Abstract
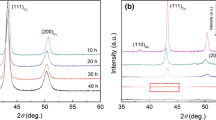
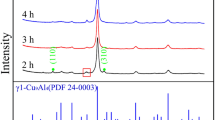
In the present work, a set of Cu-based powder mixtures containing up to 6 wt% Cr has been processed through mechanical alloying for a range of milling times up to 96 h. The mixtures were processed in a ball mill with ball to powder ratio of 10:1 and the equal numbers of 1 and 2 cm balls. The processed powder mixtures were investigated by scanning electron microscope, optical microscopic equipped with image analyzer, X-ray diffraction technique and micro hardness in order to determine the particles morphology, distribution of chromium, mean crystallite size, lattice parameter and hardness after milling, respectively. Crystallite sizes were measured by Williamson–Hall method and lattice parameters were determined using an extrapolation function. Results show that the powder behavior varies with milling time, and powder composition.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloor D, Brook R J, Flemings M C, and Mahjan S, The encyclopedia of advanced materials, pergamon press, Oxford (1994) p 1324.
suryanarayana C, processing of materials, pergamon press, Oxford (1999) p 58.
Gaffet E, louison C, Harmelin M, Faudet F, Mater Sci Eng A 134 (1991) 1380.
Ogino Y, Murayama S, and Yamasaki T, J less common Met 168 (1991) 221.
Barro MJ, Navarro E, Agudo P, Hernando A, Crespo P, and Garcia A, Sci Forum J 235–238 (1997) 553.
Benjamin J S, Proc of the novel powder metal, World congr, San Francisco, CA, USA, Pbl. Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, Advances in Powder Metallurgy 7 (1992) 155.
Suryanarayana C, Progress in Materials Science 46 (2001) 56.
Lü, L, and Lai M O, Mechanical alloying, Kluwer (1998) p 23–67.
Morris D G, Morris M A, Benghalem A, and Bissel C, Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on structural applications of mechanical alloying (1994) 353–360.
Harumatsu M, and Hidenori O, Materials Transaction 40 (9) (1999) 907–910.
Sauer C, Weiissgaerber T, Puesche W, Dehm G, Mayer J, and Kieback B, The International Journal Of Powder Metallurgy 33(1) (1997) 45–53.
Takas, L, In: Suryanarayana C, et al., Processing and properties of Nano crystalline materials. Warrendale, PA: TMS (1996) 453–64.
Takas L, Pardavi M H, J Appl Phys 75 (1994) 5864–5866.
Gavrilov D, Vinogradov O, and Shaw W J D, Proc. Inter. Conf. on Composite Materials, ICCM- 10, (eds) Poursartip A, and Street K, vol-III. Woodhead publishing, (1995) p 11.
Suryananarayana C, Grant N M, X-Ray Diffraction A Practical Approach, Plenum Press (1998) p 153–222.
Smallman R E, Bishop R J, Modern Physical Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1999) p 20.
Cottrell A H, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 212 (1958) 192.
Dieter G E, Mechanical Metallurgy, Second Edition, McGraw-Hill (1982) p 165.
Clyne T W, and Withers P J, An Introduction To Metal Matrix Composites, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press (2003) p 93.
Eckert J, Hozer J C, Krill C E, and Johnson W L, J Mater Res, 7 (1992) 1751-61.
Borner I, and Eckert J, Mater Sci Forum; 225- 227(1996) 377-82.
Aguilar C, Martinez V de P, Palacios J M, Ordonez S, and Pavez O, Scripta Materialia 57 (2007) 213–216.
Jin Y, Adachi K, Takeuchi T, Suzuki H G, Materials Letters 32 (1997) 307–311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dehaqani, M.T., Akbari, G.H. Effect of Milling Parameters and Cr Content on Morphology and Solubility of Nanostructured Cu–Cr Solid Solutions. Trans Indian Inst Met 67, 385–391 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-013-0360-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-013-0360-9