Abstract
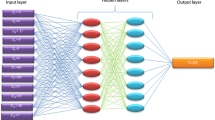
Flyrock is one of the most hazardous events in blasting operation of surface mines. There are several empirical methods to predict flyrock. Low performance of such models is due to complexity of flyrock analysis. Existence of various effective parameters and their unknown relationships are the main reasons for inaccuracy of the empirical models. Presently, application of new approaches such as artificial intelligence is highly recommended. In this paper, an attempt has been made to predict and control flyrock in blasting operation of Sangan iron mine, Iran incorporating rock properties and blast design parameters using artificial neural network (ANN) method. A three-layer feedforward back-propagation neural network having 13 hidden neurons with nine input parameters and one output parameter were trained using 192 experimental blast datasets. It was also observed that in ascending order, blastability index, charge per delay, hole diameter, stemming length, powder factor are the most effective parameters on the flyrock. Reducing charge per delay caused significant reduction in the flyrock from 165 to 25 m in the Sangan iron mine.
Abstract
يطير الصخرة هي واحدة من أكثر الأحداث الخطرة في عملية تفجير الألغام السطحية. هناك العديد من الطرق التجريبية للتنبؤ يطير الصخور. انخفاض أداء مثل هذه النماذج ومن المقرر أن تعقد يطير تحليل الصخور. وجود المعلمات الفعالة المختلفة وعلاقاتهم غير معروفة هي الأسباب الرئيسية لعدم دقة النماذج التجريبية. في الوقت الحاضر ، وتطبيق مناهج جديدة مثل الذكاء الاصطناعي (منظمة العفو الدولية) ينصح بشدة. في هذه الورقة ، وبذلت محاولة للتنبؤ ومراقبة الطيران في تفجير الصخور تشغيل منجم سنکان الحديد ، وإيران تتضمن خواص الصخور والمعلمات تصميم الانفجار باستخدام الشبكة العصبية الاصطناعية (ANN) الأسلوب. وهناك ثلاثة تغذية طبقة قدما اعادة نشر الشبكة العصبية بعد 13 الخلايا العصبية الخفية مع 9 معلمات الإدخال والإخراج 1 معلمة تم تدريب 192 باستخدام قواعد البيانات التجريبية الانفجار. لوحظ أيضا أن في ترتيب تصاعدي ، قدرة مؤشر الانفجار ، المسؤول في التأخير ، حفرة قطرها ، ووقف طول عامل مسحوق ، هي المعايير الأكثر فعالية على صخرة تطير. تخفيض رسوم التأخير تسبب في انخفاض كبير في الصخر الطيران من 165 م الى 25 م فى منجم سنکان الحديد.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas Powder Company (1987) Explosives and rock blasting. Atlas Powder Company Field Technical Operations, Dallas
Bhowmik S, Raina AK, Chakraborty AK, Ramulu M, Sahu PB, Haldar A, Choudury PB, Srinivas P, Bandopadhyay C (2004) Flyrock prediction and control in opencast mines: a critical appraisal. Mining Engineers Journal 5:6–10
Chandok JS, Kar IN, Tuli S (2008) Estimation of furnace exit gas temperature (FEGT) using optimized radial basis and back-propagation neural networks. Energy Convers Manage 49:1989–1998
Cigizoglu HK, Kis OZR (2005) Flow prediction by three back propagation techniques using k-fold partitioning of neural network training data. Nord Hydrol 36:49–64
Fletcher LR, D'Andrea DV (1986) Control of flyrock in blasting. Proc., 12th Conf on Explosives and Blasting Technique, Atlanta, Georgia, pp 167–177
Grznar J, Prasad S, Jasmine J (2007) Neural networks and organizational systems: modeling non-linear relationships. Eur J Oper Res 181:939–955
Haykin S (1999) Neural networks: a comprehensive fundation. (2nd ed.) Upper Saddle Rever, New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Hornik K (1991) Approximation capabilities of multi layer feed forward networks. Neural Netw J 4:251–257
Hustrulid W (1999) Blasting Principles for Open Pit Mining. General Design Concepts, A A Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Kalogirou S (2000) Applications of artificial neural networks for energy systems. Appl Energy 67:17–35
Khandelwal M, Singh TN (2002) Prediction of waste dump stability by an intelligent approach. Nat Sym, New Equipment—New Technology, Management and Safety, ENTMS, Bhubaneshwar, pp 38–45
