Abstract
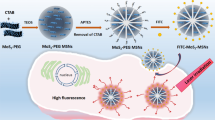
The clinical translation of many inorganic nanomaterials is severely hampered by toxicity issues because of the long-term retention of these nanomaterials in the body. In this study, we developed a bio-clearable theranostic agent based on ultra-small MoS2 nanodots, which were synthesized by a facile bottom-up approach through one-step solvothermal decomposition of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate. After modification by glutathione (GSH), the obtained MoS2-GSH nanodots exhibited sub-10-nm hydrodynamic diameters without aggregation in various physiological buffers. Without showing appreciable in vitro toxicity, such MoS2-GSH nanodots with strong near-infrared (NIR) absorbance could induce remarkable photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Upon intravenous (i.v.) injection, efficient tumor accumulation of MoS2-GSH nanodots was observed by photoacoustic imaging, and further confirmed by analysis of the biodistribution of Mo. Notably, the MoS2-GSH nanodots, in contrast to conventional MoS2 nanoflakes with larger sizes, showed rather efficient body clearance via urine, where the majority of the injected dose was cleared within just seven days. Photothermal ablation of tumors on mice was then realized with the MoS2-GSH nanodots, achieving excellent therapeutic efficacy. This study presents a new type of ultra-small nanoparticle with efficient tumor homing/treatment abilities, as well as rapid body clearance behavior, making it promising for cancer theranostics without long-term toxicity concerns.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, M. E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D. M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782.
Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Feng, L. Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Functional nanomaterials for phototherapies of cancer. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10869–10939.
Bhaumik, J.; Mittal, A. K.; Banerjee, A.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U. C. Applications of phototheranostic nanoagents in photodynamic therapy. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1373–1394.
Cobley, C. M.; Chen, J. Y.; Cho, E. C.; Wang, L. V.; Xia, Y. N. Gold nanostructures: A class of multifunctional materials for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 44–56.
William, W. Y.; Chang, E.; Drezek, R.; Colvin, V. L. Water-soluble quantum dots for biomedical applications. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 781–786.
Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. Upconversion nanoparticles and their composite nanostructures for biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 23–37.
Li, Z. W.; Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Gong, H.; Yin, S. N.; Gong, Q. F.; Li, Y. G.; Liu, Z. PEG-functionalized iron oxide nanoclusters loaded with chlorin e6 for targeted, NIR light induced, photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9160–9170.
Tian, Q. W.; Hu, J. Q.; Zhu, Y. H.; Zou, R. J.; Chen, Z. G.; Yang, S. P.; Li, R. W.; Su, Q. Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, X. G. Sub-10 nm Fe3O4@Cu2–xS core–shell nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8571–8577.
Hao, R.; Xing, R. J.; Xu, Z. C.; Hou, Y. L.; Gao, S.; Sun, S. H. Synthesis, functionalization, and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2729–2742.
Liu, Z.; Tabakman, S.; Welsher, K.; Dai, H. J. Carbon nanotubes in biology and medicine: In vitro and in vivo detection, imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 85–120.
Yang, K.; Wan, J. M.; Zhang, S.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y. J.; Liu, Z. The influence of surface chemistry and size of nanoscale graphene oxide on photothermal therapy of cancer using ultra-low laser power. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2206–2214.
Zhu, S. J.; Song, Y. B.; Zhao, X. H.; Shao, J. R.; Zhang, J. H.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381.
Vivero-Escoto, J. L.; Huxford-Phillips, R. C.; Lin, W. B. Silica-based nanoprobes for biomedical imaging and theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2673–2685.
Shen, J.; Song, G. S.; An, M.; Li, X. Q.; Wu, N.; Ruan, K. C.; Hu, J. Q.; Hu, R. G. The use of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres to encapsulate bortezomib and improve efficacy for non-small cell lung cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 316–326.
