Abstract
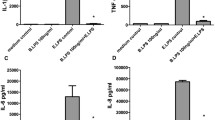
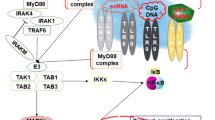
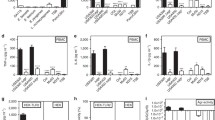
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA), a major cell wall component of Gram-positive bacteria, is associated with various inflammatory diseases ranging from minor skin diseases to severe sepsis. It is known that LTA is recognized by Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), leading to the initiation of innate immune responses and further development of adaptive immunity. However, excessive immune responses may result in the inflammatory sequelae that are involved in severe diseases such as sepsis. Although numerous studies have tried to identify the molecular basis for the pathophysiology of Gram-positive bacterial infection, the exact role of LTA during the infection has not been clearly elucidated. This review provides an overview of LTA structure and host recognition by TLR2 that leads to the activation of innate immune responses. Emphasis is placed on differential immunostimulating activities of LTAs of various Gram-positive bacteria at the molecular level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn KB, Jeon JH, Baik JE, Park OJ, Kang SS, Yun CH, Park JH, Han SH (2014) Muramyl dipeptide potentiates staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Microbes Infect 16:153–160
Akira S, Hemmi H (2003) Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett 85:85–95
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Albiger B, Dahlberg S, Henriques-Normark B, Normark S (2007) Role of the innate immune system in host defence against bacterial infections: focus on the Toll-like receptors. J Intern Med 261:511–528
Baik JE, Ryu YH, Han JY, Im J, Kum KY, Yun CH, Lee K, Han SH (2008) Lipoteichoic acid partially contributes to the inflammatory responses to Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod 34:975–982
Baik JE, Jang KS, Kang SS, Yun CH, Lee K, Kim BG, Kum KY, Han SH (2011) Calcium hydroxide inactivates lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus faecalis through deacylation of the lipid moiety. J Endod 37:191–196
Bhakdi S, Klonisch T, Nuber P, Fischer W (1991) Stimulation of monokine production by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun 59:4614–4620
Carty M, Goodbody R, Schroder M, Stack J, Moynagh PN, Bowie AG (2006) The human adaptor SARM negatively regulates adaptor protein TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Immunol 7:1074–1081
Colombo AP, Haffajee AD, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Smith CM, Cugini MA, Socransky SS (1998) Clinical and microbiological features of refractory periodontitis subjects. J Clin Periodontol 25:169–180
Danforth JM, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Arenberg DA, Vanotteren GM, Standiford TJ (1995) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha expression in vivo and in vitro: the role of lipoteichoic acid. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 74:77–83
De Kimpe SJ, Kengatharan M, Thiemermann C, Vane JR (1995) The cell wall components peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus act in synergy to cause shock and multiple organ failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10359–10363
De Nardo D (2015) Toll-like receptors: activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine 74:181–189
Ellingsen E, Morath S, Flo T, Schromm A, Hartung T, Thiemermann C, Espevik T, Golenbock D, Foster D, Solberg R, Aasen A, Wang J (2002) Induction of cytokine production in human T cells and monocytes by highly purified lipoteichoic acid: involvement of Toll-like receptors and CD14. Med Sci Monit 8:BR149–BR156
Febbraio M, Hajjar DP, Silverstein RL (2001) CD36: a class B scavenger receptor involved in angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, inflammation, and lipid metabolism. J Clin Investig 108:785–791
Gao JJ, Xue Q, Zuvanich EG, Haghi KR, Morrison DC (2001) Commercial preparations of lipoteichoic acid contain endotoxin that contributes to activation of mouse macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun 69:751–757
