Abstract
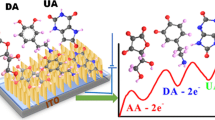
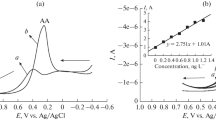
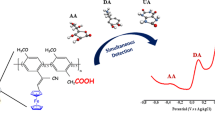
Fabrication of nonenzymatic biosensors based on the nanomaterials for highly sensitive and selective detection of single or multiple molecules coexisting in one biological sample is extremely challenging. Design of the hierarchical nanohexagonal Fe2O3 platelets (HFP) via one-pot hydrothermal treatment was employed for selective signaling of dopamine (DA) and uric acid (UA) in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA) with high sensitivity. Electrode design with the nanosized structure of parallel hexagonal platelets (20–40 nm), high surface area, multiactive site, smooth surface, and pore distribution inside/outside the surfaces renders excellent sensitivity and selectivity of DA and UA during the catalytic oxidation process. Simultaneous monitoring and selective signaling of DA and UA were successfully achieved by HFP with detection limits as low as 16 nM and 0.218 μM with a wide linear range from 1 to 200 μM and from 20 to 400 μM for DA and UA, respectively. HFP provides high stability and reproducibility with relative standard deviations in the range of 2.5–5.29% to monitor DA and UA. Furthermore, continuous monitoring of DA and UA in real human saliva/serum samples was realized with high sensitivity and selectivity. The designed HFP can be employed as a nonenzymatic biosensor for simultaneous detection of mono-bioactive molecules in the biological samples.

The electrooxidation of DA and UA at the surfaces of Fe2O3.The electrocatalytic active sites bind with the DA and UA through hydrogen bonds at the surface of Fe2O3. Through the DPV or CV scanning, the electrooxidation of DA and UA proceeded and the oxidized form quinolone-DA and keto-UA were obtained with losing of 2e−/2H+.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Shinohara, F. Wang, S.Z. Hossain, A convenient. Nat. Protoc. 3(10), 1639–1644 (2008)
Y. Zhao, Y. Gao, D. Zhan, H. Liu, Q. Zhao, Y. Kou, Y. Shao, M. Li, Q. Zhuang, Z. Zhu, Selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid by a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified electrode. Talanta 66(1), 51–57 (2005)
Y. Liu, J. Huang, H. Hou, T. You, Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid with electrospun carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 10(10), 1431–1434 (2008)
T. Nakaminami, S.-i. Ito, S. Kuwabata, H. Yoneyama, Anal. Chem. 71, 1928 (1999)
E. Popa, Y. Kubota, D.A. Tryk, A. Fujishima, Selective voltammetric and amperometric detection of uric acid with oxidized diamond film electrodes. Anal. Chem. 72(7), 1724–1727 (2000)
T.-F. Kang, G.-L. Shen, R.-Q. Yu, Voltammetric behaviour of dopamine at nickel phthalocyanine polymer modified electrodes and analytical applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 354(1-3), 343–349 (1997)
A.A. Abdelwahab, Y.-B. Shim, Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and folic acid based on activated graphene/MWCNT nanocomposite loaded Au nanoclusters. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 221, 659–665 (2015)
J. Cheng, H. Yan, Y. Lu, K. Qiu, X. Hou, J. Xu, L. Han, X. Liu, J.-K. Kim, Y. Luo, Mesoporous CuCo2O4nanograsses as multi-functional electrodes for supercapacitors and electro-catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(18), 9769–9776 (2015)
M.Y. Emran, H. Khalifa, H. Gomaa, M.A. Shenashen, N. Akhtar, M. Mekawy, A. Faheem, S.A. El-Safty, Hierarchical C-N doped NiO with dual-head echinop flowers for ultrasensitive monitoring of epinephrine in human blood serum. Microchim. Acta 184(11), 4553–4562 (2017)
M.Y. Emran, M. Mekawy, N. Akhtar, M.A. Shenashen, I.M. EL-Sewify, A. Faheem, S.A. El-Safty, Broccoli-shaped biosensor hierarchy for electrochemical screening of noradrenaline in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 100, 122–131 (2018)
