Abstract
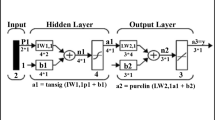
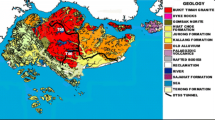
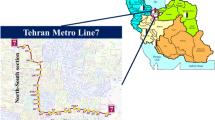
Alborz twin tunnel along with an exploratory or service tunnel between the two main tunnels, are the longest tunnels section in Tehran–Shomal highway with 6.3 km length. The service tunnel is designed to be used for geological investigations, ventilation, transportation during the construction of main tunnels, water drainage, ground improvement by grouting, and emergency exit. An open tunnel boring machine (TBM) of Wirth Company was used to drive this service tunnel. With regard to the fact that in such mechanized tunneling projects, performance of the TBMs is of the most importance, which affects the economy and timing of the projects; on the other hand, geotechnical conditions of the region play a significant role in this respect, this effect was investigated during this study. In this study, two main elements of the TBM performance including the rate of penetration and utilization factor were investigated using artificial neural network and Statistical Package for Social Sciences. It is shown that geotechnical conditions have considerable effect on the rate of penetration. Whereas, utilization is largely affected by management and non-rock mass-related parameters including delays, wasted times, maintenance, labor, etc. With regard to the available data, four parameters including uniaxial compressive strength (UCS), friction angle, Poisson’s ratio, and cohesion were selected to be studied. Based on assessments conducted using these approaches, the rate of effectiveness of four selected parameters on penetration rate, in a descending order, was as follows: UCS, friction angle, Poisson’s ratio, and cohesion. For increasing utilization, it was concluded that minimizing time delays by good management is the most effective way. Furthermore, with regard to the relative error percentages and the coefficient of correlation of the input and output data, it was concluded that the method artificial neural network yields more reliable results than the statistical approach.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alber M, Rühl S (2005) Tunnel support by fully grouted rock bolts for fast TBM advance. Proc. 31st ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress. Erdem & Solak (eds). A. A. Balkema. Leiden, pp. 743–748
Barton N (2000) TBM tunneling in jointed and faulted rock. Balkema, Rotterdam, p 173
Blindheim OT (1979) Boreability predictions for tunneling. Ph.D.thesis. Department of geological engineering. The Norwegian Institute of Technology, p 406
Bruland A (1999) Hard rock tunnel boring. vol 1–10. Ph.D. thesis. Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Trondheim. Norway
Cassinelli F, Cina S, Innaurato N, Mancini R, Sampaolo A (1982) Power consumption and metal wear in tunnel-boring machines: analysis of tunnel-boring operation in hard rock. In: Jones MJ (ed) Tunneling 82. London Institute of Mining Metallurgy, pp 73–81
Dodange D, Khosravi H (2009) TBM mechanized excavating Workshop seminar. Iranian National Dams Committee. Department of Energy – Tehran
Farokh E, Shamsi G (2009) Relationship between TBM penetration rate and rock mass quality case study: Ghomrood water conveyance tunnel. 8th Iran tunnel conference. (Sections 3 & 4).
Graham PC (1976) Rock exploration for machine manufactures. Symposium on Exploration for Rock Engineering, Johannesburg, Balkema. 1:80–173
Hamidi JK, Shahriar K, Rezai B, Rostami J (2010) Performance prediction of hard rock TBM using Rock Mass Rating (RMR) System. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 25:333–345
Hassanpour J, Rostami J, Khamechian M, Bruland A, Tavakoli HR (2010) TBM performance analysis in pyroclastic rocks: case history of Karaj Water Conveyance Tunnel. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43:427–445
Howarth DF, Adamson WR, Berndt RJ (1986) Correlation of model tunnel boring and drilling machine performances with rock properties. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 23(2):171–175
Kim T (2004) Development of a fuzzy logic based utilization predictor model for hard rock tunnel boring machines. PhD Thesis, 254p. Colorado School of Mines, Colorado USA
Kim T, Marcelo GS (2006) Fuzzy modeling approaches for the prediction of machine utilization in hard rock tunnel boring machines. 41st Industrial Application Society Annual Meeting, Industry Applications Conference, Record of the 2006 IEEE, pp. 947–954
Madanipoor S, Yasaghi A, Kanani Moghadam H, Abbasi A, Ginioski I (2009) Importance of geological investigation along with deep tunnel excavation, Alborz service tunnel, Tehran-Shomal highway. 8th Iran tunnel conference
McFeat-Smith I (1977) Rock property testing for the assessment of tunneling machine performance. Tunnels and Tunnelling, pp 29–33
Nelson P (1993) TBM performance analysis with reference to rock properties, In: Comprehensive Rock Engineering, Hudson J (Ed), Volume 4 (Chapter, 10), 261–291
Ozdemir L (1975) A laboratory and field investigation of tunnel borability. MS Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, T-1755, Golden, Co
Ribacchi R, Lembo Fazio A (2005) Influence of rock mass parameters on the performance of a TBM in a Gneissic Formation (Varzo Tunnel). Rock Mech Rock Eng 38(2):105–127
Rostami J (1997) Development of a force estimation model for rock fragmentation with disc cutters through theoretical modeling and physical measurement of crushed zone pressure. Ph.D. thesis. Colorado School of Mines. Golden. Colorado. USA, p 249
Rostami J, Ozdemir L (1993) A new model for performance prediction of hard rock TBM. In: Bowerman LD et al (eds) Proceedings of RETC. MA, Boston, pp 793–809
Roxborough FF, Phillips HR (1975) Rock excavation by disc cutter. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 12:361–366
Sanio HP (1985) Prediction of the performance of disc cutters in anisotropic rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 22(3):153–161
Tachong K (2006) A fuzzy logic-based utilization predictor model for hard rock tunnel boring machines
Tarkoy PJ (1975) Rock hardness index properties and geotechnical parameters for predicting tunnel boring machine performance. PhD thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 326p, Illinois, USA
Technical report (2009) Technical office Tehran–Shomal highway
Yagiz S (2002) Development of rock fracture and brittleness indices to quantify the effects of rock mass features and toughness in the CSM Model basic penetration for hard rock tunneling machines. PhD Thesis. 2002. 289p. Department of Mining and Earth Systems Engineering, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado, USA (unpublished)
Yagiz S (2008) Utilizing rock mass properties for predicting TBM performance in hard rock condition. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 23:326–339
Yagiz S (2009) Assessment of brittleness using rock strength and density with punch penetration test. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 24:66–74
Yagiz S, Karahan H (2011) Prediction of hard rock TBM penetration rate using particle swarm optimization. Int J Rock Mech and Mining Sci 48:427–433
Yagiz S, Merguerian C, Kim T (2010) Geological controls on the breakthrough of tunnel boring machines in hard rock crystalline terrains. In: Eurock’10-Rock Mechanics in Civil and Environmental Engineering; Proceedings of the ISRM Regional Symposium. Zhao J. et al. (Eds), 4p. June 15–18, 2010. Lausanne, Switzerland
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the authorities in Tehran–Shomal highway project, especially Mr. Afrand whose help and support was invaluable. Also the assistance and advises of Mr. Ebrahim is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torabi, S.R., Shirazi, H., Hajali, H. et al. Study of the influence of geotechnical parameters on the TBM performance in Tehran–Shomal highway project using ANN and SPSS. Arab J Geosci 6, 1215–1227 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0415-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0415-3