Gay NJ, Gangloff M (2007) Structure and function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annu Rev Biochem 76:141–165
Ghuysen JM, Hackenbeck R (1994) Bacterial cell wall. Elsevier, New York
Ginsburg I (2002) Role of lipoteichoic acid in infection and inflammation. Lancet Infect Dis 2:171–179
Ginsburg I, Ward PA, Varani J (1999) Can we learn from the pathogenetic strategies of group A hemolytic streptococci how tissues are injured and organs fail in post-infectious and inflammatory sequelae? FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 25:325–338
Gisch N, Kohler T, Ulmer AJ, Muthing J, Pribyl T, Fischer K, Lindner B, Hammerschmidt S, Zahringer U (2013) Structural reevaluation of Streptococcus pneumoniae lipoteichoic acid and new insights into its immunostimulatory potency. J Biol Chem 288:15654–15667
Grangette C, Nutten S, Palumbo E, Morath S, Hermann C, Dewulf J, Pot B, Hartung T, Hols P, Mercenier A (2005) Enhanced antiinflammatory capacity of a Lactobacillus plantarum mutant synthesizing modified teichoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10321–10326
Grundling A, Schneewind O (2007) Synthesis of glycerol phosphate lipoteichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8478–8483
Guan Y, Ranoa DR, Jiang S, Mutha SK, Li X, Baudry J, Tapping RI (2010) Human TLRs 10 and 1 share common mechanisms of innate immune sensing but not signaling. J Immunol 184:5094–5103
Hahn CL, Best AM, Tew JG (2000) Cytokine induction by Streptococcus mutans and pulpal pathogenesis. Infect Immun 68:6785–6789
Han SH, Kim JH, Martin M, Michalek SM, Nahm MH (2003) Pneumococcal lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is not as potent as staphylococcal LTA in stimulating Toll-like receptor 2. Infect Immun 71:5541–5548
Han SH, Kim JH, Seo HS, Martin MH, Chung GH, Michalek SM, Nahm MH (2006) Lipoteichoic acid-induced nitric oxide production depends on the activation of platelet-activating factor receptor and Jak2. J Immunol 176:573–579
Han F, Yu H, Tian C, Li S, Jacobs MR, Benedict-Alderfer C, Zheng QY (2009) Role for Toll-like receptor 2 in the immune response to Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mouse otitis media. Infect Immun 77:3100–3108
Hashimoto M, Tawaratsumida K, Kariya H, Aoyama K, Tamura T, Suda Y (2006a) Lipoprotein is a predominant Toll-like receptor 2 ligand in Staphylococcus aureus cell wall components. Int Immunol 18:355–362
Hashimoto M, Tawaratsumida K, Kariya H, Kiyohara A, Suda Y, Krikae F, Kirikae T, Gotz F (2006b) Not lipoteichoic acid but lipoproteins appear to be the dominant immunobiologically active compounds in Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 177:3162–3169
Haziot A, Rong GW, Silver J, Goyert SM (1993) Recombinant soluble CD14 mediates the activation of endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 151:1500–1507
Hoebe K, Georgel P, Rutschmann S, Du X, Mudd S, Crozat K, Sovath S, Shamel L, Hartung T, Zahringer U, Beutler B (2005) CD36 is a sensor of diacylglycerides. Nature 433:523–527
Hong SW, Baik JE, Kang SS, Yun CH, Seo DG, Han SH (2014) Lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus mutans interacts with Toll-like receptor 2 through the lipid moiety for induction of inflammatory mediators in murine macrophages. Mol Immunol 57:284–291
Horn DL, Morrison DC, Opal SM, Silverstein R, Visvanathan K, Zabriskie JB (2000) What are the microbial components implicated in the pathogenesis of sepsis? Report on a symposium. Clin Infect Dis 31:851–858
Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2001) TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2:835–841
Im J, Lee T, Jeon JH, Baik JE, Kim KW, Kang SS, Yun CH, Kim H, Han SH (2014) Gene expression profiling of bovine mammary gland epithelial cells stimulated with lipoteichoic acid plus peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus. Int Immunopharmacol 21:231–240
