Abstract
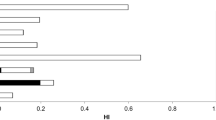
Edible 12 marine species (pelagic fish, demersal fish and shellfish) caught from the Marmara Sea, Black Sea and Aegean Sea. Samples were analysed for content in total mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb) and arsenic (As). In this study, the metal concentrations of samples and health risks in human were determined by the estimated weekly intake (EWI), hazard index (HI) and target hazard quotients (THQs). The levels of total mercury, cadmium and lead were present in bluefish, sardine, sole higher than maximum levels proposed by European legislation. EWI, HI and THQs through this fish and shellfish consumption were in tolerable limits for both female and male consumer. In contrast, total target hazard quotients (TTHQs) values of female consumers in the 15–24 age range due to consumption of certain pelagic fish species indicated that human health risk might be of concern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonso C, Lourenço HM, Dias A, Nunes ML, Castro M (2007) Contaminant metals in black scabbard fish (Aphanopus carbo) caught off Madeira and the Azores. Food Chem 101:120–125
Alkan N, Aktas M, Gedik K (2012) Comparison of metal accumulation in fish species from the southeastern Black Sea. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:807–812
Antonijevic B, Jankovic S, Curcic M, Durgo K, Stokic E, Srdic B, Tomic-Naglic D (2011) Risk characterization for mercury, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and polychlorinated biphenyls associated with fish consumption in Serbia. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2586–2593
Blanco SL, González JC, Vieites JM (2008) Mercury, cadmium and lead levels in samples of the main traded fish and shellfish species in Galicia, Spain. Food Addit Contam B 1(1):15–21
Bodin N, Burgeot T, Stanisière JY, Bocquené G, Menard D, Minier C, Boutet I, Amat A, Cherel Y, Budzinski H (2004) Seasonal variations of a battery of biomarkers and physiological indices for the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis transplanted into the northwest Mediterranean Sea. Comp Biochem Phys C 138:411–427
Bonsignorea M, Salvagio Manta D, Oliveri E, Sprovieri M, Basilone G, Bonanno A, Falco F, Traina A, Mazzola S (2013) Mercury in fishes from Augusta Bay (southern Italy): risk assessment and health implication. Food Chem Toxicol 56:184–194
Bora Başara B, Güler C, Yentür GK, Birge B, Pulgat E, Mamak Ekinci B (2013) T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı Sağlık İstatistikleri Yıllığı 2012. Sağlık Bakalığı Yayın No: 917, Sağlık Araştırmaları Genel Müdürlüğü Yayın No: SB-SAG-2013/01. p 17, 43. Ankara. http://www.saglik.gov.tr/TR/dosya/1-87578/h/istaturk2012.pdf. Accessed 21 July 2015
Burger J, Gochfeld M (2005) Heavy metals in commercial fish in New Jersey. Environ Res 99:403–412
Burger J, Gaines KF, Boring S, Stephens WL, Snodgrass J, Dixon C, McMahon M, Shukla S, Shukla T, Gochfeld M (2002) Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environ Res Sect A 89:85–97
Chung SWC, Kwong KP, Tang ASP, Xia Y, Ho PYY (2008) Mercury and methylmercury levels in the main traded fish species in Hong Kong. Food Addit Contam B 1(2):106–113
Duran A, Tüzen M, Soylak M (2014) Assessment of trace metal concentrations in muscle tissue of certain commercially available fish species from Kayseri, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 186(7):4619–4628
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2009) Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain: cadmium in food. EFSA J 980:1–139
European Commission Regulation (2006) European Commission Regulation, No 1881/2006 Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs, 19 December 2006. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0005:0024:EN:PDF. Accessed 1 Jan 2015
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2011) Statistical databases. http://faostat.fao.org/site/610/default.aspx#ancor. Accessed 10 July 2015
Herreros MA, Ińigo-Nuńez S, Sanchez-Perez E, Encinas T, Gonzalez-Bulnes A (2008) Contribution of fish consumption to heavy metals exposure in women of childbearing age from a Mediterranean country (Spain). Food Chem Toxicol 46:1591–1595
JECFA (FAO Joint WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives) (2000) Safety evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. WHO Food Addit Ser 44:273–312
Keskin Y, Baskaya R, Özyaral O, Yurdun T, Lüleci NE, Hayran O (2007) Cadmium, lead, mercury and copper in fish from the Marmara Sea, Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:258–261
Kucuksezgin F, Altay O, Uluturhan E, Kontas A (2001) Trace metal and organochlorine residue levels in red mullet (Mullus barbatus) from the eastern Aegean, Turkey. Water Res 35:2327–2332
Mendil D, Demirci Z, Tüzen M, Soylak M (2010) Seasonal investigation of trace element contents in commercially valuable fish species from the Black sea, Turkey. Food Chem Toxicol 48(3):865–870
Nadal M, Ferré-Huguet N, Martí-Cid R, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2008) Exposure to metals through the consumption of fish and seafood by the population living near the Ebro River in Catalonia, Spain: health risks. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 14:780–795
