Abstract
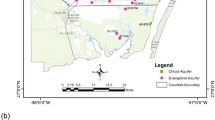
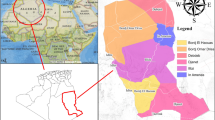
The continuous increase of industrial activities in the area of Berrahal (northeast of Algeria) resulted in an increase of waste disposal, inducing environmental pollution and contamination of groundwater. Available data on groundwater contamination were used to develop a statistical study for contaminated regions and to identify exposure scenarios of pollution. Chemical analysis of the samples shows that water of most wells and drillings is in bad quality or not drinkable, whereas statistical processing of these data by principal component analysis and discriminant factorial analysis suggests that wastewater coming from companies of the industrial park of Berrahal is very rich in organic pollutants (high percentages of BOD5 and NO2 −) and has high mineralization (has strong concentration in major elements and high electric conductivity); these constitute the main factors of the deterioration of the quality of this water. The considered exposure pathways were drinking water exploited from wells and drillings implanted in this area and its contact with soil (ingestion and dermal contact) that could threaten either humans or wildlife, on site or off site. In addition, groundwater was considered to be a potential risk pathway, especially for the ecosystem of Lake Fetzara and for the aquiferous system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelgader A, Achour F, Mudry J (1995) Influence des évènements hydroclimatologiques et du caractère lithologique sur la minéralisation des eaux karstiques. Exemple: plateau de Besançon (Jura externe, France). Academic report of sciences, Paris, 321, serie II a, p. 129–135
Abdelgader A, Achour F, Mudry J (1996) Validation of underground flows by the discriminant analysis. Rev Sci Water 9(2):219–230
Aissa D-E (1985) Etude des indices et gisements métallifères du massif de l’Edough (Annaba). Doctorate thesis of third cycle, USTHB Algiers, p 134
Arminder K, Siddharth V, Sumit R, Ankit B, Jharna G, Ranjeet ST, Komal KG (2010) Physicochemical analysis of the industrial effluent and to their impact on the soil microflora. Procedia Environ Sci 2:595–599
Bakalowicz M (1979) Contribution de la géochimie des eaux à la connaissance de l’aquifère karstique et de la karstification. Doctorate thesis, Paris VI, p 269
Coynel A, Schafer J, Dabrin A, Rirardot NR, White G (2007) Groundwater contributions to metal transport in small river affected by mining and smelting waste. Water Res 41:3420–3428. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.019
Debieche HT (2002) Evolution de la qualité des eaux (salinité, azote et métaux lourds) sous l’effet de la pollution saline, agricole et industrielle. Application à la basse plaine de la Seybouse - Nord-Est Algérien. Doctorate thesis, University Franche-Comté, p 235
Gleizes G, Boulton J, Bossiére G, Collome P (1988) Données lithologiques et pétrostructurales nouvelles sur le massif cristallophyllien de l’Edough (Est Algérien). C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 306, series II, p 1001–1008
Hilly J (1962) Etude géologique du massif de l’Edough et du Cap de Fer, (Est Constantinois). Publications of the Service of Geological Map of Algéria, vol. 19
Hotelling H (1933) Analysis of a complex of statistical variables with principal components. J Educ Psychol 24(6):417–441
Howari FM, Abu-Rukah Y, Shinaq R (2005) Hydrochemical analyses and evaluation of groundwater resources of North Jordan. Water Resour 32(5):555–564
Hubert M, Van Driessen K (2004) Fast and robust discriminant analysis. Comput Stat Data Anal 45:301–320
Laouar R, Boyce AJ, Ahmed Said Y, Ouabadi A, Fallick AE, Toubal A (2002) Stable isotope study of igneous, metamorphic and mineralized rocks of the Edough complex, Annaba, Northeast Algeria. J Afr Earth Sci 35:271–283
Lefebvre L (1980) Introduction aux analyses statistiques multidimensionnelles, 2nd edn. Maison et Cie, Paris
Mudry J (1991) Discriminant analysis, an efficient means for the validation of hydrogeological hypothesis. Rev Water Sci 4:19–37
Numberg HW (1982) Voltametric traces analysis in ecological chemistry of toxic metals. Pure Appl Chem 54(4):853–878
Obiri S (2007) Determination of heavy metals in water from boreholes in Dumasi in the Wassa West District of western region of Republic of Ghana. Environ Monit Assess 130:455–463
Pearson K (1901) On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos Mag 2(6):559–572
Pérez-López R, Miguel Nieto J, López-Cascajosa MJ et al (2011) Evaluation of heavy metals and arsenic speciation discharged by the industrial activity on the Tinto-Odiel estuary, SW Spain. Mar Pollut Bull 62:405–411
Ramesh R, Shiv Kumar K, Eswaramoorthi S, Purvaja GR (1995) Migration and contamination of major and trace elements in ground water of Madras City, India. Environ Geol 25:126–136
Rodriguez HR, Rooms-Legac D, Lehman E (2002) Initiation à l'Analyse Factorielle des Données. Fondements Mathématiques, Interprétations, Exercices corrigés. Ellipses, p 320, Paris
Rouabhia A, Baali F, Fehdi C (2010) Impact of agricultural activity and lithology on groundwater quality in the Merdja area, Tebessa, Algeria. Arab J Geosci 3:307–318
Saporta G (2006) Probabilités, analyse des données et statistique. Editions TECHNIP, Paris
Surindra S, Arvind KN, Mayuri C, Sanjay KG (2009) Assessment of metals in water and sediments of Hindon River, India: impact of industrial and urban discharges. J Hazard Mater 171:1088–1095
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach towards a rational classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38:55–94
Thornthwaite CW, Mather JR (1955) The water balance. Pub Climatol Lab Climatol Drexel Inst Technol 8:1–104
Vila JM (1980) Algerian mountain chain and the Algerian–Tunisian confines [La chaine alpine de l’Algérie orientale et des confins Algéro-Tunisiens]. Doctorate thesis in natural sciences. University Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris VI
Acknowledgments
For the term of this work, we express our deep gratitude to Professor Jacques Mudry of Franche-Comté University (France) for his assistance, to the senior lecturer Hicham Chaffai, to Professor Azzedine Hani of the University of Annaba (Algeria), and to the personnel of the Laboratory of Hydrogeology at the University of Constantine (Algeria).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khelfaoui, H., Chaffai, H., Mudry, J. et al. Use of discriminant statistical analysis to determine the origin of an industrial pollution type in the aquiferous system of the area of Berrahal, Algeria. Arab J Geosci 6, 4517–4527 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0736-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0736-x