Im J, Baik JE, Kim KW, Kang SS, Jeon JH, Park OJ, Kim HY, Kum KY, Yun CH, Han SH (2015) Enterococcus faecalis lipoteichoic acid suppresses Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-8 expression in human periodontal ligament cells. Int Immunol 27:381–391
Imler JL, Hoffmann JA (2001) Toll receptors in innate immunity. Trends Cell Biol 11:304–311
Ishii KJ, Koyama S, Nakagawa A, Coban C, Akira S (2008) Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 3:352–363
Janeway CA, Medzhitov R (2002) Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 20:197–216
Jang KS, Baik JE, Han SH, Chung DK, Kim BG (2011) Multi-spectrometric analyses of lipoteichoic acids isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407:823–830
Jin MS, Kim SE, Heo JY, Lee ME, Kim HM, Paik SG, Lee H, Lee JO (2007) Crystal structure of the TLR1–TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 130:1071–1082
Jorasch P, Warnecke DC, Lindner B, Zahringer U, Heinz E (2000) Novel processive and nonprocessive glycosyltransferases from Staphylococcus aureus and Arabidopsis thaliana synthesize glycoglycerolipids, glycophospholipids, glycosphingolipids and glycosylsterols. Eur J Biochem 267:3770–3783
Kang SS, Kim HJ, Jang MS, Moon S, Lee S, Jeon JH, Baik JE, Park OJ, Son YM, Kim GR, Joo D, Kim H, Han JY, Yun CH, Han SH (2012) Gene expression profile of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells induced by Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid. Int Immunopharmacol 13:454–460
Kang SS, Noh SY, Park OJ, Yun CH, Han SH (2015) Staphylococcus aureus induces IL-8 expression through its lipoproteins in the human intestinal epithelial cell, Caco-2. Cytokine 75:174–180
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Kawai T, Akira S (2011) Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 34:637–650
Keller R, Fischer W, Keist R, Bassetti S (1992) Macrophage response to bacteria: induction of marked secretory and cellular activities by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun 60:3664–3672
Kengatharan KM, De Kimpe S, Robson C, Foster SJ, Thiemermann C (1998) Mechanism of gram-positive shock: identification of peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid moieties essential in the induction of nitric oxide synthase, shock, and multiple organ failure. J Exp Med 188:305–315
Kim HJ, Yang JS, Woo SS, Kim SK, Yun CH, Kim KK, Han SH (2007) Lipoteichoic acid and muramyl dipeptide synergistically induce maturation of human dendritic cells and concurrent expression of proinflammatory cytokines. J Leukoc Biol 81:983–989
Kim HG, Kim NR, Gim MG, Lee JM, Lee SY, Ko MY, Kim JY, Han SH, Chung DK (2008) Lipoteichoic acid isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha production in THP-1 cells and endotoxin shock in mice. J Immunol 180:2553–2561
Kiriukhin MY, Debabov DV, Shinabarger DL, Neuhaus FC (2001) Biosynthesis of the glycolipid anchor in lipoteichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus RN4220: role of YpfP, the diglucosyldiacylglycerol synthase. J Bacteriol 183:3506–3514
Knapp S, Von Aulock S, Leendertse M, Haslinger I, Draing C, Golenbock DT, Van Der Poll T (2008) Lipoteichoic acid-induced lung inflammation depends on TLR2 and the concerted action of TLR4 and the platelet-activating factor receptor. J Immunol 180:3478–3484
Kobayashi T, Tani T, Yokota T, Kodama M (2000) Detection of peptidoglycan in human plasma using the silkworm larvae plasma test. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 28:49–53
Koch HU, Fischer W (1978) Acyldiglucosyldiacylglycerol-containing lipoteichoic acid with a poly(3-O-galabiosyl-2-O-galactosyl-sn-glycero-1-phosphate) chain from Streptococcus lactis Kiel 42172. Biochemistry 17:5275–5281
Latz E, Verma A, Visintin A, Gong M, Sirois CM, Klein DC, Monks BG, Mcknight CJ, Lamphier MS, Duprex WP, Espevik T, Golenbock DT (2007) Ligand-induced conformational changes allosterically activate Toll-like receptor 9. Nat Immunol 8:772–779
