Abstract
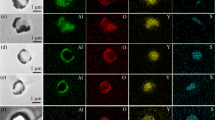
The Al2O3, MnS, and TiN inclusions in bearing steel will deteriorate the steel’s mechanical properties. Therefore, elucidating detailed characteristics of these inclusions in consumable electrode during the electroslag remelting process is important for achieving a subsequently clean ingot. In this study, a confocal scanning violet laser microscope was used to simulate the remelting process and observe, in real time, the behaviors of inclusions. The obtained images show that, after the temperature exceeded the steel solidus temperature, MnS and TiN inclusions in the specimen began to dissolve. Higher temperatures led to faster dissolution, and the inclusions disappeared before the steel was fully liquid. In the case of an observed Al2O3 inclusion, its shape changed from angular to a smooth ellipsoid in the region where the solid and liquid coexisted and it began to dissolve as the temperature continued to increase. This dissolution was driven by the difference in oxygen potential between the inclusion and the liquid steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Mitchell, Oxide inclusion behaviour during consumable electrode remelting, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1(1974), No. 3, p. 172.
F.R. Carmona, Non-metallic Inclusions in Electroslag Refined Ingots [Dissertation], The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, 1983, p. 148.
Z.B. Li, W.H. Zhou, and Y.D. Li, Mechanism of removal of non-metallic inclusions in the ESR process, Iron Steel, 15(1980), No. 1, p. 20.
J. Fu, An investigation of mechanism on the removal of oxide inclusions during ESR process, Acta Metall. Sinica, 15(1979), No. 4, p. 526.
M.E. Fraser and A. Mitchell, Mass transfer in the electroslag process: Part 1. Mass-transfer model, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 3(1976), No. 5, p. 279.
Z.B. Li, J.W. Zhang, and X.Q. Che, Control of content and composition of nonmetallic inclusion in ESR steel, J. Iron Steel Res., 9(1997), No. 2, p. 7.
J. Janis, A. Karasev, K. Nakajima, and P.G. Jönsson, Effect of secondary nitride particles on grain growth in a Fe–20 mass% Cr alloy deoxidised with Ti and Zr, ISIJ Int., 53(2013), No. 3, p. 476.
J. Fu, J. Zhu, L. Di, F.S. Tong, D.L. Liu, and Y.L. Wang, Study on the precipitation behavior of TiN in the microalloyed steels, Acta Metall. Sinica, 36(2000), No. 8, p. 801.
J.X. Chen, Manual of Chart and Data in Common Use of Steel Making, 2nd Ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2010, p. 510.
Y. Qü, Physical Chemical Calculation in Steelmaking, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1993, p. 121.
H. Goto, K.I. Miyazawa, K.I. Yamaguchi, S. Ogibayashi, and K. Tanaka, Effect of cooling rate on oxide precipitation during solidification of low carbon steels, ISIJ Int., 34(1994), No. 5, p. 414.
J.H. Wei and A. Mitchell, Changes in composition during A.C. ESR—I. Theoretical development, Acta Metall. Sinica, 20(1984), No. 5, p. B261.
L. Yang, G.G. Cheng, S.J. Li, M. Zhao, and G.P. Feng, Generation mechanism of TiN inclusion for GCr15SiMn during electroslag remelting process, ISIJ Int., 55(2015), No. 9, p. 1901.
M. Takashi and Z. Masafumi, Effect of silicon content in steel on the formation of titanium nitride and solidification structure, Tetsu-to-Hagané, 99(2013), No. 3, p. 191.
M. Ohta and K. Morita, Interaction between silicon and titanium in molten steel, ISIJ Int., 43(2003), No. 2, p. 256.
D.J. Shin and D.J. Min, Investigation on the decomposition of Al2O3 using an electrochemical method, ISIJ Int., 53(2013), No. 3, p. 434.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express thanks for the helpful advice and editing work of Professor Bryan A. Webler at Carnegie Mellon University. This work was financially supported by the Key Technology Development of Bearing Steel for Major Equipment (No. 2012AA03A503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Cheng, Gg. Characteristics of Al2O3, MnS, and TiN inclusions in the remelting process of bearing steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24, 869–875 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1472-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1472-8