Abstract
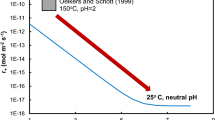
The calcite dissolution rates at 50–250 °C and 20 MPa in deionized water with flow rate varying from 0.2 to 5 mL/min were experimentally measured in a continuous flow column pressure vessel reactor. Equilibrium concentration (c eq) of calcite dissolution in deionized water at 20 MPa was determined using dissolution data according to the iterative method presented by Jeschke and Dreybrodt. The equilibrium concentrations at 50, 100, 150, 200 and 250 °C are 1.84×10−4, 2.23×10−4, 2.25×10−4, 2.31×10−4 and 2.24×10−4 mol/L, respectively. The c eq increases first and then decreases with temperature varying from 50 to 250 °C at 20 MPa, and the same variation trend occurs at 10 MPa with lower values. The maximum value (or extremum) of c eq would increase with temperature at constant pressures. The dissolution reaction of calcite in this experiment is approaching the calcite equilibrium, and the reaction order doesn’t keep a constant at different temperatures, which could imply that a change of the reaction mechanism was occurring. The Arrhenius equation shouldn’t be used to calculate apparent activation energy using rate constant data at different temperatures when the reaction order or reaction mechanism changed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Alkattan, M., Oelkers, E. H., Dandurand, J. L., et al., 1998. An Experimental Study of Calcite and Limestone Dissolution Rates as a Function of pH from −1 to 3 and Temperature from 25 to 80 °C. Chemical Geology, 151: 199–214
Berner, R. A., Morse, J. W., 1974. Dissolution Kinetics of Calcium Carbonate in Sea Water: IV. Theory of Calcite Dissolution. American Journal of Science, 274: 108–134
Buhmann, D., Dreybrodt, W., 1985a. The Kinetics of Calcite Dissolution and Precipitation in Geologically Relevant Situations of Karst Areas: 1. Open System. Chemical Geology, 48(1–4): 189–211
Buhmann, D., Dreybrodt, W., 1985b. The Kinetics of Calcite Dissolution and Precipitation in Geologically Relevant Situations of Karst Areas: 2. Closed System. Chemical Geology, 53(1–2): 109–124
Cardell-Fernández, C., Vleugels, G., Torfs, K., et al., 2002. The Processes Dominating Ca Dissolution of Limestone When Exposed to Ambient Atmospheric Conditions as Determined by Comparing Dissolution Models. Environmental Geology, 43(1–2): 160–171
Cubilias, P., Köhler, S., Prieto, M., et al., 2005. How do Mineral Coatings Affect Dissolution Rates? An Experimental Study of Coupled CaCO3 Dissolution-CdCO3 Precipitation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69: 5459–5476
Eisenlohr, L., Meteva, K., Gabrovšek, F., et al., 1999. The Inhibiting Action of Intrinsic Impurities in Natural Calcium Carbonate Minerals to Their Dissolution Kinetics in Aqueous H2O-CO2 Solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63: 989–1002
Gledhill, D. K., Morse, J. W., 2006. Calcite Dissolution Kinetics in Na-Ca-Mg-Cl Brines. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70: 5802–5813
Gong, Q. J., Deng, J., Wang, Q. F., et al., 2008. Calcite Dissolution in Deionized Water from 50 °C to 250 °C at 10 MPa: Rate Equation and Reaction Order. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82: 994–1001
Jeschke, A. A., Dreybrodt, W., 2002a. Dissolution Rates of Minerals and Their Relation to Surface Morphology. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66: 3055–3062
Jeschke, A. A., Dreybrodt, W., 2002b. Pitfalls in the Determination of Empirical Dissolution Rate Equations of Minerals from Experimental Data and a Way out: An Iterative Procedure to Find Valid Rate Equations, Applied to Ca-Carbonates and -Sulphates. Chemical Geology, 192: 183–194
Kaufmann, G., Dreybrodt, W., 2007. Calcite Dissolution Kinetics in the System CaCO3-H2O-CO2 at High Undersaturation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(6): 1398–1410
Liu, Z. H., Yuan, D. X., Dreybrodt, W., 2005. Comparative Study of Dissolution Rate-Determining Mechanism of Limestone and Dolomite. Environmental Geology, 49(2): 274–279
Morse, J. W., Arvidson, R. S., 2002. The Dissolution Kinetics of Major Sedimentary Carbonate Minerals. Earth-Science Reviews, 58(1–2): 51–84
Morse, J. W., Berner, R. A., 1972. Dissolution Kinetics of Cal cium Carbonate in Seawater: II. A Kinetic Origin for Lysocline. American Journal of Science, 272: 840–851
Plummer, L. N., Wigley, T. M. L., Parkhurst, D. L., 1978. The Kinetics of Calcite Dissolution in CO2-Water Systems at 5 °C to 60 °C and 0.0 to 1.0 atm CO2. American Journal of Science, 278(2): 179–216
Pokrovsky, O. S., Golubev, S. V., Schott, J., 2005. Dissolution Kinetics of Calcite, Dolomite and Magnesite at 25 °C and 0 to 50 atm pCO2. Chemical Geology, 217(3–4): 239–255
Sjöberg, E. L., 1976. A Fundamental Equation for Calcite Dissolution Kinetics. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 40: 441–447
Svensson, U., Dreybrodt, W., 1992. Dissolution Kinetics of Natural Calcite Minerals in CO2-Water Systems Approaching Calcite Equilibrium. Chemical Geology, 100(1–2): 129–145
Yu, B. S., Dong, H. L., Ruan, Z., 2008. Mechanism for Calcite Dissolution and Its Contribution to Development of Reservoir Porosity and Permeability in the Kela 2 Gas Field, Tarim Basin, China. Science in China (Series D), 51(4): 567–578
Zhang, H. J., Ding, L., Wang, X. L., et al., 2006. Carbonate Diagenesis Controlled by Glacioeustatic Sea-Level Changes: A Case Study from the Carboniferous-Permian Boundary Section at Xikou, China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 17(2): 103–114
Zhu, X. M., Chen, H. Q., Zhong, D. K., et al., 2008. Mechanism of Secondary Pore Formation and Prediction of Favorable Reservoir of Paleogene in Jiyang Sag, Eastern China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(6): 675–684
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2009CB421006), and the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources (No. GPMR200843).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Q., Deng, J., Wang, Q. et al. Experimental determination of calcite dissolution rates and equilibrium concentrations in deionized water approaching calcite equilibrium. J. Earth Sci. 21, 402–411 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0103-3