Abstract
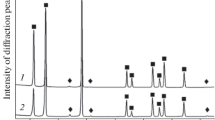
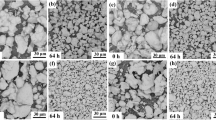
Ultrafine WC-11Co hard metals added with different proportions of graphite were prepared by spark plasma sintering at 40 MPa/1200°C for 5 min, and the influence of graphite as free carbon on the microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated. The XRD analysis showed that decarbonization could be prevented by adding graphite. Compact hard metals composed of finer and more homogeneous WC grains with little flaws can be achieved after 0 wt.% to 1.5 wt.% graphite was added. The hardness and fracture toughness increase initially with increasing graphite content, and with over 1.5 wt.% they descend due to coarse grains and more defects. Therefore, 1.5 wt.% graphite is the optimal addition content in view of the hardness and transverse rupture toughness. Furthermore, the coercive force decreases while the saturated magnetic intensity increases with the increase of graphite content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leiderman M., Bostein O., and Rose A., Sintering, microstruc-ture and properties of sub-micrometer cemented carbides. Powder Metall., 1997, 40(3): 219.
Uhrenius B., Phase equilibria and the sintering of cemented carbides, [in] Proceedings of Powder Metallurgy World Congress, Les Ulis, 1994: 1443.
Xiao Y.F., He Y.H., Feng P., and Xie H., Effects of carbon content on microstructure and properties of carbon-deficient cemented carbides, Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2007, 1: 39.
Zhang M.L., Zhu S.G., and Zhu S.X., Carbon content change and its influence on structure and properties of ultrafine and nano-cemented carbide, Cemented Carbide, 2006, 20(8): 65.
Qian K.Y., Wang X.Q., He B.S., Guo H.L., and Bai J.S., Effect of carbon content on microstructure and properties of nanosize cemented carbide, J. Shanghai Univ., 2002, 8(5): 433.
Lin X.P., Cao S.H., and Li J.Y., Effects and control of carbon in nanograined cemented carbide, Cemented Carbide, 2004, 21(2): 111.
Cha S.I. and Hong S.H., Microstructures of binderless tungsten carbides sintered by spark plasma sintering process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 356: 381.
Schubert W.D., Neumeister H., Kinger G., and Lux B., Hardness to toughness relationship of fine-grained WC-Co hardmetals, Int J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 1998, 16: 133.
Liang Y.J., Physical Chemistry, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1983: 254.
Pickens J.R. and Gurland J., The fracture toughness of WC-Co alloys measured on single edge notched beam specimens precracked by electron discharge machining, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1978, 33: 135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Yang, T., Jia, C. et al. Effects of graphite on the microstructure and properties of ultrafine WC-11Co composites by spark plasma sintering. Rare Metals 30, 63–67 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0198-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0198-4