Pastorelli AA, Baldini M, Stacchini P, Baldini G, Morelli S, Sagratella E, Zaza S, Ciardullo S (2012) Human exposure to lead, cadmium and mercury through fish and seafood product consumption in Italy: a pilot evaluation. Food Addit Contam A 29(12):1913–1921
Storelli MM (2008) Potential human health risks from metals (Hg, Cd, and Pb) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) via seafood consumption: estimation of target hazard quotients (THQs) and toxic equivalents (TEQs). Food Chem Toxicol 46:2782–2788
Storelli MM, Barone G (2013) Toxic metals (Hg, Pb, and Cd) in commercially important demersal fish from Mediterranean Sea: contamination levels and dietary exposure assessment. J Food Sci 78(2):T362–T366
Storelli MM, Giacominelli-Stuffler R, Storelli A, D’Addabbo R, Palermo C, Marcotrigiano GO (2003) Survey of total mercury and methylmercury levels in edible fish from the Adriatic Sea. Food Addit Contam 20(12):1114–1119
Storelli MM, Storelli A, Giacominelli-Stuffler R, Marcotrigiano GO (2005) Mercury speciation in the muscle of two commercially important fish, hake (Merluccius merluccius) and striped mullet (Mullus barbatus) from the Mediterranean sea: estimated weekly intake. Food Chem 89:295–300
Storelli MM, Barone G, Garofalo R, Marcotrigiano GO (2007) Metals and organochlorine compounds in eel (Anguilla anguilla) from the Lesina lagoon, Adriatic Sea (Italy). Food Chem 100:1337–1341
Tepe Y, Türkmen M, Türkmen A (2008) Assessment of heavy metals in two commercial fish species of four Turkish seas. Environ Monit Assess 146:277–284
Türk Gıda Kodeksi Bulaşanlar Yönetmeliği (2011) Resmi Gazete, Sayı : 28157 (3. Mükerrer), 29 Aralık 2011 Perşembe, Ek. 1. http://www.resmigazete.gov.tr/eskiler/2011/12/20111229M3-8-1.pdf. Accessed 01 Jan 2015
Türkmen A, Türkmen M, Tepe Y, Akyurt I (2005) Heavy metals in three commercially valuable fish species from Iskenderun Bay, Northern East Mediterranean Sea, Turkey. Food Chem 91:167–172
Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Türkmen M (2008) Metal Levels in Tissues of the European Anchovy, Engraulis encrasicolus L., 1758, and Picarel, Spicara smaris L., 1758, from Black, Marmara and Aegean Seas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:521–525
Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Türkmen M, Mutlu E (2009a) Heavy metal contaminants in tissues of the Garfish, Belone belone L., 1761, and the Bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix L., 1766, from Turkey waters. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:70–74
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Töre Y, Ateş A (2009b) Determination of metals in fish species from Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Food Chem 113:233–237
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y (2011) Comparison of metals in tissues of fish from Paradeniz Lagoon in the Coastal Area of Northern East Mediterranean. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87(4):381–385
Tüzen M (2003) Determination of heavy metals in fish samples of the middle Black Sea (Turkey) by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 80:119–123
Tüzen M (2009) Toxic and essential trace elemental contents in fish species from the Black Sea, Turkey. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1785–1790
Uluözlü OD, Tüzen M, Mendil D, Soylak M (2007) Trace metal content in nine species of fish from the Black and Aegean Seas, Turkey. Food Chem 104:835–840
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2007) Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils. Method 3051A (Revision 1 February 2007). http://www3.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/3051a.pdf. Accessed 5 February 2014
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2015) Regional Screening level (RSL) summary table (TR=1E-6, HQ=1) June 2015 (revised). http://semspub.epa.gov/work/03/2218422.pdf. Accessed 12 August 2015
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011a) Evaluation of cartain food additives and contaminats, seventy-second meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on food additives (JECFA), Rome, 15–25 February, 2010, WHO technical report series no 959. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44514/1/WHO_TRS_959_eng.pdf. Accessed 12 August 2015
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011b) Evaluation of cartain food additives and contaminats, seventy-third meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on food additives (JECFA), Geneva, 08–17 June, 2010, WHO technical report series no 960. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44515/1/WHO_TRS_960_eng.pdf. Accessed 12 August 2015
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University with the projects BYP-29654 and UDP-54644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özden, Ö., Erkan, N. Evaluation of Risk Characterization for Mercury, Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic Associated with Seafood Consumption in Turkey. Expo Health 8, 43–52 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0181-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0181-7