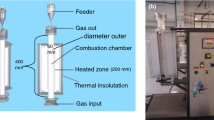
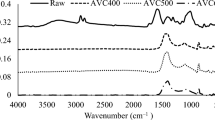
Abstract
Interest in the cultivation of plants specifically for energetic use has grown tremendously in recent years. Among the numerous tested energetic plants, Miscanthus seems to be an especially, promising ‘energy crop’. The presented data may have a contribution in developing Miscanthus pellets as a feedstock for energy recovery systems. Combustion and pyrolysis are efficient methods for controlling energy efficiency from Miscanthus. Thermogravimetric analyses were performed at heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20°C min−1 under nitrogen and air atmospheres with analysis of gaseous (CO, CO2 and VOC) pollutants and aerosols. Reactivity and kinetics measurements of Miscanthus pellets were also performed. Thermal degradation of Miscanthus pellets under inert atmosphere is similar to those found for other lignocellulosic materials. Under nitrogen, the main study was the determination of kinetic constants. These constants for main devolatilization step are not affected by variation of the heating rate with activation energy of 90 kJ mol−1 and a first reaction order. Thermal degradation of Miscanthus pellets under air occurs in main two steps: rapid decomposition and residual degradation. The amounts of CO2, CO and VOC emitted were 17.4, 3.7 and 1.0 mmol g−1, respectively. Pellets degradation produces 1.0 × 1012 particles (PM10) per gram of sample. 99% are particles with a diameter below 1 μm (57% are nanoparticles inferior to 0.1 μm). Nucleation mode dominates during the first step (190–253°C) centred at 0.04 μm whereas during the second step (253–310°C) a coagulation mode is observed centred at 0.5 μm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Styles, D., Jones, M.B.: Energy crops in Ireland: Quantifying the potential life-cycle greenhouse gas reductions of energy-crop electricity. Biomass Bioenergy 31, 759–772 (2007)
Lewandowski, I., Kicherer, A., Vonier, P.: CO2-balance for the cultivation and combustion of Miscanthus. Biomass Bioenergy 8, 81–90 (1995)
Acaroğlu, M., Aksoy, A.S.: The cultivation and energy balance of Miscanthus × giganteus production in Turkey. Biomass Bioenergy 29, 42–48 (2005)
Styles, D., Thorne, F., Jones, M.B.: Energy crops in Ireland: An economic comparison of willow and Miscanthus production with conventional farming systems. Biomass Bioenergy 32, 407–421 (2008)
Collura, S., Azambre, B., Finqueneisel, G., Zimny, T., Weber, J.V.: Miscanthus × Giganteus straw and pellets as sustainable fuels, Combustion and emission tests. Environ. Chem. Lett. 4, 75–78 (2006)
De Jong, W., Pirone, A., Wójtowicz, M.A.: Pyrolysis of Miscanthus Giganteus and wood pellets: TG-FTIR analysis and reaction kinetics. Fuel 82, 1139–1147 (2003)
Linlay, W.H., Stapleton, K.W., Zuberbulher, P.: Fine particle fraction as measure of mass depositing in the lung during inhalation of nearly isotonic nebulized aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 28, 1301–1309 (1997)
Renwick, L.C., Donaldson, K., Clouter, A.: Impairment of alveolar macrophage phagocytosis by ultrafine particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 172, 119–127 (2001)
Shi, J.P., Khan, A.A., Harrison, R.: M.: Measurements of ultrafine particle concentration and size distribution in the urban atmosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 235, 51–64 (1999)
Tsukamoto, Y., Goto, Y., Odaka, M.: Continuous measurement of diesel particulate emissions by a Electrical Low-Pressure Impactor. SAE Technical paper series 2000-01-1138 (2000)
Wierzbicka, A., Lillieblad, L., Pagels, J., Strand, M., Gudmundsson, A., Gharibi, A., Swietlicki, E., Sanati, M., Bohgard, M.: Particle emissions from district heating units operating on three commonly used biofuels. Atmos. Environ. 39, 139–150 (2005)
Johansson, L.S., Tullin, C., Leckner, B., Sjövall, P.: Particle emissions from biomass combustion in small combustors. Biomass Bioenergy 25, 435–446 (2003)
Marjamäki, M., Keskinen, J., Chen, D., Pui, D.: Performance evaluation of the electrical low pressure impactor (ELPI). J. Aerosol Sci. 31, 249–261 (2000)
Gauchet, N., Vendel, J.: Modelling of the aerosol collection efficiency by drops-influence of the distance between the drops. J. Aerosol Sci. 31, 41–42 (2000)
