Abstract
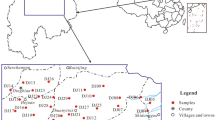
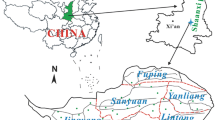
The purpose of this study was to evaluate groundwater quality and health risks of nitrogen pollution in the Shenfu mining area of northwest China. Statistical analysis, Durov diagrams, Gibbs diagrams and correlation analysis were applied to analyse the groundwater chemistry. Entropy weighted water quality index was applied for groundwater quality assessment. The non-carcinogenic risks to adults and children due to drinking nitrogen-contaminated groundwater were assessed using the models recommended by US Environmental Protection Agency. The study shows that the abundances of anions and cations are in the order of HCO3 − > SO4 2− > Cl− and Ca2+ > Na+ > Mg2+, respectively. Gibbs diagrams reveal that groundwater chemistry is mainly controlled by rock weathering. Cation exchange and the dissolution of aluminate minerals, carbonate minerals and halite are the main sources of major ions in the groundwater. More than half of the groundwater in the study area is medium quality, marginally suitable for multiple purposes. NH4–N, NO2–N and organic matter are the main pollutants which mainly derived from agricultural and industrial activities. The mean total hazard index (THI) value of nitrogen for adults and children is 1.563 and 3.126, respectively, which surpasses the permissible limit (THI = 1) recommended by USEPA. Moreover, the NO3–N level in some medium quality water, which is considered suitable for drinking purposes according to Chinese drinking water quality standards, poses high non-carcinogenic risks to adults and children. Therefore, the Chinese government should revise the concentration limit of NO3–N (20 mg/L) in medium quality water so as to ensure the safety of drinking water.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte JD, Belaval M, Olson SA, Burow KR, Flanagan SM, Hinkle SR, Lindsey BD (2015) Factors affecting temporal variability of arsenic in groundwater used for drinking water supply in the United States. Sci Total Environ 505:1370–1379. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.057
CCME (2001) Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: CCME Water Quality Index 1.0, User’s Manual. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg, Manitoba
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H (2016) Groundwater nitrate contamination and associated health risk for the rural communities in an agricultural area of Ningxia, northwest China. Expo Health 3:1–11. doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0208-8
Chotpantarat S, Ong SK, Sutthirat C, Osathaphan K (2008) Heavy metal contamination of groundwater and surrounding soils by tailing leachates from a gold mine in Thailand. J Sci Res 33:10–112
Chotpantarat Srilert, Wongsasuluk Pokkate, Siriwong Wattasit, Borjan Marija, Robson Mark (2014) Non-carcinogenic hazard maps of heavy metal contamination in shallow groundwater for adult and aging populations at an agricultural area in northeastern Thailand. Hum Ecolo Risk Assess 20(3):1546–1560. doi:10.1080/10807039.2013.832998
Dong SG, Liu BW, Jia ZB, Wang ZY (2012) Gangue yards vegetation restoration and groundwater pollution control in arid zone-a field application. Adv Mater Res 518–523:2535–2538
Durov SA (1948) Classification of natural waters and graphic presentation of their composition. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 59(1):87–90
Fagbote EO, Olanipekun EO, Uyi HS (2014) Water quality index of the ground water of bitumen deposit impacted farm settlements using entropy weighted method. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(1):127–138. doi:10.1007/s13762-012-0149-0
Gao Y, Yu G, Luo C, Zhou P (2012) Groundwater nitrogen pollution and assessment of its health risks: a case study of a typical village in rural-urban continuum, China. PLoS ONE 7(4):172–174. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033982
Gharibi H, Sowlat MH, Mahvi AH, Mahmoudzadeh H, Arabalibeik H, Keshavarz M, Karimzadeh N, Hassani G (2012) Development of a dairy cattle drinking water quality index (DCWQI) based on fuzzy inference systems. Ecol Ind 20(9):228–237. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.015
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090. doi:10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Han DM, Tong XX, Jin MG, Hepburn E, Tong CS, Song XF (2013) Evaluation of organic contamination in urban groundwater surrounding a municipal landfill, Zhoukou, China. Environ Monit Assess 185(4):3413–3444. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2801-z
Hosseinimarandi H, Mahdavi M, Ahmadi H, Motamedvaziri B, Adelpur A (2014) Assessment of groundwater quality monitoring network using cluster analysis, Shib-Kuh Plain, Shur Watershed, Iran. J Water Resour Prot 06(6):618–624. doi:10.4236/jwarp.2014.66060
Komnitsas K, Paspaliaris I, Zilberchmidt M (2001) Groudev SN (2001) Environmental impacts of coal waste disposal sites-efficiency of desulfurization technologies. Global Nest 3(2):109–116
Li P (2016) Groundwater Quality in Western China: challenges and Paths Forward for Groundwater Quality Research in Western China. Expo Health 8(3):305–310. doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0210-1
Li P, Qian H (2011) Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan City, Northwest China. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 8(1):41–48
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2010a) Groundwater quality assessment based on entropy weighted osculating value method. Int J Environ Sci 27(3):31–34. doi:10.6088/ijes.00104020018
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2010b) Groundwater quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. J Chem 7(S1):S209–S216. doi:10.1155/2010/451304
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2011) Application of set pair analysis method based on entropy weight in groundwater quality assessment-a case study in Dongsheng City, Northwest China. J Chem 8(2):851–858. doi:10.1155/2011/879683
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2013a) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2013b) Major Ion Chemistry of Shallow Groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Miner Water Environ 32(3):195–206. doi:10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2014a) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36(4):693–712. doi:10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014b) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in shallow alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015a) Building a new and sustainable ‘‘Silk Road economic belt’’. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015b) Heavy metal contamination of Yellow River alluvial sediments, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3403–3415. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3628-4