Yang, G. B.; Gong, H.; Qian, X. X.; Tan, P. L.; Li, Z. W.; Liu, T.; Liu, J. J.; Li, Y. Y.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanorods intrinsically doped with photosensitizers as a multifunctional drug carrier for combination therapy of cancer. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 751–764.
Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mä dler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627.
Song, X. J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z. Recent advances in the development of organic photothermal nano-agents. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 340–354.
Longmire, M.; Choyke, P. L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: Considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717.
Choi, H. S.; Liu, W. H.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J. P.; Ipe, B. I.; Bawendi, M. G.; Frangioni, J. V. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170.
Liu, J. B.; Yu, M. X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, S. Y.; Ning, X. H.; Zheng, J. Passive tumor targeting of renal-clearable luminescent gold nanoparticles: Long tumor retention and fast normal tissue clearance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4978–4981.
Tang, S. H.; Chen, M.; Zheng, N. F. Multifunctional ultrasmall Pd nanosheets for enhanced near-infrared photothermal therapy and chemotherapy of cancer. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 165–174.
Huang, X.; Zeng, Z. Y.; Zhang, H. Metal dichalcogenide nanosheets: Preparation, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1934–1946.
Chen, Y.; Tan, C. L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Z. Two-dimensional graphene analogues for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2681–2701.
Zhang, H. Ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9451–9469.
Tan, C. L.; Zhang, H. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheet-based composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2713–2731.
Liu, T.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Two dimensional transitional metal dichalcogenides for biomedical applications. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 902–912.
Cheng, L.; Liu, J. J.; Gu, X.; Gong, H.; Shi, X. Z.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, G.; Xing, H. Y. et al. PEGylated WS2 nanosheets as a multifunctional theranostic agent for in vivo dual-modal CT/photoacoustic imaging guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1886–1893.
Liu, Q.; Sun, C. Y.; He, Q.; Khalil, A.; Xiang, T.; Liu, D. B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, L. Stable metallic 1T-WS2 ultrathin nanosheets as a promising agent for near-infrared photothermal ablation cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3982–3991.
Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Gong, H.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X. Z.; Feng, L. Z.; Sun, B. Q.; Liu, Z. Drug delivery with PEGylated MoS2 nano-sheets for combined photothermal and chemotherapy of cancer. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3433–3440.
Yin, W. Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, J.; Tian, G.; Zhou, L. J.; Zheng, X. P.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, Z. J. et al. High-throughput synthesis of single-layer MoS2 nanosheets as a near-infrared photothermal-triggered drug delivery for effective cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6922–6933.
Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Yang, B.; Song, X.-R.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Cao, D.-R.; Shi, W.-R.; Chen, G.-N. Topological insulator bismuth selenide as a theranostic platform for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1998.
Qian, X. X.; Shen, S. D.; Liu, T.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional TiS2 nanosheets for in vivo photoacoustic imaging and photothermal cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6380–6387.
Liu, T.; Shi, S. X.; Liang, C.; Shen, S. D.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Song, X. J.; Goel, S.; Barnhart, T. E.; Cai, W. B. et al. Iron oxide decorated MoS2 nanosheets with double PEGylation for chelator-free radiolabeling and multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 950–960.
Yang, G. B.; Gong, H.; Liu, T.; Sun, X. Q.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional magnetic WS2@Fe3O4 nanocomposite with mesoporous silica coating for drug delivery and imagingguided therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 62–71.
Cheng, L.; Shen, S. D.; Shi, S. X.; Yi, Y.; Wang, X. Y.; Song, G. S.; Yang, K.; Liu, G.; Barnhart, T. E.; Cai, W. B. et al. FeSe2-decorated Bi2Se3 nanosheets fabricated via cation exchange for chelator-free 64Cu-labeling and multimodal image-guided photothermal-radiation therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2185–2197.
Cheng, L.; Yuan, C.; Shen, S. D.; Yi, X.; Gong, H.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Bottom-up synthesis of metal-ion-doped WS2 nanoflakes for cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11090–11101.