Lebeer S, Claes IJ, Vanderleyden J (2012) Anti-inflammatory potential of probiotics: lipoteichoic acid makes a difference. Trends Microbiol 20:5–10
Lee JK, Baik JE, Yun CH, Lee K, Han SH, Lee W, Bae KS, Baek SH, Lee Y, Son WJ, Kum KY (2009) Chlorhexidine gluconate attenuates the ability of lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus faecalis to stimulate toll-like receptor 2. J Endod 35:212–215
Leemans JC, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Florquin S, Van Kessel KP, Van Der Poll T (2002) Differential role of interleukin-6 in lung inflammation induced by lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:1445–1450
Leemans JC, Heikens M, Van Kessel KP, Florquin S, Van Der Poll T (2003) Lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus synergistically induce neutrophil influx into the lungs of mice. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 10:950–953
Leendertse M, Willems RJ, Giebelen IA, Van Den Pangaart PS, Wiersinga WJ, De Vos AF, Florquin S, Bonten MJ, Van Der Poll T (2008) TLR2-dependent MyD88 signaling contributes to early host defense in murine Enterococcus faecium peritonitis. J Immunol 180:4865–4874
Letiembre M, Echchannaoui H, Ferracin F, Rivest S, Landmann R (2005) Toll-like receptor-2 deficiency is associated with enhanced brain TNF gene expression during pneumococcal meningitis. J Neuroimmunol 168:21–33
Manukyan M, Triantafilou K, Triantafilou M, Mackie A, Nilsen N, Espevik T, Wiesmuller KH, Ulmer AJ, Heine H (2005) Binding of lipopeptide to CD14 induces physical proximity of CD14, TLR2 and TLR1. Eur J Immunol 35:911–921
Medzhitov R (2007) Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 449:819–826
Medzhitov R, Janeway CA (1997) Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell 91:295–298
Miyauchi M, Kitagawa S, Hiraoka M, Saito A, Sato S, Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Takata T (2004) Immunolocalization of CXC chemokine and recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the rat molar periodontal tissue after topical application of lipopolysaccharide. Histochem Cell Biol 121:291–297
Morath S, Geyer A, Hartung T (2001) Structure–function relationship of cytokine induction by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med 193:393–397
Morath S, Geyer A, Spreitzer I, Hermann C, Hartung T (2002a) Structural decomposition and heterogeneity of commercial lipoteichoic acid preparations. Infect Immun 70:938–944
Morath S, Stadelmaier A, Geyer A, Schmidt RR, Hartung T (2002b) Synthetic lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus is a potent stimulus of cytokine release. J Exp Med 195:1635–1640
Muller-Anstett MA, Muller P, Albrecht T, Nega M, Wagener J, Gao Q, Kaesler S, Schaller M, Biedermann T, Gotz F (2010) Staphylococcal peptidoglycan co-localizes with Nod2 and TLR2 and activates innate immune response via both receptors in primary murine keratinocytes. PLoS One 5:e13153
Nakayama M, Underhill DM, Petersen TW, Li B, Kitamura T, Takai T, Aderem A (2007) Paired Ig-like receptors bind to bacteria and shape TLR-mediated cytokine production. J Immunol 178:4250–4259
Nakayama M, Kurokawa K, Nakamura K, Lee BL, Sekimizu K, Kubagawa H, Hiramatsu K, Yagita H, Okumura K, Takai T, Underhill DM, Aderem A, Ogasawara K (2012) Inhibitory receptor paired Ig-like receptor B is exploited by Staphylococcus aureus for virulence. J Immunol 189:5903–5911
Neuhaus FC, Baddiley J (2003) A continuum of anionic charge: structures and functions of d-alanyl-teichoic acids in gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:686–723
Nilsen NJ, Vladimer GI, Stenvik J, Orning MP, Zeid-Kilani MV, Bugge M, Bergstroem B, Conlon J, Husebye H, Hise AG, Fitzgerald KA, Espevik T, Lien E (2015) A role for the adaptor proteins TRAM and TRIF in toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J Biol Chem 290:3209–3222
Noh SY, Kang SS, Yun CH, Han SH (2015) Lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits Pam2CSK4-induced IL-8 production in human intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Immunol 64:183–189
