Abstract
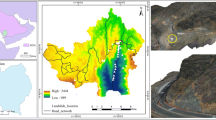
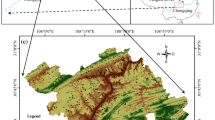
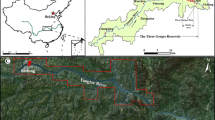
Numerous researches have been published on the application of landslide susceptibility assessment models; however, they were only applied in the same areas as the models were originated, the effect of applying the models to other areas than the origin of the models has not been explored. This study is purposed to develop an optimized random forest (RF) model with best ratios of positive-to-negative cells and 10-fold cross-validation for landslide susceptibility mapping (LSM), and then explore its generalization ability not only in the area where the model is originated but also in area other than the origin of the model. Two typical counties (Fengjie County and Wushan County) in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China, which have the same terrain and geological conditions, were selected as an example. To begin with, landslide inventory was prepared based on field investigations, satellite images, and historical records, and 1 522 landslides were then identified in Fengjie County. 22 landslide-conditioning factors under the influence of topography, geology, environmental conditions, and human activities were prepared. Then, combined with 10-fold cross-validation, three typical ratios of positive-to-negative cells, i.e., 1:1, 1:5, and 1:10, were adopted for comparative analyses. An optimized RF model (Fengjie-based model) with the best ratios of positive-to-negative cells and 10-fold cross-validation was constructed. Finally, the Fengjie-based model was applied to Fengjie County and Wushan County, and the confusion matrix and area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve value (AUC) were used to estimate the accuracy. The Fengjie-based model delivered high stability and predictive capability in Fengjie County, indicating a great generalization ability of the model to the area where the model is originated. The LSM in Wushan County generated by the Fengjie-based model had a reasonable reference value, indicating the Fengjie-based model had a great generalization ability in area other than the origin of the model. The Fengjie-based model in this study could be applied in other similar areas/countries with the same terrain and geological conditions, and a LSM may be generated without collecting landslide information for modeling, so as to reduce workload and improve efficiency in practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Ayalew, L., Yamagishi, H., 2005. The Application of GIS-Based Logistic Regression for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Kakuda-Yahiko Mountains, Central Japan. Geomorphology, 65(1/2): 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.06.010
Bakillah, M., Liang, S., Mobasheri, A., et al., 2014. Fine-Resolution Population Mapping Using OpenStreetMap Points-of-Interest. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 28(9): 1940–1963. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2014.909045
Breiman, L., 2001. Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45(1): 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010933404324
Can, A., Dagdelenler, G., Ercanoglu, M., et al., 2017. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping at Ovacık-Karabük (Turkey) Using Different Artificial Neural Network Models: Comparison of Training Algorithms. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 78(1): 89–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1034-3
Chen, W., Peng, J. B., Hong, H. Y., et al., 2018a. Landslide Susceptibility Modelling Using GIS-Based Machine Learning Techniques for Chongren County, Jiangxi Province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 626: 1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.124
Chen, W., Yan, X. S., Zhao, Z., et al., 2018b. Spatial Prediction of Landslide Susceptibility Using Data Mining-Based Kernel Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes and RBFNetwork Models for the Long County Area (China). Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 78(1): 247–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1256-z
Chen, W., Zhang, S., Li, R. W., et al., 2018c. Performance Evaluation of the GIS-Based Data Mining Techniques of Best-First Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Naïve Bayes Tree for Landslide Susceptibility Modeling. Science of the Total Environment, 644: 1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.389
Das, I., Stein, A., Kerle, N., et al., 2012. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping along Road Corridors in the Indian Himalayas Using Bayesian Logistic Regression Models. Geomorphology, 179: 116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.08.004
Dou, J., Yunus, A. P., Bui, D. T., et al., 2019a. Improved Landslide Assessment Using Support Vector Machine with Bagging, Boosting, and Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning Framework in a Mountainous Watershed, Japan. Landslides, 17(3): 641–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5
Dou, J., Yunus, A. P., Bui, D. T., et al., 2019b. Assessment of Advanced Random Forest and Decision Tree Algorithms for Modeling Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 662: 332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.221
Fourniadis, I. G., Liu, J. G., Mason, P. J., 2007. Landslide Hazard Assessment in the Three Gorges Area, China, Using ASTER Imagery: Wushan-Badong. Geomorphology, 84(1/2): 126–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.07.020
Han, J. W., Kamber, M., 2006. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Data Mining Concepts Models Methods & Algorithms Second Edition, 5(4): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118029145.ch1
