Abstract
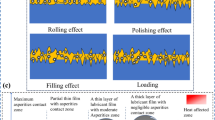
In general, the friction and wear property of lubricating grease has great influence on the usability of bearings. Copper oxide (CuO) was added in the base grease to prepare composite grease, followed by the investigation of anti-fraction properties to analyze the role of CuO and identify the optimum content. CuO nanoparticles were characterized first by series of techniques, including surface area and micropore analysis, particle size analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, atomic force microscope (AFM) scanning, infrared and Raman spectroscopic analysis. Composite greases were prepared by added CuO nanoparticles into the base grease, then examined via AFM and infrared spectrum. The friction and wear property of composite greases was investigated by friction test on a four-ball friction test machine. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and three-dimensional (3D) profilometer were utilized to observe the wear surface and helped to unravel the anti-friction mechanism. The formation of oil films on wear surface was identified and investigated by Raman spectrum and 3D morphology height, demonstrating the anti-friction effect. When CuO content was 0.60 wt%, only a small number of furrows were observed on the wear surface. The composite grease showed the lowest average friction coefficient and wear scar diameter, which were 30% and 13% lower than the base grease, respectively. According to 3D morphology scanning and Raman spectrum, CuO-contained oil films were detected on the wear surface. This lowered furrow number and the roughness of wear surface, demonstrating the great role of CuO in the enhanced anti-friction property of composite grease.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed AMK, Peng F, Hussein YA (2018) Fuel economy in gasoline engines using Al2O3/TiO2, nanomaterials as nanolubricant additives. Appl Energy 211:461–478
Alves SM, Mello VS, Faria EA, Camargo APP (2019) Nanolubricants developed from tiny CuO nanoparticles. Tribol Int 100:263–271
Asrul M, Zulkifli NWM, Masjuki HH, Kalam MA (2013) Anti-fraction properties and lubricant mechanism of nanoparticle in engine oil. Proc Eng 68:320–325
Borda FLG, de Oliveira SJR, Lazaro LMSM, Leiróz AJK (2018) Experimental investigation of the tribological behavior of lubricants with additive containing copper nanoparticles. Tribol Int 117:52–58
Diana B, Ali E, Anirudha SV (2018) Approaches for achieving superlubricity in two-dimensional materials. ACS Nano 12(3):2122–2137
He Q, Li A, Guo Y, Liu S, Zhang Y, Kong L (2018) Anti-fraction properties of nanometer cerium oxide as additives in lithium grease. J Rare Earths 36(2):209–214
Kedzierski MA (2015) Effect of concentration on R134a/Al 2 O 3 nanolubricant mixture boiling on a reentrant cavity surface. Int J Refrig 49:36–48
Li Z, Hou X, Yu L, Zhang Z, Zhang P (2014) Preparation of lanthanum trifluoride nanoparticles surface-capped by tributyl phosphate and evaluation of their anti-fraction properties as lubricant additive in liquid paraffin. Appl Surf Sci 292:971–977
Li S, Qin H, Zuo R, Bai Z (2015a) Tribological performance of Mg/Al/Ce layered double hydroxides nanoparticles and intercalated products as lubricant additives. Appl Surf Sci 353:643–650
Li S, Qin H, Zuo R, Bai Z (2015b) Friction properties of La-doped Mg/Al layered double hydroxide and intercalated product as lubricant additives. Tribol Int 91:60–66
Nagare P, Kudal H (2018) A Taguchi Approach on influence of graphite as an anti-wear additive on the performance of lithium grease. Proc Manuf 20:487–492
Padgurskas J, Rukuiza R, Prosyčevas I, Kreivaitis R (2013) Anti-fraction properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and Co nanoparticles. Tribol Int 60:224–232
Sanukrishna SS, Vishnu S, Krishnakumar TS, Jose Prakash M (2018) Effect of oxide nanoparticles on the thermal, rheological and tribological behaviours of refrigerant compressor oil: an experimental investigation. Int J Refrig 90:32–45
Tao C, Wang B, Barber GC, David Schall J, Lan H (2018) Tribological behaviour of SnO2 nanoparticles as an oil additive on brass. Lubr Sci 30(5):323–327
Torres H, Vuchkov T, Rodríguez Ripoll M, Prakash B (2018) Tribological behaviour of MoS2-based self-lubricating laser cladding for use in high temperature applications. Tribol Int 126:153–165
Uflyand IE, Zhinzhilo VA, Lapshina LS, Novikova AA, Burlakova VE, Dzhardimalieva GI (2018) Conjugated thermolysis of metal chelate monomers based on cobalt acrylate complexes with polypyridyl ligands and tribological performance of nanomaterials obtained. Chem Select 3(31):8998–9007
Vengudusamy B, Enekes C, Spallek R (2019) On the film forming and friction behaviour of greases in rolling/sliding contacts. Tribol Int 129:323–327
Zhang J, Li J, Wang A, Edwards BJ, Yin H, Li Z, Ding Y (2018) Improvement of the anti-fraction properties of a lithium-based grease by addition of graphene. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(10):7163–7169
Acknowledgements
This research project was supported by the development plan for academics in Huanshui, The Natural Science Foundation of the Henan Province (182300410169), and The Support project of scientific and technological innovation talents of universities in Henan Province (19HASTIT023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, B., Zhou, J., Jia, X. et al. Friction and wear property of lithium grease contained with copper oxide nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 10, 1355–1367 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01219-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01219-7