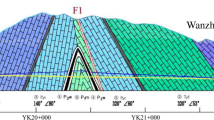
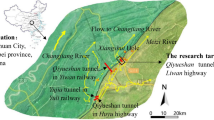
Abstract
In this study, a water inrush model test system for high ground stresses and hypertonic tunnels is developed to examine the evolution process of karst cave water inrush events induced by tunnel construction and rainfall. A 3D fluid-solid coupling model test is performed to simulate the tunnel excavation and increasing karst cave water pressure, and the evolutionary mechanism of karst water inrush induced by tunnel construction is revealed. The results indicate that seepage occurs during the tunnel excavation, and water seepage ceases after timely support. During hydraulic loading, the experiment successively obtained the stages corresponding to the occurrence of partial dripping, water streams, support bulging, partial and complete support block falls, and water inrush. The influence of tunnel excavation on the stability of the surrounding rock of the monitoring surface increases sharply when the distance between the tunnel excavation surface and the monitoring surface is approximately 0.5–1 times the diameter of the tunnel. The research results are significant for studies examining the water inrush mechanism and the prevention of tunnel water inrush disasters.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alija S, Torrijo FJ, Quinta-Ferreira M (2013) Geological engineering problems associated with tunnel construction in karst rock masses: the case of Gavarres tunnel (Spain). Eng Geol 157:103–111
Day MJ (2004) Karstic problems in the construction of Milwaukee’s Deep Tunnels. Environ Geol 45:859–863
Hu J, Li S, Li L et al (2018a) Field, experimental, and numerical investigation of a rockfall above a tunnel portal in southwestern China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1365–1382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1152-y
Hu H, Zhang B, Zuo Y et al (2018b) The mechanism and numerical simulation analysis of water bursting in filling karst tunnel. Geotech Geol Eng 36(2):1197–1205
Knez M, Slabe T et al (2016) Development and karstification of the karst aquifer as discovered between Klanec and Črni Kal. cave exploration in Slovenia. Springer International Publishing
Li S, Zhang Q (2014) Tunnel and underground engineering water burst mechanism and governance. China Communications Press, Beijing
Li L, Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Study of mechanism of water inrush induced by hydraulic fracturing in karst tunnels. Rock Soil Mech 02:523–528
Li S, Zhou Z, Li L et al (2013) Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 38:50–58
Liang D, Jiang Z, Zhu S, Sun Q, Qian Z (2016) Experimental research on water inrush in tunnel construction. Nat Hazards 81(1):467–480
Liu XM, Sheng Q, Chen J et al (2015) Seismic shaking table test for large-scale underground cavern group (II): test scheme. Rock Soil Mech 06:1683–1690
Ma D, Bai H et al (2016) Compaction and seepage properties of crushed limestone particle mixture: an experimental investigation for ordovician karst collapse pillar groundwater inrush. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4799-3
Marinos P (2001) Tunneling and mining in karstic terrane; an engineering challenge. In: Beck BF, Herring JG (eds) Geotechnical and environmental applications of karst geology and hydrology. Balkema, Lisse, pp 3–16
Milanovic P (2004) Water resources engineering in karst. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Petrovic A, Calic J, Spalevic A et al (2016) Evolution of collapse valleys in karst-examples from the Carpatho-Balkanides of Serbia //EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 18: 680
Qian Q (2012) The challenge and countermeasure of underground engineering construction safety. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(10):1945–1956
Stevanovic Z, Milanovic P (2015) Engineering challenges in kast/inzenirski izzivi krasu. Acta Carsol 44(3):381
Toran L, Herman EK, White WB (2007) Comparison of flowpaths to a well and spring in a karst aquifer. Ground Water 45(3):281–287
Wang L, Song Y, Miao X (2003) Study on prediction of water-inrush from coal floor based on cusp catastrophic model. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 22(4):573–577
Zarei HR, Uromeihy A, Sharifzadeh M (2012) Identifying geological hazards related to tunneling in carbonate karstic rocks - Zagros, Iran. Arab J Geosci 5(3):457–464
Zhong G, Xu G, Yan C et al (2004) Study of water-inrush from water-pressed floor based on cusp catastrophic model. Min R D 24(6):88–90
Funding
Much of the work presented in this paper was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51879148, 51979154), Shandong Provincial Keypoint Research and Invention program (Grant No. 2019GSF111018), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019M660937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marco Barla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Yang, X., Fang, Z. et al. Model test for water inrush caused by karst caves filled with confined water in tunnels. Arab J Geosci 12, 749 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4907-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4907-x