He, S. W., Pan, P., Dai, L., et al., 2012. Application of Kernel-Based Fisher Discriminant Analysis to Map Landslide Susceptibility in the Qinggan River Delta, Three Gorges, China. Geomorphology, 171/172: 30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.04.024
Heckmann, T., Gegg, K., Gegg, A., et al., 2014. Sample Size Matters: Investigating the Effect of Sample Size on a Logistic Regression Susceptibility Model for Debris Flows. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 14(2): 259–278. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-259-2014
Hong, H. Y., Naghibi, S. A., Pourghasemi, H. R., et al., 2016a. GIS-Based Landslide Spatial Modeling in Ganzhou City, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(2): 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2094-y
Hong, H. Y., Pourghasemi, H. R., Pourtaghi, Z. S., 2016b. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in Lianhua County (China): A Comparison between a Random Forest Data Mining Technique and Bivariate and Multivariate Statistical Models. Geomorphology, 259: 105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.02.012
Huang, F. M., Yin, K. L., Huang, J. S., et al., 2017. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Based on Self-Organizing-Map Network and Extreme Learning Machine. Engineering Geology, 223: 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.013
Huang, Y., Zhao, L., 2018. Review on Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Support Vector Machines. CATENA, 165: 520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.03.003
Hussin, H. Y., Zumpano, V., Reichenbach, P., et al., 2016. Different Landslide Sampling Strategies in a Grid-Based Bi-Variate Statistical Susceptibility Model. Geomorphology, 253: 508–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.10.030
Jiang, P., Chen, J. J., 2016. Displacement Prediction of Landslide Based on Generalized Regression Neural Networks with K-Fold Cross-Validation. Neurocomputing, 198: 40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.08.118
Jin, Y. F., Yin, Z. Y., Zhou, W. H., et al., 2019. Bayesian Model Selection for Sand with Generalization Ability Evaluation. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 43(14): 2305–2327. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2979
Kalantar, B., Pradhan, B., Naghibi, S. A., et al., 2017. Assessment of the Effects of Training Data Selection on the Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Comparison between Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 9(1): 49–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1407368
Lee, S., 2019. Current and Future Status of GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Literature Review. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 35: 179–193. https://doi.org/10.7780/kjrs.2019.35.1.12
Li, C. D., Fu, Z. Y., Wang, Y., et al., 2019. Susceptibility of Reservoir-Induced Landslides and Strategies for Increasing the Slope Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area: Zigui Basin as an Example. Engineering Geology, 261: 105279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105279
Liu, Z. H., Zhan, W. F., Lai, J. M., et al., 2019. Balancing Prediction Accuracy and Generalization Ability: A Hybrid Framework for Modelling the Annual Dynamics of Satellite-Derived Land Surface Temperatures. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 151: 189–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.03.013
Moore, I. D., Wilson, J. P., 1992. Length-Slope Factors for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation: Simplified Method of Estimation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 47(5): 423–428. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.1.271
Pandey, V. K., Pourghasemi, H. R., Sharma, M. C., 2018. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Maximum Entropy and Support Vector Machine Models along the Highway Corridor, Garhwal Himalaya. Geocarto International, 35(2): 168–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1510038
Pham, B. T., Prakash, I., Khosravi, K., et al., 2018. A Comparison of Support Vector Machines and Bayesian Algorithms for Landslide Susceptibility Modelling. Geocarto International, 34(13): 1385–1407. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1489422
Pourghasemi, H. R., Mohammady, M., Pradhan, B., 2012. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Index of Entropy and Conditional Probability Models in GIS: Safarood Basin, Iran. CATENA, 97: 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.05.005
Reichenbach, P., Rossi, M., Malamud, B. D., et al., 2018. A Review of Statistically-Based Landslide Susceptibility Models. Earth-Science Reviews, 180: 60–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Sahin, E. K., Colkesen, I., Kavzoglu, T., (2018. A Comparative Assessment of Canonical Correlation Forest, Random Forest, Rotation Forest and Logistic Regression Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Geocarto International, 35(4): 341–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1516248
Sestraş, P., Bilaşco, Ş., Roşca, S., et al., 2019. Landslides Susceptibility Assessment Based on GIS Statistical Bivariate Analysis in the Hills Surrounding a Metropolitan Area. Sustainability, 11(5): 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051362
Shirzadi, A., Bui, D. T., Pham, B. T., et al., 2017. Shallow Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using a Novel Hybrid Intelligence Approach. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6374-y
Silalahi, F. E. S., Pamela, Arifianti, Y., et al., 2019. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Frequency Ratio Model in Bogor, West Java, Indonesia. Geoscience Letters, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-019-0140-4
Sun, D. L., Wen, H. J., Wang, D. Z., et al., 2020. A Random Forest Model of Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Based on Hyperparameter Optimization Using Bayes Algorithm. Geomorphology, 362: 107201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107201
