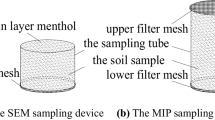
Abstract
Soil structure and particle distribution determine the action form of water and the distribution and movement form of water in the soil, which may cause many engineering and environmental problems, so it is of great significance to study the distribution form of soil particles under different moisture content. Taking the silt as the research object, the surface micro features of soil samples with the same dry density and different moisture content were collected, and the binarization analysis and particle statistics were carried out to study the action mode between water and particles. The results show that (1) moisture content has a certain impact on the micro features. With the increase of moisture content, the pores between soil particles gradually decrease, and the fractal dimension of surface particles also decreases. (2) In the case of the difference of specific surface area, the smaller the particle size, the more obvious the response to water. For this silt sample, the particles with a size of 0.03~0.05 mm are relatively stable. With the increase of moisture content, small particles flocculate to form large particles under a series of forces. (3) When the moisture content was 8.92% and 13.78%, the soil features changed significantly, which may be the critical moisture contents affecting the structural quality of the sample. (4) Advantage orientation of silt particles is 90°~105°, which may cause the soil mechanics characteristics of anisotropy. (5) The interaction model between water and soil particles is as follows: dissolution, the change of stress on particles, and the change of electrical double layer on the surface of soil particles.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aba A, Al-Dousari AM, Ismael A (2016) Depositional characteristics of 7Be and 210Pb in Kuwaiti dust. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4129-y.2015.KISR:12192
Ahmed M, Al-Dousari NA, Al-Dousari A (2016) The role of dominant perennial native plant species in controlling the mobile sand encroachment and fallen dust problem in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 9:134. 12112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2216-6
Al-Awadhi JM, Al-Dousari AM, Khalaf FI (2014) Influence of land degradation on the local rate of dust fallout in Kuwait. Atmos Clim Sci 4(03):403–437. https://doi.org/10.4236/acs.2014.43042
Al-Dousari AM (2005) Causes and indicators of land degradation in the north-western part of Kuwait. Arab Gulf J Sci Res (1989) 23(2):69–79
Al-Dousari AM, Al-Hazza A (2013) Physical properties of aeolian sediments within major dune corridor in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 6(2):519–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0353-0
Al-Dousari AM, Aba A, Al-Awadhi S, Ahmed M, Al-Dousari N (2016) Temporal and spatial assessment of pollen, radionuclides, minerals and trace elements in deposited dust within Kuwait. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 9(2):95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2182-z
Al-Dousari AM, Ibrahim MI, Al-Dousari N, Ahmed M, Al-Awadhi S (2019a) Environmental and economic importance of native plants and green belts in controlling mobile sand and dust hazards. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2415–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1879-4
Al-Dousari A, Al-Nassar W, Al-Hemoud A, Alsaleh A, Ramadan A, Al-Dousari N, Ahmed M (2019b) Solar and wind energy: challenges and solutions in desert regions. Energy 176:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.180
Al-Ghadban AN, Uddin S, Beg MU, Al-Dousari AM, Gevao B, Al-Yamani F (2008) Ecological consequences of river manipulations and drainage of Mesopotamian marshes on the Arabian Gulf ecosystem: investigations on changes in sedimentology and environmental quality, with special reference to Kuwait Bay. Kuwait Instit Sci Res (KISR) 9362:1–141
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Dousari A, Al-Shatti A, Al-Khayat A, Behbehani W, Malak M (2018) Health impact assessment associated with exposure to PM10 and dust storms in Kuwait. Atmosphere 9(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9010006
Beuselinck L, Govers V, Poesen J, Degraer G, Froyen L (1998) Grain-size analysis by laser diffractometry: comparison with the sieve-pipette method. Catena 32:193–208
Blott S, Al-Dousari AM, Pye K, Asye SE (2004) Three-dimensional characterization of sand grain shape and surface texture using a nitrogen gas adsorption technique. J Sediment Res 74(1):156–159