O’Neill LA, Bowie AG (2007) The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 7:353–364
Pai AB, Patel H, Prokopienko AJ, Alsaffar H, Gertzberg N, Neumann P, Punjabi A, Johnson A (2012) Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus induces lung endothelial cell barrier dysfunction: role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. PLoS One 7:e49209
Park OJ, Han JY, Baik JE, Jeon JH, Kang SS, Yun CH, Oh JW, Seo HS, Han SH (2013) Lipoteichoic acid of Enterococcus faecalis induces the expression of chemokines via TLR2 and PAFR signaling pathways. J Leukoc Biol 94:1275–1284
Percy MG, Grundling A (2014) Lipoteichoic acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:81–100
Perea Velez M, Verhoeven TL, Draing C, Von Aulock S, Pfitzenmaier M, Geyer A, Lambrichts I, Grangette C, Pot B, Vanderleyden J, De Keersmaecker SC (2007) Functional analysis of D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid in the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3595–3604
Pluddemann A, Mukhopadhyay S, Gordon S (2011) Innate immunity to intracellular pathogens: macrophage receptors and responses to microbial entry. Immunol Rev 240:11–24
Rahman O, Dover LG, Sutcliffe IC (2009) Lipoteichoic acid biosynthesis: two steps forwards, one step sideways? Trends Microbiol 17:219–225
Rainard P, Fromageau A, Cunha P, Gilbert FB (2008) Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid triggers inflammation in the lactating bovine mammary gland. Vet Res 39:52
Ray A, Cot M, Puzo G, Gilleron M, Nigou J (2013) Bacterial cell wall macroamphiphiles: pathogen-/microbe-associated molecular patterns detected by mammalian innate immune system. Biochimie 95:33–42
Reichmann NT, Grundling A (2011) Location, synthesis and function of glycolipids and polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid in gram-positive bacteria of the phylum Firmicutes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 319:97–105
Reid CW, Vinogradov E, Li J, Jarrell HC, Logan SM, Brisson JR (2012) Structural characterization of surface glycans from Clostridium difficile. Carbohydr Res 354:65–73
Ryu YH, Baik JE, Yang JS, Kang SS, Im J, Yun CH, Kim DW, Lee K, Chung DK, Ju HR, Han SH (2009) Differential immunostimulatory effects of gram-positive bacteria due to their lipoteichoic acids. Int Immunopharmacol 9:127–133
Santos-Sierra S, Deshmukh SD, Kalnitski J, Kuenzi P, Wymann MP, Golenbock DT, Henneke P (2009) Mal connects TLR2 to PI3Kinase activation and phagocyte polarization. EMBO J 28:2018–2027
Schneewind O, Missiakas D (2014) Lipoteichoic acids, phosphate-containing polymers in the envelope of gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 196:1133–1142
Shiraishi T, Yokota S, Morita N, Fukiya S, Tomita S, Tanaka N, Okada S, Yokota A (2013) Characterization of a Lactobacillus gasseri JCM 1131T lipoteichoic acid with a novel glycolipid anchor structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3315–3318
Standiford TJ, Arenberg DA, Danforth JM, Kunkel SL, Vanotteren GM, Strieter RM (1994) Lipoteichoic acid induces secretion of interleukin-8 from human blood monocytes: a cellular and molecular analysis. Infect Immun 62:119–125
Stuart LM, Deng J, Silver JM, Takahashi K, Tseng AA, Hennessy EJ, Ezekowitz RA, Moore KJ (2005) Response to Staphylococcus aureus requires CD36-mediated phagocytosis triggered by the COOH-terminal cytoplasmic domain. J Cell Biol 170:477–485
Takeda K, Akira S (2005) Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol 17:1–14
Takeuchi O, Akira S (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140:805–820
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 11:443–451
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Akira S (2000) Cutting edge: TLR2-deficient and MyD88-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol 165:5392–5396
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Mühlradt PF, Morr M, Radolf JD, Zychlinsky A, Takeda K, Akira S (2001) Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol 13:933–940