M.Y. Emran, M.A. Shenashen, M. Mekawy, A.M. Azzam, N. Akhtar, H. Gomaa, M.M. Selim, A. Faheem, S.A. El-Safty, Ultrasensitive in-vitro monitoring of monoamine neurotransmitters from dopaminergic cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 259, 114–124 (2018)
K. Ghanbari, M. Moloudi, Flower-like ZnO decorated polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Biochem. 512, 91–102 (2016)
C. Sumathi, C.V. Raju, P. Muthukumaran, J. Wilson, G. Ravi, Au–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles anchored on α-Fe2O3nonenzymatic hybrid nanoelectrocatalyst for simultaneous electrochemical detection of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Mater. Chem. B 4(15), 2561–2569 (2016)
J.-y. Sun, T. Gan, Y.-p. Deng, Z.-x. Shi, Z. Lv, Pt nanoparticles-functionalized hierarchically porous γ-Al2O3 hollow spheres based electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive guaiacol detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 211, 339–345 (2015)
J. Hou, C. Xu, D. Zhao, J. Zhou, Facile fabrication of hierarchical nanoporous AuAg alloy and its highly sensitive detection towards dopamine and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 225, 241–248 (2016)
Y. Liu, P. She, J. Gong, W. Wu, S. Xu, J. Li, K. Zhao, A. Deng, A novel sensor based on electrodeposited Au–Pt bimetallic nano-clusters decorated on graphene oxide (GO)–electrochemically reduced GO for sensitive detection of dopamine and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 221, 1542–1553 (2015)
R. Ojani, J.-B. Raoof, A.A. Maleki, S. Safshekan, Chin. J. Catal. 35, 423 (2014)
Z. Yang, X. Zheng, J. Zheng, A facile one-step synthesis of Fe 2 O 3/nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for enhanced electrochemical determination of dopamine. J. Alloys Compd. 709, 581–587 (2017)
Z. Yu, H. Li, J. Lu, X. Zhang, N. Liu, X. Zhang, Hydrothermal synthesis of Fe2O3/graphene nanocomposite for selective determination of ascorbic acid in the presence of uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 158, 264–270 (2015)
H. Filik, A.A. Avan, S. Aydar, Simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and tryptophan with Azure A-interlinked multi-walled carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticles composite modified electrode. Arab. J. Chem. 9(3), 471–480 (2016)
N. Akhtar, M.Y. Emran, M.A. Shenashen, H. Khalifa, T. Osaka, A. Faheem, T. Homma, H. Kawarada, S.A. El-Safty, J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 7985 (2017)
Y. Li, X. Lin, Simultaneous electroanalysis of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid by poly (vinyl alcohol) covalently modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 115(1), 134–139 (2006)
N. Akhtar, S.A. El-Safty, M. Khairy, Chem. Aust. 2, 235 (2014)
N. Akhtar, S.A. El-Safty, M. Khairy, W.A. El-Said, Fabrication of a highly selective nonenzymatic amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide based on nickel foam/cytochrome c modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 207, 158–166 (2015)
D. Hassen, S.A. El-Safty, K. Tsuchiya, A. Chatterjee, A. Elmarakbi, M.A. Shenashen, M. Sakai, Sci. Rep. 6, 24330 (2016)
D. Hassen, M. Shenashen, S. El-Safty, M. Selim, H. Isago, A. Elmarakbi, A. El-Safty, H. Yamaguchi, Nitrogen-doped carbon-embedded TiO 2 nanofibers as promising oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. J. Power Sources 330, 292–303 (2016)
M. Khairy, S.A. El-Safty, Mesoporous NiO nanoarchitectures for electrochemical energy storage: influence of size, porosity, and morphology. RSC Adv. 3(45), 23801 (2013)
M. Khairy, S.A. El-Safty, M. Ismael, H. Kawarada, Mesoporous NiO nanomagnets as catalysts and separators of chemical agents. Appl. Catal. B 127, 1–10 (2012)
Y. Zeng, C. Li, C. Tang, X.B. Zhang, G. Shen, R. Yu, The electrochemical properties of Co(TPP), tetraphenylborate modified glassy carbon electrode: application to dopamine and uric acid analysis. Electroanalysis 18(5), 440–448 (2006)
