Abstract
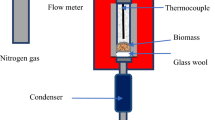
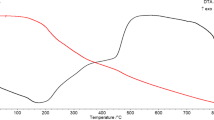
The fast pyrolysis of biomass, empty fruit bunches from the palm mill industries, was conducted in a lab-scale bubbling fluidized bed reactor with a throughput of 1 kg/hr at temperatures ranging from 400 to 650 °C. For producing a higher yield of bio-crude oil with better homogeneity, washing methods were applied to the empty fruit bunch with water and nitric acid to remove ash and alkali and alkaline earth metallic species. After washing, the ash content decreased from 5.9 to 1.53 wt%, and over 80 wt% of alkali and alkaline earth metals, such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium, was removed. For considering economic feasibility and efficiency, the biomass treated with tap water for 1 day could be enough to produce oil with the highest yield of 48 wt% at 500 °C. The homogeneity of bio-crude oil produced by fast pyrolysis from the empty fruit bunches with nitric acid washing increased to 98%. The results of chemical compounds in oil could also confirm such quality improvement by less number and higher fraction of phenol compounds.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministry of Environment, Enforcement regulations of “law of resource reduction and recycling promotion–revision of a part” (2012)
Cho, K.Y.: Evaluation on national greenhouse gas reduction goal and present implications. Korea Economic Research Institute. 39–45 (2010)
Jeong, H.C., Kim, G.Y., So, K. H., Shim, K.M., Lee, S.B., Lee, D.B.: Assessment on greenhouse gas emissions in Korea cropland sector from 1990 to 2008. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 43(6), 911–916 (2010)
Kim, S.W., Koo, B.S., Ryu, J.W., Lee, J.S., Kim, C.J., Lee, D.H., Choi, S.: Bio-oil from the pyrolysis of palm and Jatropha wastes in a fluidized bed. Fuel Process. Technol. 108, 118–124 (2013)
Lee, J.K., Kim, J.H., Lee, S.H., Choi, Y.C., Kim, Y.K., Yoo, K.S., Lee, S.H.: Development of fluidized bed reactor for the pyrolysis and gasification of agricultural and forestry wastes. Korea Inst Energy Res 19–73 (2005)
Abdullah, N., Gerhauser, H.: Bio-oil derived from empty fruit bunches. Fuel. 87(12), 2606–2613 (2008)
Yoo, H.M., Choi, H.S., Lee, J.S., Park, H.C., Yang, W.S., Seo, Y.C.: The fast pyrolysis characteristics of palm empty fruit bunch: The yield and homogeneity of bio-crude oil affected by ash. Environ. Prog. Sust. Energ. 33(3), 706–710 (2014)
Mourant, D., Wang, Z., He, M., Wang, X.S., Garcia-Perez, M., Ling, K., Li, C.Z.: Mallee wood fast pyrolysis: effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on the yield and composition of bio-oil. Fuel. 90(9), 2915–2922 (2011)
Park, H.J., Dong, J.I., Jeon, J.K., Park, Y.K., Yoo, K.S., Kim, S.S., Kim, J.S., Kim, S.D.: Effects of the operating parameters on the production of bio-oil in the fast pyrolysis of Japanese larch. Chem. Eng. J. 143, 124–132 (2008)
Scott, D.S., Paterson, L., Piskorz, J., Radlein, D.: Pretreatment of poplar wood for fast pyrolysis: rate of cation removal. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 57, 167–176 (2000)
Kim, I.G., Lee, B.M., Park, J.Y., Choi, S.A., Han, J.I.: Effect of nitric acid on pretreatment and fermentation for enhancing ethanol production of rice straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 99, 563–567 (2014)
Eom, I.Y., Kim, K.H., Kim, J.Y., Lee, S.M., Yeo, H.M., Choi, I.G.: Characterization of primary thermal degradation features of lignocellulosic biomass after removal of inorganic metals by diverse solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 3437–3444 (2011)
Rafiqul, I.S.M., Sakinah, A.M.: Design of process parameters for the production of xylose from wood sawdust. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 90(9), 1307–1312 (2012)
Sjösten, J., Golriz, M.R., Grace, J.R.: Further study on the influence of particle coating on fluidized bed heat transfer. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 49(21), 3800–3806 (2006)
Bridgwater, A.V.: Principles and practice of biomass fast pyrolysis processes for liquids. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 51(1), 3–22 (1999)
Kim, J.H., Kim, Y.H., Shin, S.M., Yoon, J.Y., Choi, J.H.: Food Science, pp. 24–27. Yangseowon publication (2012) (Korean)
Kim, J.S., Park, Y.K., Kang, B.S., Park, H.J., Lee, K.H., Kim, E.Y.: Production of clean bio-fuel from rice straw by flash pyrolysis and catalytic upgrading. Korea Minist. Environ. 43, 4079–4088 (2005)
Piskorz, J., Majerski, P., Radlein, D., Scott, D.S., Bridgwater, A.V.: Fast pyrolysis of sweet sorghum and sweet sorghum bagasse. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 46(1), 15–29 (1998)
Manurung, R., Wever, D.A.Z., Wildschut, J., Venderbosch, R.H., Hidayat, H., van Dam, J.E.G., Leijenhorst, E.J., Broekhuis, A.A., Heeres, H.J.: Valorisation of Jatropha curcas L. plant part: nut shell conversion to fast pyrolysis oil. Food Bioprod. Process. 87, 187–196 (2009)
Hwang, H.W., Oh, S.Y., Cho, T.S., Choi, I.G., Choi, J.W.: Fast pyrolysis of potassium impregnated poplar wood and characterization of its influence on the formation as well as properties of pyrolytic products. Bioresour. Technol. 150, 359–366 (2013)
Lian, J., Chen, S., Zhou, S., Wang, Z., O’Fallon, J., Li, C-Z., Garcia, P.M.: Separation, hydrolysis and fermentation of pyrolysis sugars to produce ethanol and lipids. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 9688–9699 (2010)
Elliott, D.C.: Historical developments in hydroprocessing bio-oils. Energy Fuels 21, 1792–1815 (2007)
Choi, H.S., Choi, Y.S., Park, H.C.: The influence of fast pyrolysis condition on biocrude-oil yield and homogeneity. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27(4), 1164–1169 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by Korean Ministry of Knowledge Economy as the “Development of bio-energy production technology using palm-oil byproducts” and the Korean Ministry of Environment (MOE) as “Knowledge-based environmental service (Waste-to-energy recycling) Human resource development Project”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, HM., Seo, YC., Park, SW. et al. Removal Effect of Ash and Metallic Species by Washing from Empty Fruit Bunch Byproducts in Palm Mills on Pyrolytic Characteristics to Produce Bio-Crude Oil. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 491–502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9807-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9807-7