Khandelwal M, Singh TN (2006) Prediction of blast induced ground vibration and frequency in opencast mines. J of Sound Vibr 289:711–725
Kim CY, Bae GJ, Hong SW, Park CH, Moon HK, Shin HS (2001) Neural network based prediction of ground surface settlements due to tunneling. Comput Geotech 28:517–547
Langefors U, Kishlstrom B (1963) The modern technique of rock blasting. Wiley, New York
Lundborg N (1974) The hazards of fly rock in rock blasting, Report DS1974. Swedish Detonic Research Foundation, p 12
Lundborg N, Persson A, Ladegaard-Pedersen A, Holmberg R (1975) Keeping the lid on flyrock in open-pit blasting. Engineering Mining Journal 176:95–100
Massey JB, Siu KL (2003) Investigation of flyrock incident at Clear Water Bay Road on 6 June. Civil Engineering Department, the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Hong Kong, p 49
Maulenkamp F, Grima MA (1999) Application of neural networks for the prediction of the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) from Equotip Hardness. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 36:29–39
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1988) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133
Monjezi M, Dehghani H (2008) Evaluation of effect of blasting pattern parameters on back break using neural networks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 45:1446–1453
Monjezi M, Yazdian A, Hesami SM (2006) Use of back propagation neural network to estimate burden in tunnel blasting. Mines Met Fuels 54:424–429
Monjezi M, Dehghan H, Samimi Namin F (2007) Application of TOPSIS method in controlling fly rock in blasting operations. In: Proceedings of the seventh international science conference SGEM. Sofia, Bulgaria, pp 41–49
Neaupanea KM, Achet SH (2004) Use of backpropagation neural network for landslide monitoring: a case study in the higher Himalaya. Eng Geol 74:213–226
Parker DB (1985) Learning logic. Technical Report TR-47. Center for Computational Research in Economics and Management Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA
Reed RD, Marks RJ (1998) Neural Smithing: Supervised Learning in Feed Forward Artificial Neural Networks. MIT Press, Cambridge
Rosenblatt F (1988) The perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol Rev 65:386–408
Roth JA (1979) A model for the determination of flyrock range as a function of shot condition. US Department of Commerce, NTIS Report No PB81222358, p 61
Salah A (2004) Coal Mine, Panel BYH. MSc thesis, Grad School Appl Natur Sci, Middle East Tech Univ, Ankara, Turkey, pp 31–40
Seiberl W, Ahl A, Winkler E (1998) Interpretation of airborne electromagnetic data with neural networks. Explor Geophys 29:152–156
Simpson PK (1990) Artificial neural system: foundation, paradigms, applications and implementations. Pergamon, New York
Singh TN, Singh V (2005) An intelligent approach to prediction and control ground vibration in mines. Geotech Geol Eng 23:249–262
Tawadrous AS (2006) Evaluation of artificial neural networks. Int Soc Explos Eng 1:1–12
Verakis HC, Lobb TE (2003) An analysis of blasting accidents in mining operations. In: Proc of the 29th Annual Conference on Explosives and Blasting Technique, Vol. 2, 2–5 February, Cleveland, OH: International Society of Explosives Engineers, pp 119–129
Yang Y, Zhang Q (1997) A hierarchical analysis for rock engineering using artificial neural networks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 30:207–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monjezi, M., Bahrami, A., Varjani, A.Y. et al. Prediction and controlling of flyrock in blasting operation using artificial neural network. Arab J Geosci 4, 421–425 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0091-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0091-8