Abstract
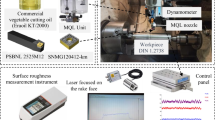
In this experimental study, the effects of cutting parameters and insert types on the surface roughness and cutting force components were investigated during hard turning of high chromium AISI D2 tool steel under dry cutting conditions. Three different cutting speeds, feed rates, and cutting depths were chosen as machining parameters, while cubic boron nitride and ceramic inserts with two different nose radii were selected as tool material. The design of the experiment was carried out based on the Taguchi L36 mixed orthogonal array. The response surface method was used to establish the relation between input and output parameters. Analysis of variance was performed to show the most significant parameters on the response. In addition, an artificial neural network was implemented for output modeling. The results revealed that surface roughness was mainly affected by the feed rate with almost 90.53%. Following feed rate, the nose radius was also significant on the surface roughness. Based on the results, the cubic boron nitride insert exhibited better performance than the ceramic insert in terms of minimum surface roughness. The cutting force components were mostly affected by the insert type. Cubic boron nitride insert caused greater forces during machining compared to the ceramic insert. The results revealed that the artificial neural network and response surface methodology exhibited very good accuracy with experimental data. However, the artificial neural network shows better accuracy and can predict the responses with 99.51% accuracy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartarya G, and Choudhury S, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 53 (2012) 1.
Gaitonde V, Karnik S, Figueira L, and Davim J P, Mater Manuf Processes 24 (2009) 1373.
Patel V D, and Gandhi A H, Measurement 138 (2019) 34.
Choudhary R, Kumar H, and Singh S, J Mater Eng Perform 22 (2013) 3665.
Kumar R, Sahoo A K, Mishra P C, and Das R K, Adv Manuf 6 (2018) 155.
Kahrobaee S, and Kashefi M, J Mater Eng Perform 24 (2015) 1192.
Şahinoğlu A, and Rafighi M, Mater Test 62 (2020) 85.
Özdemir M, Mechanics 25 (2019) 397.
Umer U, J Mater Eng Perform 21 (2012) 1857.
Salimi Asl A, Erdem A, and Rafighi M, Sci Iran 24 (2017) 2864.
Özdemir M, Kaya M T, and Akyildiz H K, Mechanics 26 (2020) 231.
Kalyon A, Günay M, and Özyürek D, Adv. Manuf 6 (2018) 419.
Gaitonde V, Karnik S, and Davim J P, J Mater Eng Perform 18 (2009) 231.
Şahinoğlu A, and Rafighi M, Arabian J Sci Eng 45 (2020) 765.
Srithar A, Palanikumar K, and Durgaprasad B, Mater Today: Proc 16 (2019) 1061.
Kumar R, Sahoo A K, Mishra P C, Panda A, Das R K, and Roy S, Mater Today: Proc 18 (2019) 2486.
Özbek O., and Saruhan H, J Mater Res Technol 9 (2020) 2762.
Davim J P, and Figueira L, Mater Des 28 (2007) 1186.
Dosbaeva G, El Hakim M, Shalaby M, Krzanowski J, and Veldhuis S, Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 50 (2015) 1.
Gabay T, Jakobs E, Ben-Jacob E, and Hanein Y, Physica A, 350 (2005) 611.
Rao K V, Murthy B, and Rao N M, Measurement 51 (2014) 63.
Cavaleri L, Chatzarakis G E, Di Trapani F, Douvika M G, Roinos K, Vaxevanidis N M, and Asteris P G, Adv Mater Res 6 (2017) 169.
Davim J P, Gaitonde V, and Karnik S, J Mater Process Technol 205 (2008) 16.
Basheer A C, Dabade U A, Joshi S S, Bhanuprasad V, and Gadre V, J Mater Process Technol 197 (2008) 439.
Karayel D, J Mater Process Technol 209 (2009) 3125.
Munoz-Escalona P, and Maropoulos P G, J Mater Eng Perform 19 (2010) 185.
Kara F, Karabatak M, Ayyıldız M, and Nas E, J Mater Res Technol 9 (2020) 969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafighi, M., Özdemir, M., Al Shehabi, S. et al. Sustainable Hard Turning of High Chromium AISI D2 Tool Steel Using CBN and Ceramic Inserts. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 1639–1653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02245-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02245-2