Abstract
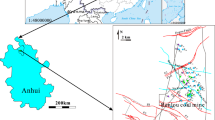
Coal mining is bound to destroy natural hydrochemical environment. However, in the concealed coal field in North China, the hydrogeochemical characteristics of discharge aquifers under mining-induced disturbance has not been researched from view of space and time, and the true hydrochemical feature and spatio-temporal evolution mechanism could not be well revealed. For this reason, taking the Linhuan coal-mining district as study area, conventional ions and trace elements are studied by principal component analysis (PCA). The results show that main formations of hydrochemical composition are lixiviation and dissolution for the first principal component and cation exchange and absorption for the second principal component, respectively. In general, the main formation of hydrochemical composition in the unconsolidated pore aquifer is lixiviation and dissolution. The main formation in the coal and sandstone cranny aquifer is cation exchange and absorption, which are gradually weakened with lixiviation and dissolution. The main formation in the karst aquifer is lixiviation and dissolution, which are gradually strengthened with cation exchange and absorption. The research provides theoretical foundation for the water-inrush precaution and the protection and utilization of water resources in concealed coal field in North China.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen HJ, Li XB, Liu AH, Peng SQ (2009) Identifying of mine water inrush sources by fisher discriminant analysis method. J Cent South Univ 40(4):1114–1120
Chen LW, Yin XX, Chen YP (2013) Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope tracing of deep groundwater circulation under mining-induce disturbance in mining district. Geogra Geo-Inf Sci 29(2):85–90
Chen LW, Yin XX, Xie WP, Feng XQ (2014) Calculating groundwater mixing ratios in groundwater-inrushing aquifers based on environmental stable isotopes (D, 18O) and hydrogeochemistry. Nat Hazards 71(1):937–953
Cidu R, Biddau R, Fanfani L (2009) Impact of past mining activity on the quality of groundwater in SW Sardinia (Italy). J Geoch Explor 100(2–3):125–132
Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, Savardc MM (2008) Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J Hydrol 353(3–4):294–313
Dou HP, Ma ZY, Cao HD, Liu F, Hu WW, Li T (2011) Application of isotopic and hydro-geochemical methods in identifying sources of mine inrushing water. Min Sci Technol (China) 21(3):319–323
Edelev AV (2013) Composition of drainage mine waters interacting with sulfide-containing rock: a predictive estimation. Russ Geol Geophys 54(1):110–119
Garzonio CA, Piccinini L, Gargini A (2014) Groundwater modeling of fractured aquifers in mines: the case study of gavorrano (Tuscany, Italy). Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(3):905–921
Gui HR, Chen LW (2007) Geochemical evolution of the mining area of groundwater hydrology and recognition. Geological Publishing Press, Beijing
Guo PK, Cheng YP, Jin K, Liu YP (2014) The impact of faults on the occurrence of coal bed methane in Renlou coal mine, Huaibei coalfield, China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 17:151–158
Jiang B, Qu ZH, Geoff GX, Wang ML (2010) Effects of structural deformation on formation of coalbed methane reservoirs in Huaibei coalfield, China. Int J Coal Geol 82(3–4):175–183
Qiao XJ, Li GM, Li M, Zhou JL, Du J, Du CY, Sun ZH (2011) Influence of coal mining on regional karst groundwater system: a case study in West Mountain area of Taiyuan City, northern China. Environ Earth Sci 64(6):1525–1535
Sahraei PH, Samani N (2013) Geochemical evolution and quality assessment of water resources in the Sarcheshmeh copper mine area (Iran) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ Earth Sci 69(5):1699–1718
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B, Mondal GC, Singh TB (2011) Hydrogeochemistry, elemental flux, and quality assessment of mine water in the Pootkee-Balihari mining area, Jharia coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 30(3):197–207
Tan JQ, Ju YW, Yuan WM, Hou QL, Pan JN, Fan JJ (2011) Thermochronological and structural evolution of the Huaibei coalfield in eastern China: constrains from zircon fission-track data. Radiat Meas 46(2):183–189
Wang XY, Xu T, Huang D (2011) Application of distance discriminance in identifying water inrush resource in similar coalmine. J China Coal Soc 36(8):1354–1358
Wu Q, Zhao SQ, Dong SN, Li JS, Yin SX, Liu SQ (2012) Dissection of main technical points in “coal mine safety regulations” (water control part) modification. Coal Geol China 24(7):34–47
Wu Q, Liu YZ, Luo LH, Liu SQ, Sun WJ, Zeng YF (2015) Quantitative evaluation and prediction of water inrush vulnerability from aquifers overlying coal seams in Donghuantuo coal mine, China. Environ Earth Sci 74(2):1429–1437
Yang QC, Zhang JN, Wang YL, Fang YN, Martín JD (2015) Multivariate statistical analysis of hydrochemical data for shallow ground water quality factor identification in a coastal aquifer. Pol J Environ Stud 24(2):769–776
Zheng LG, Liu GJ, Qi CC, Zhang Y, Wong MH (2008) The use of sequential extraction to determine the distribution and modes of occurrence of mercury in Permian Huaibei coal, Anhui province, China. Int J Coal Geol 73(2):139–155
Zhong XL, Zhou SL, Zhao QG, Li GT, Liao QL (2007) Coregionalization, spatia-correlation and spatial-factor analysis of soil available heavy metals in a typical region of the Yangtze river delta. Environ Sci 28(12):2758–2765
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 41372244, 41172216, 41373095) and the Anhui Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 1308085ME61). The authors would like to express sincere thanks to the reviewers for their thorough reviews and useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Xie, W., Feng, X. et al. Formation of hydrochemical composition and spatio-temporal evolution mechanism under mining-induced disturbance in the Linhuan coal-mining district. Arab J Geosci 10, 57 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2831-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2831-5