Abstract
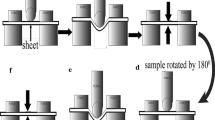
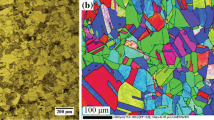
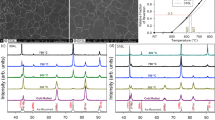
In this research, the influence of post-annealing treatment on the microstructure, hardness, and tensile properties of cold-rolled austenitic stainless steel was investigated. The AISI 304 steel was asymmetrically rolled and then annealed in the temperature range of 700–900 °C for 10–60 min. By increasing the time and temperature of annealing treatment, the number of twins and strain-induced martensite (M) decreased. The reversion of martensite to austenite at 700 ℃ occurred through both shear and diffusional mechanisms. However, at higher temperatures, the shear reversion was the dominant mechanism. The microstructure of the annealed sample at 700 ℃ for 60 min showed a combination of continuous and discontinuous recrystallization grains, which was due to the simultaneous occurrence of shear and diffusional reversion transformation in this sample. After 10 min of annealing at 800 °C, the hardness dropped sharply to 293.6 HV, followed by a slight decrease with increasing time, which was a characteristic of continuous recrystallization. The results showed that with increasing annealing time at 700 °C, the yield strength (YS) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of steel decreased, while the total elongation (TE) value increased. As the time of annealing treatment increased, the depth and diameter of the dimples increased and the fracture surface became more ductile.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
F. Forouzan, A. Najafizadeh, A. Kermanpur, A. Hedayati, R. Surkialiabad, Production of nano/submicro grained AISI 304L stainless steel through the martensite reversion process, Materials Science and Engineering A 527 (2010) 7334–7339.
M. Eskandari, A. Najafizadeh, A. Kermanpur, M. Karimi, Potential application of nanocrystalline 301 austenitic stainless steel in lightweight vehicle structures, Materials and Design 30 (2009) 3869–3872.
B. Roy, R. Kumar, J. Das, Effect of cryorolling on the microstructure and tensile properties of bulk nano-austenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering A 631 (2015) 241–247.
L.P. Karjalainen, T. Taulavuori, M. Sellman, A. Kyröläinen, Some strengthening methods for austenitic stainless steels, Steel Research International 79 (2008) 404–412.
C. Ptian, T. Hashimoto, M. Kawazoc, J. Nagahora, K. Higashi, Microstructure and texture evolution in ECAE processed A5056, Materials Science and Engineering A 280 (2000) 62–68.
A.P. Zhilyaev, G.V. Nurislamova, B.K. Kim, M.D. Baró, J.A. Szpunar, T.G. Langdon, Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion, Acta Materialia 51 (2003) 753–765.
A.L.M. Costa, A.C.C. Reis, L. Kestens, M.S. Andrade, Ultra grain refinement and hardening of IF-steel during accumulative roll-bonding, Materials Science and Engineering A 406 (2005) 279–285.
A. Belyakov, T. Sakai, H. Miura, R. Kaibyshev, Substructures and internal stresses developed under warm severe deformation of austenitic stainless steel, Scripta Materialia 42 (2000) 319–325.
H. Lianxi, L. Yuping, W. Erde, Y. Yang, Ultrafine grained structure and mechanical properties of a LY12 Al alloy prepared by repetitive upsetting-extrusion, Materials Science and Engineering A 422 (2006) 327–332.
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, N. Tsuji, T. Sakai, Novel ultra-high straining process for bulk materials—development of the accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process, Acta Materialia 47 (1999) 579–583.
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, Overview of processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained bcc steels, Materials Science and Engineering A 441 (2006) 1–17.
Y. Ma, J.E. Jin, Y.K. Lee, A repetitive thermomechanical process to produce nano-crystalline in a metastable austenitic steel, Scripta Materialia 52 (2005) 1311–1315
B. Ravi Kumar, S. Sharma, B.P. Kashyap, N. Prabhu, Ultrafine grained microstructure tailoring in austenitic stainless steel for enhanced plasticity, Materials and Design 68 (2015) 63–71.
G.S. Sun, L.X. Du, J. Hu, R.D.K. Misra, Microstructural evolution and recrystallization behavior of cold rolled austenitic stainless steel with dual phase microstructure during isothermal annealing, Materials Science and Engineering A 709 (2018) 254–264.
D.M. Xu, G.Q. Li, X.L. Wan, R.D.K. Misra, X.G. Zhang, G. Xu, K.M. Wu, The effect of annealing on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties in phase reversed 316LN austenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering A 720 (2018) 36–48.
N. Solomon, I. Solomon, Deformation induced martensite in AISI 316 stainless steel, Revista de Metalurgia 46 (2010) 21–28.
S. Vercammen, B. Blanpain, B.C. De Cooman, P. Wollants, Cold rolling behaviour of an austenitic Fe–30Mn–3Al–3Si TWIP-steel: the importance of deformation twinning, Acta Mateialia 52 (2004) 2005–2012.
I. Tamura, Deformation-induced martensitic transformation and transformation induced plasticity in steels, Metal Science 6 (1982) 245–253.
D.L. Johnnsen, A. Kyrolainen, P.J. Ferreira, Influence of annealing treatment on the formation of nano/submicron grain size AISI 301 austenitic stainless steels, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 37 (2006) 2325–2338.