Tsai, R., Liang, L.J.: Correlation for thermophoretic deposition of aerosol particles onto cold plates. J. Aerosol Sci. 32, 473–487 (2001)
Friedl, A., Padouvas, E., Rotter, H., Varmuza, K.: Prediction of heating values of biomass fuel from elemental composition. Anal. Chim. Acta 544, 191–198 (2005)
Varhegi, G., Antal, M.J., Jakab, E., Piroska, S.: Kinetic modelling of biomass pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 42, 73–87 (1997)
Manasray, G.K., Ghaly, A.E.: Thermal degradation of rice husks in nitrogen atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 65, 13–20 (1998)
Vamvuka, D., Kakaras, E., Kastanaki, E., Grammelis, P.: Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of biomass residuals mixtures with lignite. Fuel 82, 1949–1960 (2003)
Grønli, M.G., Várhegyi, G., Di Blasi, C.: Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41, 4201–4208 (2002)
Munir, S., Daood, S.S., Nimmo, W., Cunliffe, A.M., Gibbs, B.M.: Thermal analysis and devolatilization kinetics of cotton stalk, sugar cane bagasse and shea meal under nitrogen and air atmospheres. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 1413–1418 (2009)
Jeguirim, M., Trouvé, G.: Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of Arundo Donax using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 4026–4031 (2009)
Jeguirim, M., Dorge, S., Loth, A., Trouvé, G.: Devolatilization kinetics of Miscanthus straw from thermogravimetric analysis. Int. J. Green Energy 7, 164–173 (2010)
Órfão, J.J.M., Antunes, F.J.A., Figueiredo, J.L.: Pyrolysis kinetics of lignocellulosic materials—three independent reactions model. Fuel 78, 349–358 (1999)
Mészáros, E., Várhegyi, G., Jakab, E., Marosvölgyi, B.: Thermogravimetric and reaction kinetic analysis of biomass samples from an energy plantation. Energy Fuels 18, 497–507 (2004)
Zhang, X., Xu, M., Sun, R., Sun, L.: Study on biomass pyrolysis kinetics. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 128, 493–496 (2006)
Nassar, M.M., Ashour, E.A., Wahid, S.S.: Thermal characteristics of bagasse. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 61, 885–890 (1996)
Chouchene, A., Jeguirim, M., Khiari, B., Trouvé, G., Zagrouba, F.: Thermal degradation behavior of olive solid waste: Influence of the particle size and oxygen atmosphere. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 54, 271–277 (2010)
Mansaray, K.G., Ghaly, A.E.: Thermal degradation of rice husks in nitrogen atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 65, 13–20 (1998)
Kumar, A., Wang, L., Dzenis, Y.A., Jones, D.D., Hanna, M.A.: Thermogravimetric characterization of corn stover as gasification and pyrolysis feedstock. Biomass Bioenergy 32, 460–467 (2008)
Biagini, E., Tognotti, L.: Comparison of devolatilization/char oxidation and direct oxidation of solid fuels at low heating rate. Energy Fuels 20, 986–992 (2006)
Altun, N.E., Kok, M.V., Hicyilmaz, C.: Effect of particle size and heating rate on the combustion of Silopi asphaltite. Energy Fuels 16, 785–790 (2002)
Jeguirim, M., Dorge, S., Trouvé, G.: Thermogravimetric analysis and emission characteristics of two energy crops in air atmosphere: Arundo donax and Miscanthus giganthus. Biores. Tech. 101, 788–793 (2010)
Dorge, S., Kehrli, D., Trouvé, G.: Caractérisation des fractions fines (PM2.5) et ultrafines (PM0.1) d’aérosols issus de la combustion de bois de pin par thermogravimétrie. Revue Internationale sur l’Ingénierie des Risques Industriels 1, 169–183 (2008)
Dorge, S., Kehrli, D., Jeguirim, M., Trouvé, G.: Study of aerosol formation during the oxidation of wood samples and lignocellulosic polymers by thermogravimetry. 11th Conference Process Integration Modelling and Optimization for energy Saving and Pollution Reduction, pp.1397–1398. Prague, Tchéquie, 24–28th Aug 2008
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the Alsace Regional Council for supporting research in the GRE and Novabiom France for supplying Miscanthus pellets.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorge, S., Jeguirim, M. & Trouvé, G. Thermal degradation of Miscanthus pellets: kinetics and aerosols characterization. Waste Biomass Valor 2, 149–155 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-010-9060-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-010-9060-4