Buurman P, Pape T, Reijneveld JA, de Jong F, van Gelder E (2001) Laser-diffraction and pipette-method grain sizing of Dutch sediments: correlations for fine fractions of marine, fluvial, and loess samples. Geol Mijn Neth J Geosci 80(2):49–57
Capa-Morocho MI, Ruiz-Ramos M, Marquis AM (2011) The influence of the binarization threshold in soil percolation: relationships between soil physical properties. J
Filgueira RR, Fournier LL, Cerisola CI, Gelati P, García MG (2006) Particle-size distribution in soils: a critical study of the fractal model validation. Geoderma 134(3–4):327–334
Gee GW, Bauder JW 1986. Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis: part 1. Physical and Mineralogical methods, 2nd edn., Agronomy, 9. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp. 383–411
Hardin BO (1985) Journal of geotechnical engineering. J Crushing of Soil Particle 111(10):1177–1192
Hegarty TW, Royle SM (1978) Combined effects of moisture content prior to compaction, compaction effort and rainfall quantity on soil crust strength. Int J Eur J Soil Sci 29(2):167–173
Hu F, Xu C, Hang L, Song L, Yu Z, Yue L (2015) Particles interaction forces and their effects on soil aggregates breakdown. J Soil & Tillage Res 147(5):1–9
Jacques D, Šimůnek J, Mallants D, van Genuchten MT (2008) Modeling coupled water flow, solute transport and geochemical reactions affecting heavy metal migration in a podzol soil. J Geod 145:449–461
Kemper WD, Noonan L (1970) Runoff as affected by salt treatments and soil texture. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34(1):126–130
Li Y (2018) A review of shear and tensile strengths of the Malan Loess in China. Int J Eng Geol 236:4–10
Liu T (1985) Loess and the environment. China Ocean Press, Beijing, p 481
Mamedov AI, Levy GJ, Shainberg I, Letty J (2001) Wetting rate, sodicity, and soil texture effects on infiltration rate and runoff. Aust J Soil Res. 39(6):1293–1305. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR01029
McCave IN, Bryant RJ, Cook HF, Coughanowr CA (1986) Evaluation of a laser-diffraction-size analyzer for use with natural sediments. J Sediment Petrol 56:561–564. https://doi.org/10.1306/212F89CC-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Miller DE, Aarstad JS (1973) Effective available water and its relation to evapotranspiration rate, depth of wetting, and soil texture. Soil Sci Soc Am J 37(5):763–766
Peng D, Xu Q, Qi X, Fan X, Dong X, Li S, Ju Y (2016) Study on early recognition of loess landslides based on field investigation. Int J Geohazards Environ 2(2):32–52
Petersen LW, Moldrup P, Jacobsen OH, Rolston DE (1996) Relations between specific surface area and soil physical and chemical properties. J Soil Sci 161(1):9–21
Rodríguez-Lado L, Lado M (2017) The relation between soil-forming factors and scaling properties of particle size distributions derived from the multifractal analysis in topsoils from Galicia (NW Spain). Int J Geoderma 287:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.08.005
Saxton KE, Rawls WJ, Romberger JS, Papendick RI (1986) Estimating generalized soil-water characteristics from texture. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50(4):1031–1036
Shepherd G, Terradellas E, Baklanov A, Kang U, Sprigg WA, Nickovic S, Boloorani AD, Al-Dousari AM, Basart S, Benedetti A, Sealy A, Tong D, Zhang X, Guillemot J, Kebin Z, Knippertz P, Mohammed AAA, Al-Dabbas M, Cheng L, Otani SH, Wang F, Zhang CH, Ryoo SB, Cha J. (2016) Global assessment of sand and dust storms. UNEP, WMO, UNCCD. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi
Taubner H, Roth B, Tippkotter R (2009) Determination of soil texture: comparison of the sedimentation method and the laser-diffraction analysis. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 172(2):161–171
Tyler SW, Wheatcraft SW (1992) Fractal scaling of soil particle-size distributions: analysis and limitations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56(2):362–369
Vereecken H, Maes J, Feyen J, Darius P (1989) Estimating the soil-moisture retention characteristic from texture, bulk density, and carbon content. Soil Sci 148(6):389–403
Verwey EJW, Overbeek JTG (1948) Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Zhang H, Liu P, Wang J, Wang X (2009) Generation and detachment of surface crust on ancient earthen architectures. J Rock Soil Mech 30(7):1883–1891
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihua Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Wang, Y. Study on the surface particle distribution characteristics of silt with different moisture content. Arab J Geosci 13, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5007-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5007-7