Abstract
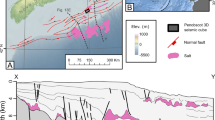
During northward movement of the Indian sub-continent, after its breakup from the Gondwanaland in the Late Cretaceous, the western part of India traversed over the Reunion plume. The Saurashtra peninsula and the Cambay Basin are two important geological regions in this part. Two and half dimensional density models, based on the crustal seismic structure, were generated to establish a relationship between these two regions. These models indicate that the crust is 32–33 km thick in the eastern Saurashtra and the northern part of the Cambay Basin. The shallower crust is in a triangular region formed by the extension of the western limb of the Proterozoic Aravalli trend in Saurashtra, its eastern limb and the Narmada fault in the south. Compared to 36–37 km thick crust to the west and 38–40 km to the east of this region the crust in the above triangular region is uplifted by 4 to 6 km. This uplift took place either after the deposition of Mesozoic sediments or was concomitant with the rise of Reunion plume prior to the extrusion of the Deccan volcanics as the region was close to the axis of the plume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besse, J. and Courtillot, V. (1988) Paleogeographic maps of the continents bordering the Indian ocean since the early Jurassic. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.93, pp.11791–11808.
Bijendra Singh, Prajapati, S.K. and Mishra, D.C. (2003) Presence of Anomalous Crustal root Beneath Saurashtra Peninsula-Inference from Gravity Modeling, Jour. Geophys., v.XXIV, pp.25–29.
Biswas, S.K. (1982) Rift basins in the western margin of India and their Hydrocarbon prospects, Bull. Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol., v.66, pp.1497–1513.
Biswas, S.K. (1987) Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India. Tectonophysics, v.135, pp.307–327.
Campbell, I.H. and Griffiths, R.W. (1990) Implications of mantle plume structure for the evolution of food basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.99, pp.79–93.
Chandrasekhar, D.V., Mishra, D.C., Poornachandra Rao, G.V.S. and Mallikharjuna Rao, J. (2002) Gravity and magnetic signatures of volcanic plugs related to Deccan volcanism in Saurashtra, India and their physical and geochemical properties. Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett., v.201, pp.277–292.
GM-SYS (2002) Two and half D gravity magnetic modeling system for OASIS Montaj™ Geosoft Canada.
GSI/NGRI (2006) Gravity map series of India.
Kaila, K.L., Tewari H.C. and Sarma P.L.N. (1980) Crustal structure from deep seismic sounding studies along Navibandar-Amreli profile in Saurashtra, India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, No.3, pp.218–232.
Kaila, K.L., Krishna, V.G. and Mall, D.M. (1981) Crustal structure along Mehmadabad- Billimora profile in the Cambay Basin, India, from deep seismic soundings. Tectonophysics, v.76, pp.99–130.
Kaila, K.L., Tewari, H.C., Krishna, V.G., and Dixit, M.M., Sarkar, D. and Reddy, M.S. (1990) Deep seismic sounding studies in the north Cambay and Sanchor Basins, India. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.103, pp.621–63.
Kailasam. L.N. and Qureshi, M.N. (1964) On some anomalous bouguer gravity anomalies in India. In: A.P. Subramanian and S. Balakrishna (Eds.), Advancing frontiers in Geology and Geophysics. Indian Geophysical Union, pp.135–146.
Kennett, B.L.N. and Widiyantoro (1999) A low seismic wave speed anomaly beneath North Western India: a seismic structure of Deccan hotspot? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.165, pp.145–155.
McKenzie, D.P. and Sclater, J.G. (1971) The evolution of the Indian Ocean since the late Cretaceous. Geophy. Jour. Asr. Soc., v.25, pp.437–528.
Mishra, D.C., et al. (2001) Major lineaments and gravity-magnetic trends in Saurashtra, India. Curr. Sci., v.80, pp.270–280.
Negi, B.S. (1952) Gravity and magnetic survey in subsurface structures in the Borsad area, Khera District. Geol. Surv. India. Rep.(unpublished).
Raju, A.T.R. and Srinivasan. S. (1983) More Hydrocarbon from well explored Cambay basin. Petrol. Asia. Jour., v.6, pp.25–35.
Rao, G.S.P. and Tewari, H.C. (2005) The seismic structure of the Saurashtra crust in northwest India and its relation ship with the Reunion plume. Geophy. Jour. Internat., v.160, pp.318–330.
Rao, N.D.J. (1968) An interpretation of gravity data of Cambay basin. ONGC Bull., v.4, pp.74–80.
Raval, U. and Veeraswamy, K. (2003) India-Madagascar separation: breakup along a pre-existing mobile belt and chipping of the craton. Gondwana Res., v.6, pp.467–485.
Raval, U. and Veeraswamy, K. (2000) The radial and linear modes of interaction between mantle plume and continental lithosphere: a case study from western India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.56, pp.525–536.
Ramanathan. S. (1981) Some aspects of Deccan volcanism of western Indian shelf and Cambay Basin. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.3, pp.198–217.
Satpal, O.P., Sar, D., Chatterjee S.M. and Sanjeev Sawai (2006) Integrated interpretation for sub-basalt imaging in Saurashtra Basin, India. The Leading Edge, v.6, pp.882–885.
Sen Gupta, S.N. (1967) Structure of the Gulf of Cambay, Proc. Symp. Upper Mantle Project. Hyderabad, pp.334–341.
Singh, D., Alat, C.A., Singh, R.N. and Gupta, V.P. (1997) Source rock characteristics and Hydrocarbon generating potential of Mesozoic sediments in Lodhika Area, Saurashtra Basin, Gujarat, India. Proc. Second Int. Pet. Conf. and Exbn., PETROTECH., New Delhi, pp.205–220.
Talwani, M., Worzel, T.L. and Landisman, M. (1959) Rapid computations for two-dimensional bodies with applications to Mendocino Submarine fracture zone. Jour. Geophy. Res., v.64, pp.49–54.
Tewari, H.C., Dixit., M.M., Sarkar. D. and Kaila, K.L. (1991) A Crustal density model across the Cambay Basin, India, and its relationship with the Aravallis. Tectonophysics, v.194, pp.123–130.
Tewari, H.C., Dixit, M.M. and Sarkar, D. (1995) Relationship of the Cambay rift basin to the Deccan volcanism. Jour. Geodyn., v.20, pp.85–95.
Tewari, H.C. and Prakash Kumar (2003) Deep Seismic Sounding Studies in India and their tectonic implications. In: Mita Rajaram (Ed.), Geophysics. Window to Indian Geology. Jour. Virtual Explorer, v.12, pp.34–50.
Verma, R.K., Gupta, M.L., Hamza, V.M., Venkateshwr Rao, G. and Rao, R.U.M. (1968) Heat flow and crustal structure near Cambay, Gujarat, India. Bull. National. Geophy. Res. Inst., v.6, pp.153–166.
White, R.S. and McKenzie D.P. (1989) Magmatism at rift zones: The generation of volcanic continental margins and flood basalts. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.94, pp.7685–7729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tewari, H.C., Surya Prakasa Rao, G. & Rajendra Prasad, B. Uplifted crust in parts of western India. J Geol Soc India 73, 479–488 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0033-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0033-9