon in the gulf of Trieste (N Adriatic): stable carbon isotope evidence. Estuaries and Coasts 38(1): 1–14.
Tank, S.E. et al. 2012. A land-to-ocean perspective on the magnitude, source and implication of DIC flux from major Arctic rivers to the Arctic Ocean. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 26. doi: 10.1029/2011GB004192.
Wang, Z.A., and W.-J. Cai. 2004. Carbon dioxide degassing and inorganic carbon export from a marsh-dominated estuary (the Duplin River): a marsh CO2 pump. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 341–354.
Wang, G., et al. 2015. Net subterranean estuarine export fluxes of dissolved inorganic C, N, P, Si, and total alkalinity into the Jiulong River estuary, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 149: 103–114.
Wanninkhof, R. 1992. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans (1978–2012) 97: 7373–7382.
Weinstein, Y., W. Burnett, P. Swarzenski, Y. Shalem, Y. Yechieli, and B. Herut. 2007. Role of aquifer heterogeneity in fresh groundwater discharge and seawater recycling: An example from the Carmel coast, Israel. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (1978–2012) 112. DOI: 10.1029/2007JC004112.
Weiss, R.F. 1974. Carbon dioxide in water and seawater: the solubility of a non-ideal gas. Marine Chemistry 2: 203–215.
Wiesenburg, D.a., and N.L. Guinasso. 1979. Equilibrium solubilities of methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen in water and sea water. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data 24(4): 356–360.
Winter, P.E., T.A. Schlacherl, and D. Baird. 1996. Carbon flux between an estuary and the ocean: a case for outwelling. Hydrobiologia 337: 123–132.
Zhang, G., J. Zhang, S. Liu, J. Ren, J. Xu, and F. Zhang. 2008. Methane in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and its adjacent marine area: riverine input, sediment release and atmospheric fluxes. Biogeochemistry 91: 71–84.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Christian Sanders, Luciana Sanders, Paul Macklin, Ashley McMahon, Benjamin Stewart, Jennifer Taylor, and Judith Rosentreter for their support during field campaigns. IRS and DTM are funded through Australian Research Council DECRA Fellowships (DE140101733 and DE150100581). We acknowledge support from the Australian Research Council (DP120101645 and LE120100156). We would also like to acknowledge the Associate Editor Alberto Borges and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments which helped strengthen our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Alberto Vieira Borges
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadat-Noori, M., Maher, D.T. & Santos, I.R. Groundwater Discharge as a Source of Dissolved Carbon and Greenhouse Gases in a Subtropical Estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 39, 639–656 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-015-0042-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-015-0042-4