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016a) Regulation of secondary soil salinization in semi-arid regions: a simulation research in the Nanshantaizi area along the Silk Road, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 75(8):698. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5381-3
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhou W (2016b) Distribution, enrichment and sources of trace metals in the topsoil in the vicinity of a steel wire plant along the Silk Road economic belt, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):909. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5719-x
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016c) Preliminary assessment of hydraulic connectivity between river water and shallow groundwater and estimation of their transfer rate during dry season in the Shidi River, China. Environ Earth Sci 75(2):99. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4949-7
Li P, Li X, Meng X, Li M, Zhang Y (2016d) Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Expo Health 3:1–19. doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016e) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger desert, Northwest China. Expo Health 8(3):331–348. doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Li P, Qian H, Zhou W (2017) Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: an introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environ Earth Sci 76(3):105. doi:10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Liu CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313(1–3):77–89. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6
Liu CW, Wang SW, Jang CS, Lin KH (2006) Occurrence of arsenic in ground water in the Choushui River alluvial fan, Taiwan. J Environ Qual 35(1):68–75. doi:10.2134/jeq2005.0129
Liu CW, Jang CS, Chen CP, Lin CN, Lou KL (2008) Characterization of groundwater quality in Kinmen Island using multivariate analysis and geochemical modelling. Hydrol Process 22(3):376–383. doi:10.1002/hyp.6606
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China (2006) Industry standard of the People’s Republic of China: the specification of testing quality management for geological laboratories (DZ/T 0130.1-2006). Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Mohebbi MR, Saeedi R, Montazeri A, Vaghefi KA, Labbafi S, Oktaie S, Abtahi M, Mohagheghian A (2013) Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of Iran using a modified drinking water quality index (DWQI). Ecol Ind 30(30):28–34. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.02.008
Ni FQ, Liu GD, Ren HZ, Yang SC, Jian Y, Lu XY, Yang M (2009) Health risk assessment on rural drinking water safety-a case study in Rain City District of Ya’an City of Sichuan Province. J Water Resour Prot 01(2):128–135. doi:10.4236/jwarp.2009.12017
Ponsai W, Chotpantarat S (2014) The analysis of shallow groundwater quality around Laemchabang sanitary landfill, Chonburi, Thailand. Adv Maters Res 931–932:716–720. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.931-932.716
Sârbu C, Pop HF (2005) Principal component analysis versus fuzzy principal component analysis: a case study: the quality of Danube water (1985–1996). Talanta 65(5):1215–1220. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.08.047
Su X, Wang H, Zhang Y (2013) Health risk assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study of an agricultural area in northeast China. Water Resour Manag 27(8):3025–3034. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0330-3
Suthar S, Bishnoi P, Singh S, Mutiyar PK, Nema AK, Patil NS (2009) Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):189–199. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.111
Ugran V, Desai NN, Chakraborti D, Masali KA, Mantur P, Kulkarni S, Deshmukh N, Chadchan KS, Das SN, Tanksali AS, Arwikar AS, Guggarigoudar SP, Vallabha T, Patil SS, Das KK (2016) Groundwater fluoride contamination and its possible health implications in Indi taluk of Vijayapura District (Karnataka State), India. Environ Geochem Health. doi:10.1007/s10653-016-9869-2
USEPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund, volume1: human health evaluation manual (part A). Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington DC
Voudouris KS, Lambrakis NJ, Papatheothorou G, Daskalaki P (1997) An application of factor analysis for the study of the hydrogeological conditions in Plio-Pleistocene aquifers of NW Achaia (NW Peloponnesus, Greece). Math Geosci 29(1):43–59. doi:10.1007/BF02769619
Wang Y (2012) Research of the Sustainable Development in Mining Area of Shenmu Based on Ecological Footprint Mode. A Dissertation Submitted for the Degree of Master of Agronomy, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shaanxi (in Chinese)
Wei C, Guo H, Zhang D, Wu Y, Han S, An Y, Zhang F (2016) Occurrence and hydrogeochemical characteristics of high-fluoride groundwater in Xiji County, southern part of Ningxia Province, China. Environ Geochem Health 38(1):1–16. doi:10.1007/s10653-015-9716-x
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182. doi:10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health 8(3):311–329. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2011) Groundwater quality in Jingyuan County, a semi-humid area in Northwest China. J Chem 8(2):787–793. doi:10.1155/2011/163695
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Duan Z, Zhang X (2014) Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab J Geosci 7(10):3973–3982. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2015a) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4018-2
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Chen J (2015b) On the sensitivity of entropy weight to sample statistics in assessing water quality: statistical analysis based on large stochastic samples. Environ Earth Sci 74(3):2185–2195. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4208-y
Yan J, Liu J, Ma M (2014) In situ variations and relationships of water quality index with periphyton function and diversity metrics in Baiyangdian Lake of China. Ecotoxicology 23(4):495–505. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1199-5
Acknowledgments
The authors are deeply grateful for the funds granted by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (41630639), the Land and Resources Survey Project of China (1212011220982), the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (91025019), and the Joint Foundation of Key Laboratory of Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (KF201607). Anonymous reviewers and the editor are sincerely acknowledged for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Kang, W., Xu, Y. et al. Assessing Groundwater Quality and Health Risks of Nitrogen Pollution in the Shenfu Mining Area of Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Expo Health 10, 77–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0247-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0247-9