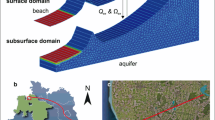
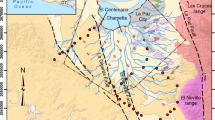
Abstract
Coastal karst features are supposed to be generated by the coupling between the infiltration of undersaturated rain water together with mixing from the fresh–saltwater interface. A coupled density-driven flow and reactive solute transport numerical model is presented which is able to duplicate conditions in such a morphogenetic conceptual model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo C, Postma D (1994) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. A.A. Balkema, Amsterdam
Bauer-Gottwein P, Langer T, Prommer H, Wolski P, Kinzelbach W (2007) Okavango Delta Islands: interaction between density-driven flow and geochemical reactions under evapo-concentration. J Hydrol 335(3–4):389–405
Christensen F, Engesgaard P, Kipp K (2001) A reactive transport investigation of seawater intrusion experiment in a shallow aquifer, Skansehage, Denmark. In: Proceedings of the first international conference on saltwater intrusion and coastal aquifers, Essaouira, Morocco
Encinas JA (1997) Inventari espeleològic de les Illes Balears. Endins. 21 103–128, Palma de Mallorca
Freedman V, Ibaraki M (2002) Effects of chemical reactions on density-dependent fluid flow: on the numerical formulation and the development of instabilities. Adv Water Resour 25(4):439–453
Garrels R, Christ C (1965) Solutions, minerals, and equilibria. Freeman, Cooper and Company, San Fransisco
Ginés J (2001) El karst litoral en el levante de Mallorca: una aproximación al conocimiento de su morfologénesis y cronología. Endins 24
Guo W, Langevin C (2002) User’s guide to SEWAT: a computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variable-density ground-water flow. United States Geological Survey
Hanshaw BB, Van Driel JN (1984) Role of groundwater in shaping the eastern coastline of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Groundwater as a geomorphic agent. Allen and Unwin, Boston, pp 281–293
Helgeson H, Kirkham D (1974) Theoretical prediction of the thermodynamic behavior of aqueous electrolytes at high pressures and temperatures. I. Summary of the thermodynamic/electrostatic properties of the solvent. Am J Sci 274(10):1089–1198
James JM, Rogers P, Spate AP (1989) The role of missing corrosion in the genesis of the caves of the Nullarbor plain, Australia. In: Proc 10th Int Congress Speleol 1. pp 263–265, Budapest
Lasaga AC, Soler JM, Ganor J, Burch TE, Nagy KL (1994) Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:2361–2386
Mangold D, Tsang C (1991) A summary of subsurface hydrological and hydrochemical models. Rev Geophys 29(1):51–80
Mao X, Prommer H, Barry D, Langevin C, Panteleit B, Li L (2006) Three-dimensional model for multi-component reactive transport with variable density groundwater flow. Environ Model Softw 21(5):615–628
Molinero J, Raposo J, Galindez J, Arcos D, Guimera J (2008) Coupled hydrogeological and reactive transport modelling of the Simpevarp area (Sweden). Appl Geochem 23(7):1957–1981
Olivella S, Gens A, Carrera J, Alonso J (1996) Numerical formulation for a simulator (CODE_BRIGHT) for the coupled analysis of saline media. Eng Comput 13(7):87–112
Parkhurst D (1995) User’s guide to PHREEQC—a computer program for speciation, reaction-path, advective-transport, and inverse geochemical calculations
Plummer L (1975) Mixing of sea water with calcium carbonate ground water. Memoir, 219
Post V, Prommer H (2007) Multicomponent reactive transport simulation of the Elder problem: effects of chemical reactions on salt plume development. Water Resour Res 43(10):W10404
Rezaei M, Sanz E, Raeisi E, Ayora C, Vázquez-Suñé E, Carrera J (2005) Reactive transport modeling of calcite dissolution in the fresh–salt water mixing zone. J Hydrol 311(1–4):282–298
Saaltink M, Ayora C, Carrera J (1998) A mathematical formulation for reactive transport that eliminates mineral concentrations. Water Resour Res 34(7):1649–1656
Saaltink M, Batlle F, Ayora C, Carrera J, Olivella S (2004a) RETRASO, a code for modeling reactive transport in saturated and unsaturated porous media. Geol Acta 2(3):235–251
Saaltink MW, Carrera J, Olivella S (2004b) Mass balance errors when solving the convective form of the transport equation in transient flow problems Water Resour Res 40:W05107
Sanford W, Konikow L (1989) Simulation of calcite dissolution and porosity changes in saltwater mixing zones in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Res 25(4):655–667
Smart PL, Dawans JM, Whitaker FF (1988) Carbonate dissolution in a modern mixing zone, South Andros, Bahamas. Nature 335:811–813
van der Lee J, Windt LD (2001) Present state and future directions of modeling of geochemistry in hydrogeological systems. J Contam Hydrol 47(2–4):265–282
Wolery T (1992) EQ3/6, a software package for geochemical modeling of aqueous systems: package overview and installation guide (Version 7.0). Technical report, UCRL-MA–110662-Pt. 1, Lawrence Livermore National Lab., CA (United States)
Yeh G, Tripathi V (1991) A model for simulating transport of reactive multispecies components: model development and demonstration. Water Resour Res 27(12):3075–3094
Zhang H, Schwartz F (1995) Multispecies contaminant plumes in variable density flow systems. Water Resour Res 31(4):837–847
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sáinz García, Á.M., Molinero Huguet, J.J. & Saaltink, M.W. Numerical modeling of coastal aquifer karst processes by means of coupled simulations of density-driven flow and reactive solute transport phenomena. Carbonates Evaporites 26, 19–27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-011-0051-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-011-0051-8