Abstract
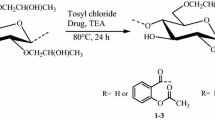
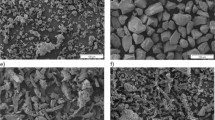
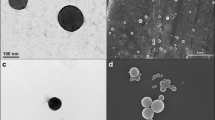
This article presents the synthesis of novel hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)-aspirin (ASP) conjugates, i.e. macromolecular prodrugs, through the reaction of HPMC with ASP after its in situ activation by 4-methylbenzenesulfonyl chloride. The highly pure ASP prodrugs obtained by this homogeneous and elegant esterification method were characterized using different spectroscopic and chromatographic techniques. Nanoparticulate drug design was successfully achieved by the conversion of free hydroxyls of the polymer into acetates. Transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy showed nanoparticle formation with the major population size distribution of around 450 nm. Nevertheless, the pharmacokinetics of the HPMC conjugates were studied using high performance liquid chromatography. The pharmacokinetic data indicated that a single dose of 132.6 mg of HPMC-ASP was well tolerated in animal studies without any adverse effects. The maximum plasma concentration (C
max
) of HPMC-ASP was found to be 14.6 μg·L−1 with a t
max
of 1 h. The plasma half-life and clearance and the volume of HPMC-ASP distribution were 4.6 h, 3.23 L·h−1, and 21.8 L·kg−1, respectively. The elimination of HPMC-ASP followed first-order kinetics with r
2 of 0.9643. The results presented in this paper show the great potential of HPMCASP as a more effective, safe, and stable prodrug.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Testa, Biochem. Pharmacol., 68, 2097 (2004).
J. F. Gilmer, A. L. Simplício, and J. M. Clancy, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 24, 315 (2005).
A. Jain, Y. Gupta, and S. K. Jain, J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 10, 86 (2007).
M. A. Hussain, M. Badshah, M. S. Iqbal, M. N. Tahir, W. Tremel, S. V. Bhosale, M. Sher, and M. T. Haseeb, J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem., 47, 4202 (2009).
S. S. Dhaneshwar, M. Kandpal, N. Gairola, and S. S. Kadam, Ind. J. Pharm. Sci., 68, 705 (2006).
B. Sandrime, H. Richard, and F. Elias, Am. J. Drug Deliv., 3, 171 (2005).
Y. Takakura, Yakugaku Zasshi, 116, 519 (1996).
M. H. N. Tabrizi, S. Davaran, and A. A. Entezami, Iran. Polym. J., 5, 243 (1996).
C. Parejo, A. Gallardo, and J. S. Roman, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 9, 803 (1998).
M. Babazadeh, Int. J. Pharm., 316, 68 (2006).
L. Ochoa, M. Igartua, M. Rosa, R. M. Hernandez, A. R. Gascon, and J. L. Pedraz, J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 8, 132 (2005).
K. R. Reddy, S. Mutalik, and S. Reddy, AAPS PharmSciTech, 4, 1 (2003).
M. S. El-Samaligy, S. A. El-Shakhs, S. Mansour, and N. A. Sabry, Egypt. J. Pharm. Sci., 44, 73 (2003).
M. H. Amaral, J. M. S. Lobo, and D. C. Ferreira, AAPS Pharm-SciTech, 2, 14 (2001).
H. Ichikawa, H. Onishi, T. Takahata, Y. Machi-da, and T. Nagai, Drug Des. Discov., 10, 343 (1993).
B.-J. Lee, S.-G. Ryu, and J.-H. Cui, Int. J. Pharm., 88, 71 (1999).
Y. Shimizu and J. Hayashi, Sen-I Gakkaishi, 44, 451(1988).
W. G. Glasser, U. Becker, and J. G. Todd, Carbohydr. Polym., 42, 393 (2000).
M. A. Hussain, J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem., 46, 747 (2008).
V. P. Shah, K. K. Midha, J. W. A. Findlay, H. M. Hill, J. D. Hulse, I. J. McGilveray, G. McKay, K. J. Miller, R. N. Patnaik, M. L. Powell, A. Tonelli, C. T. Viswanathan, and A. Yacobi, Pharm. Res., 17, 1551 (2000).
C. B. Elliot, R. L. Lesley, B. Felix, and M. I. Debra, Ther. Drug Monit., 2, 365 (1980).
M. S. Iqbal, M. Sher, H. Pervez, and M. Saeed, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 124, 283 (2008).
G. Levy, Pediatrics, 62, 867 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, M.A., Abbas, K., Sher, M. et al. Macromolecular prodrugs of aspirin with HPMC: A nano particulate drug design, characterization, and pharmacokinetic studies. Macromol. Res. 19, 1296–1302 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-011-1212-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-011-1212-2