Tanji H, Ohto U, Shibata T, Miyake K, Shimizu T (2013) Structural reorganization of the Toll-like receptor 8 dimer induced by agonistic ligands. Science 339:1426–1429
Thiemermann C (2002) Interactions between lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus: a structural and functional analysis. Microbes Infect 4:927–935
Timmerman CP, Mattsson E, Martinez-Martinez L, De Graaf L, Van Strijp JA, Verbrugh HA, Verhoef J, Fleer A (1993) Induction of release of tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes by staphylococci and staphylococcal peptidoglycans. Infect Immun 61:4167–4172
Torres D, Barrier M, Bihl F, Quesniaux VJ, Maillet I, Akira S, Ryffel B, Erard F (2004) Toll-like receptor 2 is required for optimal control of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun 72:2131–2139
Tsutsui O, Kokeguchi S, Matsumura T, Kato K (1991) Relationship of the chemical structure and immunobiological activities of lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus faecalis (Enterococcus hirae) ATCC 9790. FEMS Microbiol Immunol 3:211–218
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS (1995) Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol 13:437–457
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS (1999) Recognition of gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin by the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 11:19–22
Von Aulock S, Morath S, Hareng L, Knapp S, Van Kessel KP, Van Strijp JA, Hartung T (2003) Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus is a potent stimulus for neutrophil recruitment. Immunobiology 208:413–422
Wang JE, Jorgensen PF, Almlof M, Thiemermann C, Foster SJ, Aasen AO, Solberg R (2000) Peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus induce tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL-6), and IL-10 production in both T cells and monocytes in a human whole blood model. Infect Immun 68:3965–3970
Wang JE, Dahle MK, Mcdonald M, Foster SJ, Aasen AO, Thiemermann C (2003) Peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid in gram-positive bacterial sepsis: receptors, signal transduction, biological effects, and synergism. Shock 20:402–414
Wang JE, Dahle MK, Yndestad A, Bauer I, Mcdonald MC, Aukrust P, Foster SJ, Bauer M, Aasen AO, Thiemermann C (2004) Peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus causes inflammation and organ injury in the rat. Crit Care Med 32:546–552
Wang S, Liu K, Seneviratne CJ, Li X, Cheung GS, Jin L, Chu CH, Zhang C (2015) Lipoteichoic acid from an clinical strain promotes TNF-alpha expression through the NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in differentiated THP-1 macrophages. Biomed Rep 3:697–702
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC (1990) CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 249:1431–1433
Xing J, Moldobaeva N, Birukova AA (2011) Atrial natriuretic peptide protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung injury and endothelial barrier dysfunction. J Appl Physiol (1985) 110:213–224
Yoshimura A, Lien E, Ingalls RR, Tuomanen E, Dziarski R, Golenbock D (1999) Cutting edge: recognition of gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via Toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol 163:1–5
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, which is funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2015R1A2A1A15055453 and NRF-2015M2A2A6A01044894), Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (PJ01112401 and PJ01112402), Rural Development Administration, and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, which is funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (HI14C0469), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, SS., Sim, JR., Yun, CH. et al. Lipoteichoic acids as a major virulence factor causing inflammatory responses via Toll-like receptor 2. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 1519–1529 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0804-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0804-y