Taalab, K., Cheng, T., Zhang, Y., 2018. Mapping Landslide Susceptibility and Types Using Random Forest. Big Earth Data, 2(2): 159–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/20964471.2018.1472392
Tian, Y. Y., Xu, C., Hong, H. Y., et al., 2018. Mapping Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Susceptibility by Use of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Models: An Example of the 2013 Minxian (China) Mw 5.9 Event. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 10(1): 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1487471
Tian, Y. Y., Xu, C., Ma, S. Y., et al., 2019. Inventory and Spatial Distribution of Landslides Triggered by the 8th August 2017 MW 6.5 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake, China. Journal of Earth Science, 30(1): 206–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-0869-2
Tsangaratos, P., Ilia, I., Hong, H. Y., et al., 2016. Applying Information Theory and GIS-Based Quantitative Methods to Produce Landslide Susceptibility Maps in Nancheng County, China. Landslides, 14(3): 1091–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0769-4
Wang, Y., Sun, D. L., Wen, H. J., et al., 2020. Comparison of Random Forest Model and Frequency Ratio Model for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping (LSM) in Yunyang County (Chongqing, China). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12): 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124206
Wang, Y. M., Wu, X. L., Chen, Z. J., et al., 2019. Optimizing the Predictive Ability of Machine Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using SMOTE for Lishui City in Zhejiang Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3): 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030368
Wen, H. J., Xie, P., Xiao, P., et al., 2016. Rapid Susceptibility Mapping of Earthquake-Triggered Slope Geohazards in Lushan County by Combining Remote Sensing with the AHP Model Developed for the Wenchuan Earthquake. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 76(3): 909–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0957-4
Wen, H. J., Wang, G. L., Huang, X. L., 2017. A Preliminary Evaluation Method of Slope Stability Based on Topographic Map and Geological Map. Chinese patent No 2017105719823 (in Chinese)
Wu, W. Y., Xu, C., Wang, X. Q., et al., 2020. Landslides Triggered by the 3 August 2014 Ludian (China) Mw 6.2 Earthquake: An Updated Inventory and Analysis of Their Spatial Distribution. Journal of Earth Science, 31(4): 853–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1297-7
Xie, P., Wen, H. J., Ma, C., et al., (2018. Application and Comparison of Logistic Regression Model and Neural Network Model in Earthquake-Induced Landslides Susceptibility Mapping at Mountainous Region, China. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 9(1): 501–523. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1451399
Xu, C., Xu, X. W., Dai, F. C., et al., 2012. Landslide Hazard Mapping Using GIS and Weight of Evidence Model in Qingshui River Watershed of 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake Struck Region. Journal of Earth Science, 23(1): 97–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0236-7
Yao, Y., Liu, X. P., Li, X., et al., 2017. Mapping Fine-Scale Population Distributions at the Building Level by Integrating Multisource Geospatial Big Data. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 13(1): 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2017.1290252
Yu, L. B., Cao, Y., Zhou, C., et al., 2019. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Combining Information Gain Ratio and Support Vector Machines: A Case Study from Wushan Segment in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Applied Sciences, 9(22): 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224756
Zêzere, J. L., Pereira, S., Melo, R., et al., 2017. Mapping Landslide Susceptibility Using Data-Driven Methods. Science of the Total Environment, 589: 250–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.188
Zhang, T. Y., Han, L., Zhang, H., et al., 2019. GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Hybrid Integration Approaches of Fractal Dimension with Index of Entropy and Support Vector Machine. Journal of Mountain Science, 16(6): 1275–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5337-z
Zhou, Q. F., Zhou, H., Zhou, Q. Q., et al., 2014. Structure Damage Detection Based on Random Forest Recursive Feature Elimination. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 46(1): 82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.12.013
Zhu, A. X., Miao, Y. M., Wang, R. X., et al., 2018. A Comparative Study of an Expert Knowledge-Based Model and Two Data-Driven Models for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. CATENA, 166: 317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.04.003
Acknowledgments
We want to express our gratitude to Chongqing Meteorological Administration for providing essential meteorological data and also to Chongqing Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources for offering valuable research data on historical landslides. We are also grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on this manuscript. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41807498), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1505501), and the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 20XJAZH002). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1072-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Xu, J., Wen, H. et al. An Optimized Random Forest Model and Its Generalization Ability in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: Application in Two Areas of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Earth Sci. 31, 1068–1086 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1072-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1072-9