Abstarct
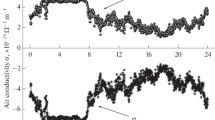
This paper presents an analysis of atmospheric electrical conductivity during monsoon period at a semi-urban site of Northern India. Continuous measurements of unipolar positive conductivity along with some meteorological parameters were made from June to August 2010 at Roorkee (29°52′N, 77°53′E, 275 m above sea level). The electrical conductivity for the three consecutive months was in the range of (25.2–19.5), (65–18) and (53–26) × 10−16 S/m respectively. The atmospheric electrical conductivity was positively correlated with wind speed, relative humidity and rain fall while it was found to be negatively correlated with average temperature in the monsoon period. Possible causes for the variation of atmospheric electrical conductivity in the light of meteorological parameters were discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C G Deshpande and A K Kamra Atmos. Res. 65 51 (2002)
P S Praveen et al. Atmos. Environ. 41 825 (2007)
B Tyagi and A N V Satyanarayana J. Atmos. Terrs. Phys. 72 224 (2010)
D Retalis, A Pitta and P Psallidas Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 46 197 (1991)
A M Selvam, R Vijay Kumar and A S R Murthy Theor. Appl Cimat. 48 15 (1993)
C G Deshpande and A K Kamra Atmos. Res. 70 77 (2004)
K Nagaraja, B S N Prasad and J Datta Advan. in Space Res. 44 1067 (2009)
W A Hoppel and G M Frick Aeros. Sci. Tech. 5 1 (2007)
H Tammet et al. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 6 3135 (2006)
S S Dhanorkar, C G Deshpande and A K Kamra Atmos. Environ. 23 839 (1989)
G K Manohar, S S Kandalgaonkar and M K Kulkarni J. Geophys. Res. 100 20805 (1995)
J S Pillai, S Saxena and K G Vernekar Bound. Layer Meteorol. 89 197 (1998)
T Madhavi Latha, P Peddi Naidu, D N Madhusudhana Rao and M Indira Devi Indian J. Phys. 86 947 (2012)
P K Jana and I Saha Indian J. Phys. 85 667 (2011)
A J Bennett and R G Harrison J. Atmos. Terrs. Phys. 70 373 (2008)
R G Harrison and Ilya Usoskin J. Atmos. Terrs. Phys. 72 176 (2010)
D Saxena, R Yadav and A Kumar Indian J. Phys. 84 383 (2010)
V N R Mukku Ph D thesis University of Roorkee, India (1982)
D Beysens et al. Atmos. Environ. 40 3710 (2006)
E F Nymphas et al. J. Atmos. Terrs. Phys. 80 28 (2012)
N Yackerson Sci. Total Envir. 293 107 (2002)
D Singh et al. Atmos. Res. 84 91 (2007)
D Siingh, D Chate and K Ali Kamra Int. J. Remote Sensing 33 962 (2012)
S K Midya, D Ghosh, S C Ganda and H Sarkar Indian J. Phys. 85 1247 (2011)
V Pant, D Siingh and A K Kamra Atmos. Environ. 45 5138 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The corresponding author (AK) is thankful to Prof J Rai, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India for providing the necessary experimental facilities and fruitful discussion in completing the present work. Author is grateful to Prof A L Verma, Amity Institute of Applied Sciences, Amity University, Noida, India for providing the necessary computational facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A. Variation of atmospheric electrical conductivity during monsoon period at a semi-urban tropical station of Northern India. Indian J Phys 87, 411–418 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0250-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0250-3