K. Nohara, Y. Ono, N. Ohashi, Composition and grain size dependencies of strain-induced martensitic transformation in metastable austenitic stainless steels, Tetsu-to-Hagané 63 (1977) 772–782.
P. Fajfar, A.Š. Lah, J. Kraner, G. Kugler, Asymmetric rolling process, Materials and Geoenvironment 64 (2017) 151–160.
L.S. Tóth, B. Beausir, D. Orlov, R. Lapovok, A. Haldar, Analysis of texture and R value variations in asymmetric rolling of IF steel, Journal of Materials Processing Technology 212 (2012) 509–515.
S. Li, X. Li, L. Yang, Role of strain path change in grain refinement by severe plastic deformation: A case study of equal channel angular extrusion, Acta Materialia 61 (2013) 4398–4413.
Y.H. Ji, J.J. Park. Development of severe plastic deformation by various asymmetric rolling processes, Materials Science and Engineering A 499 (2009) 14–17.
A.M. Pesin, Modeling and development of the processes of asymmetric deformation to improve sheet rolling: thesis, Magnitogorsk, 2003.
Y.H. Li, J.J. Park, W.J. Kim, Finite element analysis of severe deformation in Mg–3Al–1Zn sheets through differential-speed rolling with a high speed ratio, Materials Science and Engineering A 454–455 (2007) 570–574.
S. Tamimi, J.J. Gracio, A.B. Lopes, S. Ahzi, F. Barlat, Asymmetric rolling of interstitial free steel sheets: microstructural evolution and mechanical properties, Journal of Manufacturing Processes 31 (2018) 583–592.
J. Liu, R. Kawalla, Influence of asymmetric hot rolling on microstructure and rolling force with austenitic steel, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 22 (2012) s504–s511.
M.C. Somani, M. Jaskari, S. Sadeghpour, C. Hu, R.D.K. Misra, T.T. Nyo, C. Yang, L. Pentti Karjalainen, Improving the yield strength of an antibacterial 304Cu austenitic stainless steel by the reversion treatment, Materials Science and Engineering A 793 (2020) 139885.
L. Jinlong, L. Hongyun, Influence of tensile pre-strain and sensitization on martensite reversion mechanism in austenitic stainless steel, Materials Characterization 77 (2013) 10–14.
P. Mallick, N.K. Tewary, S.K. Ghosh, P.P. Chattopadhyay, Microstructure-tensile property correlation in 304 stainless steel after cold deformation and austenite reversion, Materials Science and Engineering A 707 (2017) 488–500.
I. Shakhova, V. Dudko, A. Belyakov, K. Tsuzaki, R. Kaibyshev, Effect of large strain cold rolling and subsequent annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of an austenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering A 545 (2012) 176–186.
A. Kisko, A.S. Hamada, J. Talonen, D. Porter, L.P. Karjalainen, Effects of reversion and recrystallization on microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-alloyed low-Ni high-Mn austenitic stainless steels, Materials Science and Engineering A 657 (2016) 359–370.
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, Y. Tokunaga, Reversion mechanism from deformation induced martensite to austenite in metastable austenitic stainless steels, ISIJ international 31 (1991) 1431–1437.
R.D.K. Misra, Z. Zhang, P.K.C. Venkatasurya, M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, Martensite shear phase reversion-induced nanograined/ultrafine-grained Fe–16Cr–10Ni alloy: The effect of interstitial alloying elements and degree of austenite stability on phase reversion, Materials Science and Engineering A 527 (2010) 7779–7792.
M.C. Somani, P. Juntunen, L.P. Karjalainen, R.D.K. Misra, A. Kyröläinen, Enhanced mechanical properties through reversion in metastable austenitic stainless steels, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 40 (2009) 729–744.
L. Kaufman, E.V. Clougherty, R.J. Weiss, The lattice stability of metals—III. Iron, Acta Metallurgica 11 (1963) 323–335.
K.B. Guy, E.P. Butler, D.R.F. West, Reversion of bcc α′ martensite in Fe–Cr–Ni austenitic stainless steels, Metal Science 17 (1983) 167–176.
A. Belyakov, K. Tsuzaki, Y. Kimura, Y. Mishima, Annealing behavior of a ferritic stainless steel subjected to large-strain cold working, Journal of Materials Research 22 (2007) 3042–3051.
A. Amininejad, R. Jamaati, S.J. Hosseinipour, Achieving superior strength and high ductility in AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel via asymmetric cold rolling, Materials Science and Engineering A 767 (2019) 138433.
G.S. Sun, L.X. Du, J. Hu, H. Xie, R.D.K. Misra, Low temperature superplastic-like deformation and fracture behavior of nano/ultrafine-grained metastable austenitic stainless steel, Materials and Design 117 (2017) 223–231.
R.D.K. Misra, X.L. Wan, V.S.A. Challa, M.C. Somani, L.E. Murr, Relationship of grain size and deformation mechanism to the fracture behavior in high strength–high ductility nanostructured austenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering A 626 (2015) 41–50.
V. Scarpini Cândido, S.N. Monteiro, The Effect of Phase Transformation on the Tensile Fracture of Austenitic Stainless Steel, Materials Science Forum 869 (2016) 508–513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amininejad, A., Jamaati, R. & Hosseinipour, S.J. Influence of Deformation and Post-Annealing Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 1799–1807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02277-8