N. Akhtar, S.A. ElSafty, M.E. Abdelsalam, H. Kawarada, Adv. Healthc. Mater. 4, 2110 (2015)
N. Akhtar, S.A. El-Safty, M.E. Abdelsalam, M.A. Shenashen, H. Kawarada, Biosens. Bioelectron. 77, 656 (2016)
D. Bruns, Detection of transmitter release with carbon fiber electrodes. Methods 33(4), 312–321 (2004)
A.G. Nasibulin, S. Rackauskas, H. Jiang, Y. Tian, P.R. Mudimela, S.D. Shandakov, L.I. Nasibulina, S. Jani, E.I. Kauppinen, Simple and rapid synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanowires under ambient conditions. Nano Res. 2(5), 373–379 (2009)
S.A. El-Safty, M.A. Shenashen, M. Ismael, M. Khairy, Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 3013 (2012)
S.A. El-Safty, Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of highly ordered hexagonal and cubic composite monoliths. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 319(2), 477–488 (2008)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Khairy, M.A. Shenashen, E. Elshehy, W. Warkocki, M. Sakai, Optical mesoscopic membrane sensor layouts for water-free and blood-free toxicants. Nano Res. 8(10), 3150–3163 (2015)
S.A. El-Safty, Y. Kiyozumi, T. Hanaoka, F. Mizukami, Appl. Catal. A 121, 337 (2008)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Sakai, M.M. Selim, A.A. Alhamid, Mesotubular-structured hybrid membrane nanocontainer for periodical monitoring, separation, and recovery of cobalt ions from water. Chem. Asian J. 10(9), 1909–1918 (2015)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Sakai, M.M. Selim, A.A. Hendi, Mesosponge optical sinks for multifunctional mercury ion assessment and recovery from water sources. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(24), 13217–13231 (2015)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Shenashen, Optical mesosensor for capturing of Fe(III) and Hg(II) ions from water and physiological fluids. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 183, 58–70 (2013)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Shenashen, M. Khairy, Bioadsorption of proteins on large mesocage-shaped mesoporous alumina monoliths. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 103, 288–297 (2013)
S.A. El-Safty, M. Shenashen, A. Shahat, Tailor-made micro-object optical sensor based on mesoporous pellets for visual monitoring and removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous media. Small 9(13), 2288–2296 (2013)
S.A. El-Safty, M.A. Shenashen, N. Akhtar, M.M. Selim, W.M. Morsy, H. Yamaguchi, S. Kawada, A.A. Alhamid, N. Ohashi, I. Ichinose, Chem. Asian J. 12, 1952 (2017)
M.S. Selim, A. Elmarakbi, A.M. Azzam, M.A. Shenashen, A.M. EL-Saeed, S.A. El-Safty, Eco-friendly design of superhydrophobic nano-magnetite/silicone composites for marine foul-release paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 116, 21–34 (2018)
M.S. Selim, M.A. Shenashen, A. Elmarakbi, A.M. El-Saeed, M.M. Selim, S.A. El-Safty, Sunflower oil-based hyperbranched alkyd/spherical ZnO nanocomposite modeling for mechanical and anticorrosive applications. RSC Adv. 7(35), 21796–21808 (2017)
M.S. Selim, M.A. Shenashen, A. Elmarakbi, N.A. Fatthallah, S.-i. Hasegawa, S.A. El-Safty, Chem. Eng. J. 320, 653 (2017)
M.A. Shenashen, S.A. El-Safty, M. Khairy, J. Porous. Mater. 20, 679 (2013)
M.A. Shenashen, E. Elshehy, S.A. El-Safty, M. Khairy, Visual monitoring and removal of divalent copper, cadmium, and mercury ions from water by using mesoporous cubic Ia3d aluminosilica sensors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 116, 73–86 (2013)
M.A. Shenashen, S.A. El-Safty, E.A. Elshehy, Monolithic scaffolds for highly selective ion sensing/removal of Co(ii), Cu(ii), and Cd(ii) ions in water. Analyst 139(24), 6393–6405 (2014)
M.A. Shenashen, S.A. El-Safty, E.A. Elshehy, Synthesis, morphological control, and properties of silver nanoparticles in potential applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 31(3), 293–316 (2014)