Xu, S. J.; Li, D.; Wu, P. Y. One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1127–1136.
Wang, T. Y.; Zhu, H. C.; Zhuo, J. Q.; Zhu, Z. W.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Lubarsky, G.; Lin, J.; Li, M. X. Biosensor based on ultrasmall MoS2 nanoparticles for electrochemical detection of H2O2 released by cells at the nanomolar level. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10289–10295.
Yong, Y.; Cheng, X. J.; Bao, T.; Zu, M.; Yan, L.; Yin, W. Y.; Ge, C. C.; Wang, D. L.; Gu, Z. J.; Zhao, Y. L. Tungsten sulfide quantum dots as multifunctional nanotheranostics for in vivo dual-modal image-guided photothermal/radiotherapy synergistic therapy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12451–12463.
Wang, X. W.; Sun, G. Z.; Li, N.; Chen, P. Quantum dots derived from two-dimensional materials and their applications for catalysis and energy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2239–2262.
Zhang, X.; Lai, Z. C.; Liu, Z. D.; Tan, C. L.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, M. T.; Xie, L. H.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H. A facile and universal top-down method for preparation of monodisperse transition-metal dichalcogenide nanodots. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 5515–5518.
Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Sun, J.; Li, D. H.; Yang, X. R. Enhanced catalytic activities of surfactant-assisted exfoliated WS2 nanodots for hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2159–2166.
Zhang, X.-D.; Zhang, J. X.; Wang, J. Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Deng, J.; Deng, D. H.; Long, W.; Sun, Y.-M. et al. Highly catalytic nanodots with renal clearance for radiation protection. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4511–4519.
Zong, X.; Na, Y.; Wen, F. Y.; Ma, G. J.; Yang, J. H.; Wang, D. G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, L. C.; Li, C. Visible light driven H2 production in molecular systems employing colloidal MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4536–4538.
Lince, J. R.; Frantz, P. P. Anisotropic oxidation of MoS2 crystallites studied by angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Tribol. Lett. 2001, 9, 211–218.
Gopalakrishnan, D.; Damien, D.; Shaijumon, M. M. MoS2 quantum dot-interspersed exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5297–5303.
Baker, M. A.; Gilmore, R.; Lenardi, C.; Gissler, W. of S from MoS2 and determination of MoSx stoichiometry from Mo and S peak positions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 150, 255–262.
Stipp, S. L.; Hochella, M. F., Jr. Structure and bonding environments at the calcite surface as observed with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and low energy electron diffraction (LEED). Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1991, 55, 1723–1736.
Zeng, Z. Y.; Yin, Z. Y.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; He, Q. Y.; Lu, G.; Boey, F.; Zhang, H. Single-layer semiconducting nanosheets: High-yield preparation and device fabrication. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11093–11097.
Chou, S. S.; De, M.; Kim, J.; Byun, S.; Dykstra, C.; Yu, J.; Huang, J. X.; Dravid, V. P. Ligand conjugation of chemically exfoliated MoS2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4584–4587.
Li, S.-D.; Huang, L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 496–504.
Rosencwaig, A.; Gersho, A. Theory of the photoacoustic effect with solids. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 64–69.
Gong, Q. F.; Cheng, L.; Liu, C. H.; Zhang, M.; Feng, Q. L.; Ye, H. L.; Zeng, M.; Xie, L. M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. G. Ultrathin MoS2(1–x)Se2x alloy nanoflakes for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2213–2219.
Cheng, L.; He, W. W.; Gong, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, Z. P.; Liu, Z. PEGylated micelle nanoparticles encapsulating a non-fluorescent near-infrared organic dye as a safe and highly-effective photothermal agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5893–5902.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These two authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Chao, Y., Gao, M. et al. Ultra-small MoS2 nanodots with rapid body clearance for photothermal cancer therapy. Nano Res. 9, 3003–3017 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1183-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1183-x