Abstract
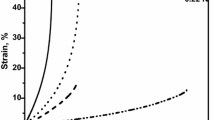
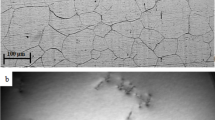
Nitrogen-alloyed 316LN stainless steel is used as a structural material for high temperature fast breeder reactor components. With a view to increase the design life of the components up to 60 years and beyond, studies are being carried out to develop nitrogen alloyed 316LN stainless steel with superior tensile, creep and low cycle fatigue properties. This paper presents the results from studies on the influence of nitrogen on the high temperature creep properties of this material. The influence of nitrogen on the creep behaviour of 316LN stainless steel has been studied at nitrogen levels of 0.07, 0.11, 0.14 and 0.22 wt%. Creep tests were carried out at 923 K at stress levels 140, 175, 200 and 225 MPa. Creep rupture strength increased substantially with increase in nitrogen content. The variation of steady state creep rate with stress showed a power law relationship. The power law exponent varied between 6.4 and 13.7 depending upon the nitrogen content. Rupture ductility was generally above 40% at all the test conditions and for all the nitrogen contents. It was observed that the internal creep damage and surface damage decreased with increase in nitrogen content. Fracture mode was found to generally shift from intergranular failure to transgranular failure with increasing nitrogen content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valentine G Gavriljuk and Hans Berns, ’High Nitrogen Steels’, 135 (1999) New York, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Kearns J R and Lula R A, Proceedings of Conference on New Developments in Stainless Steel Technology, ASM, Metals Park, OH 117 (1985)
Mathew M D and Srinivasan V S, Mechanical Behaviour of Nitrogen-bearing Steels in Monograph on High Nitrogen Austenitic Steels and Stainless Steels, Kamachi Mudali U and Baldev Raj (Eds.), Narosa Publications, New Delhi, (2004) 182.
Degallix S, Foct J and Hendry A, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2 (1986) 946.
ASTM Standard Practice for Conducting Creep, Creep Rupture and Stress Rupture Tests on Metallic Materials, E139-83, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, (1990).
Matsuo T, Morioka N, Kaise S, Kikuchi M and Tanaka R, “Effect of nitrogen on creep deformaiton of 25Cr-28Ni austenitic steels — solid solution strengthening due to nitrogen”, Foct J and Hendry A (eds.), HNS 88, Lille, France. May 1988, The Institute of Metals, London, (1989) 213.
Nakazawa T, Abo H, Tanino M, Komatsu H, Nishida T and Tashimo M, Effects of nitrogen and carbon on creep properties of type 316 stainless steels, Foct J and Hendry A (eds.), HNS 88, Lille, France, May 1988, The Institute of Metals, London, (1989) 218–224.
G.Byrnes M L, Grujici M and Owen W S, Acta Met., 35 (1987) 1853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesan, V., Mathew, M.D., Parameswaran, P. et al. Creep strengthening of low carbon grade type 316LN stainless steel by nitrogen. Trans Indian Inst Met 63, 417–421 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-010-0057-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-010-0057-2