M.A. Shenashen, D. Hassen, S.A. El-Safty, H. Isago, A. Elmarakbi, H. Yamaguchi, Axially oriented tubercle vein and X-crossed sheet of N-Co 3 O 4 @C hierarchical mesoarchitectures as potential heterogeneous catalysts for methanol oxidation reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 313, 83–98 (2017)
M.A. Shenashen, D. Hassen, S.A. El-Safty, M.M. Selim, N. Akhtar, A. Chatterjee, A. Elmarakbi, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 3, 1600743 (2016)
M.A. Shenashen, S. Kawada, M.M. Selim, W.M. Morsy, H. Yamaguchi, A.A. Alhamid, N. Ohashi, I. Ichinose, S.A. El-Safty, Nano 9, 7947 (2017)
I.M. El-Sewify, M.A. Shenashen, A. Shahat, H. Yamaguchi, M.M. Selim, M.M. Khalil, S.A. El-Safty, Ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for Zn2+ ions in environmental samples using supermicroporous organic-inorganic structures as potential platforms. ChemistrySelect 2(34), 11083–11090 (2017)
A.M. Azzam, M.A. Shenashen, M.M. Selim, H. Yamaguchi, I.M. El-Sewify, S. Kawada, A.A. Alhamid, S.A. El-Safty, Nanospherical inorganic α-Fe core-organic shell necklaces for the removal of arsenic(V) and chromium(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 109, 78–88 (2017)
A. Derbalah, S.A. El-Safty, M.A. Shenashen, N.A. Abdel Ghany, Mesoporous alumina nanoparticles as host tunnel-like pores for removal and recovery of insecticides from environmental samples. ChemPlusChem 80(7), 1119–1126 (2015)
M.A. Shenashen, A. Derbalah, A. Hamza, A. Mohamed, S.A. El Safty, Antifungal activity of fabricated mesoporous alumina nanoparticles against root rot disease of tomato caused byFusarium oxysporium. Pest Manag. Sci. 73(6), 1121–1126 (2017)
D. De Faria, F. Lopes, Heated goethite and natural hematite: can Raman spectroscopy be used to differentiate them? Vib. Spectrosc. 45(2), 117–121 (2007)
M.M. Rahman, A.M. Asiri, Development of ionic-sensor based on sono-chemically prepared low-dimensional β-Fe2O3 nanoparticles onto flat-gold electrodes by an electrochemical approach. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 4, 109–117 (2015)
D. Hassan, S.A. El-Safty, K.A. Khalil, M. Dewidar, G. Abu El-Maged, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 8374 (2016)
M. Khairy, S.A. El-Safty, Nanosized rambutan-like nickel oxides as electrochemical sensor and pseudocapacitor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 193, 644–652 (2014)
D. Buttry, A. Bard, Electroanalytical chemistry, vol 17 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1991)
P. Zuman, R.N. Adams, Electrochemistry at solid electrodes: M. Dekker, New York, xiii+ 402, Elsevier, (1970)
H. Ibrahim, Y. Temerk, Sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of uric acid and xanthine in human biological fluids based on the nano-boron doped ceria modified glassy carbon paste electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 780, 176–186 (2016)
K. Schwab, G. Heubel, H. Bartels, Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. J. Forum Eur. Clin. Chem. Soc, 541–544 (1992)
S.A. El-Safty, S. Abdellatef, M. Ismael, A. Shahat, Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2, 854 (2013)
H. Gomaa, H. Khalifa, M. Selim, M. Shenashen, S. Kawada, A.S. Alamoudi, A. Azzam, A. Alhamid, S.A. El-Safty, Selective, photoenhanced trapping/detrapping of arsenate anions using mesoporous blobfish head TiO2 monoliths. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5(11), 10826–10839 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 496 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emran, M.Y., Shenashen, M.A., Abdelwahab, A.A. et al. Nanohexagonal Fe2O3 Electrode for One-Step Selective Monitoring of Dopamine and Uric Acid in Biological Samples. Electrocatalysis 9, 514–525 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-018-0468-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-018-0468-0