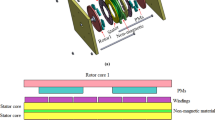
Abstract
A direct-drive generator for large-scale wind turbine provides higher energy density in comparison with a gear train type generator. An AFPM (Axial Flux Permanent Magnet)-type machine has been the most attractive for the direct-drive generator due to its higher torque effect per unit volume and higher power density. The electronic machine system with a very large diameter, however, has to be used due to operation at low rotational speed of main shaft. Supported structures for the electronic machine system occupy at least 80% of total weight of the direct-drive generator. The light weight design, therefore, is at issue in the industries manufacturing the AFPM-type generator for large-scaled wind turbines. In this study, a topology model of the direct-drive generator for 2.5MW wind turbine using the AFPM-type machine was proposed, which has hollow shapes of the rotor with annular disc, the stator and the main shaft mounted on coupled slew bearings. Analytic results obtained from an electro-magnetic and structural interaction analysis showed that the structural weight of the proposed model compared to conventional generator can be reduced by 30% in a condition satisfying the requirements of the structural behaviors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- f n :
-
component of axial electromagnetic force
- f t :
-
component of radial electromagnetic force
- B n :
-
axial magnetic flux density
- B t :
-
radial magnetic flux density
- \(\vec n\) :
-
axial vector
- \(\vec t\) :
-
radial vector
- µ 0 :
-
air permeability
References
Park, C. W., Kwon, K. S., Kim, W. B., Min, B. K., Park, S. J., and et al., “Energy Consumption Reduction Technology in Manufacturing-A Selective Review of Policies, Standards, and Research” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 5, pp. 151–173, 2009.
Lab-Volt Ltd., “Principles of Doubly-Fed Induction Generators (DFIG)” 2011.
Delli Colli, V., Marignetti, F., and Attaianese, C., “Analytical and Multiphysics Approach to the Optimal Design of a 10-MW DFIG for Direct-Drive Wind Turbines” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 59, No. 7, pp. 2791–2799, 2012.
Zavvos, A., McDonald, A., Mueller, M., Bang, D., and Polinder, H., “Structural Comparison of Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Generator Topologies for 5MW Wind Turbines” Proc. of 6th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2012), pp. 1–6, 2012.
Zavvos, A., McDonald, A., and Mueller, M., “Electromagnetic and Mechanical Optimisation of Direct-Drive Generators for Large Wind Turbines” Proc. of 5th IET International Conference on Power Electronics Machines and Drives, 2010.
Grauers, A., “Design of Direct-Driven Permanent-Magnet Generators for Wind Turbines” Ph.D. Thesis, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, 1996.
McDonald, A., Mueller, M., and Polinder, H., “Structural Mass in Direct-Drive Permanent Magnet Electrical Generators” IET Renewable Power Generation, Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 3–15, 2008.
Polinder, H., Mecrow, B. C., Jack, A. G., Dickinson, P. G., and Mueller, M. A., “Conventional and TFPM Linear Generators for Direct-Drive Wave Energy Conversion” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 260–267, 2005.
Bevington, C. M., Bywaters, G. L., Coleman, C. C., Costin, D. P., Danforth, W. L., and et al., “Wind Turbine having a Direct-Drive Drivetrain” US Patent, No. US7431567B1, 2008.
Bianchi, N., “Electrical Machine Analysis using Finite Elements” CRC press, pp. 11–24, 2005.
JSOL Corporation, “JMAG 11 User’s Guide” 2011.
ANSYS Inc., “ANSYS User’s Guide ver. 12.0” 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, DW., Ro, YC., Kim, YG. et al. Light weight design of direct-drive generator for large-scale wind turbine. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 15, 1223–1228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0460-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0460-4