Abstract
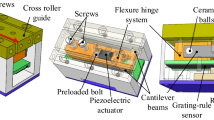
This paper presents a second-generation linear-rotary (Z-θZ) micro-stage driven by impact friction. The micro-stage was constructed by miniaturizing a previously developed linear-rotary stage. The moving element of the micro-stage, which was a steel cylinder, could be actuated along and around the Z-axis in millimeter-scale range. The steel cylinder was supported by two driving units. Each unit consisted of a permanent magnet and two piezoelectric actuators (PZTs) for generating the impact friction motions in the Z- and θZ-directions. The size of the micro-stage was made to be 11.0 mm (L) × 11.0 mm (W) × 5.7 mm (H). For enhancement of the stage velocity, the transfer function of the micro-stage with the voltage applied to the PZT as the input and the PZT displacement as the output, was established. An improved waveform of the input voltage was then obtained based on the established transfer function for getting a triangular-shaped PZT displacement, which was an ideal waveform for the impact friction motion. The characteristics of the stage velocity before and after the improvement of the input voltage were verified and the effectiveness of the improved input voltage for enhancement of the stage velocity was confirmed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendrela, E. A. and Gierczak, E., “Double-winding rotary-linear induction motor,” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, Vol. EC-2, No. 1, pp. 47–54, 1987.
Iwatsuki, N., Hayashi, I., Yamamoto, R., and Shibata, J., “Precision positioning with a rotary-linear motor driven by a pair of 2-D ultrasonic actuators,” Proc. of the IEEE 7th International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, pp. 183–188, 1996.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, W. J., Hesselbach, J., and Kerle, H., “Development of a two-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric rotarylinear actuator with high driving force and unlimited linear movement,” Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 77, No. 3, pp. 035112–035119, 2006.
Gao, W., Sato, S., and Arai, Y., “A linear-rotary stage for precision positioning,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 301–306, 2010.
Gao, W., Sato, S., Sakurai, Y., and Kiyono, S., “Design of a precision linear-rotary positioning actuator,” Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp. 803–807, 2006.
Peng, Y. X., Ito S., Shimizu Y., and Gao W., “A micro-stage for linear-rotary positioning,” Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 523–524, pp. 650–655, 2012.
Peng, Y. X., Kaneko, J., Arai, Y., Shimizu, Y., Gao, W., Okamoto, K., Chiba, M., and Aisawa, S., “A linear micro-stage with a long stroke for precision positioning of micro-objects,” Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 221–227, 2011.
Furutani, K., Higuchi, T., Yamagata, Y., and Mohri, N., “Effect of lubrication on impact drive mechanism,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 22, No. 2, pp. 78–86, 1998.
Okamoto, Y. and Yoshida, R., “Development of linear actuators using piezoelectric elements,” Electronics and Communication in Japan(Part 3), Vol. 81, No. 11, pp. 11–17, 1998.
Fan, K. C. and Lai, Z. F., “An intelligent nano-positioning control system driven by an ultrasonic motor,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 40–45, 2008.
Huang, F. L., Wang, X. M., Chen, Z. Q., He, X. H., and Ni, Y. Q., “A new approach to identification of structural damping ratios,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, Vol. 303, No. 1–2, pp. 144–153, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Ito, S., Sakurai, Y. et al. Construction and verification of a linear-rotary microstage with a millimeter-scale range. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 14, 1623–1628 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0219-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0219-3