Abstract
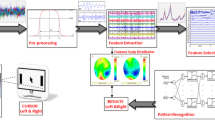
Brain computer interface (BCI) is a new communication way between man and machine. It identifies mental task patterns stored in electroencephalogram (EEG). So, it extracts brain electrical activities recorded by EEG and transforms them machine control commands. The main goal of BCI is to make available assistive environmental devices for paralyzed people such as computers and makes their life easier. This study deals with feature extraction and mental task pattern recognition on 2-D cursor control from EEG as offline analysis approach. The hemispherical power density changes are computed and compared on alpha–beta frequency bands with only mental imagination of cursor movements. First of all, power spectral density (PSD) features of EEG signals are extracted and high dimensional data reduced by principle component analysis (PCA) and independent component analysis (ICA) which are statistical algorithms. In the last stage, all features are classified with two types of support vector machine (SVM) which are linear and least squares (LS-SVM) and three different artificial neural network (ANN) structures which are learning vector quantization (LVQ), multilayer neural network (MLNN) and probabilistic neural network (PNN) and mental task patterns are successfully identified via k-fold cross validation technique.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFarland DJ, Lefkowicz AT, Wolpaw JR (1997) Design and operation of an EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI) with digital signal processing technology. Behav Res Meth Inst Comp 29:337–345
Kostov A, Polak M (2000) Parallel man-machine training in development of EEG-based cursor control. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 8(2):203–205
Fabiani GE, McFarland DJ, Wolpaw JR, Pfurtscheller G (2004) Conversion of EEG activity into cursor movement by a brain-computer interface (BCI). IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 12(3):331–338
Wolpaw JR, McFarland DJ (2004) Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(51):17849–17854
Kayagil T, Bai O, Lin P, Furlani S, Vorbach S, Hallett M (2007) Binary EEG control for two-dimensional cursor movement: an online approach. Int Conf Complex Med Eng. doi:10.1109/ICCME.2007.4382005
Wilson JA, Schalk G, Walton LM, Williams JC (2009) Using an EEG-based brain-computer interface for virtual cursor movement with BCI2000. J Vis Exp 29:1319
Li Y, Long J, Yu T, Yu Z, Wang C, Zhang H, Guan C (2010) An EEG-based BCI system for 2-D cursor control by combining Mu/Beta rhythm and P300 potential. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(10):2495–2505
Boudria Y, Feltane A, Besio W (2014) Significant improvement in one-dimensional cursor control using Laplacian electroencephalography over electroencephalography. J Neural Eng 11(3):035014
Rambabu C, Murthy BR (2014) EEG signal with feature extraction using SVM and ICA classifiers. Int J Comp App 85(3):1–7
Singla R, Chambayil B, Khosla A, Santosh J (2011) Comparison of SVM and ANN for classification of eye events in EEG. J Biom Sci Eng 4:62–69
Bascil MS, Tesneli AY, Temurtas F (2015) Multi-channel EEG signal feature extraction and pattern recognition on horizontal mental imagination task of 1-D cursor movement for brain computer interface. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 38(2):229–239
Jasper H (1958) The ten twenty electrode system of the international federation. Electro Clin Neuro 10(2):370–375
Bhardwaj S, Jadhav P, Adapa B, Acharyya A, Naik GR (2015) Online and automated reliable system design to remove blink and muscle artefact in EEG. In 37th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. pp 6784–6787
Acar E (2011) Classification of motor imagery tasks in EEG signal and its application to a brain–computer interface for controlling assistive environmental devices. The Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Middle East Technical University, Ankara
Proakis JG, Manolakis DG (1996) Digital signal processing-principles, algorithms and applications, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, New York [chapter 12]
Stoica P, Moses R (2005) Spectral analysis of signals. Prentice-Hall International, New York
Pearson K (1901) On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Phil Mag 2(6):559–572
Cao LJ, Chua KS, Chong WK, Lee HP, Gu OM (2003) A comparison of PCA, KPCA and ICA for dimensionality reduction in support vector machine. Neurocomputing 55(1):321–336
Semmlow JL (2014) Biosignal and biomedical image processing MATLAB-based applications, 1st edn. Marcel Dekker, New York [chapter 9]
Naik GR, Kumar DK (2011) An overview of independent component analysis and its applications. Informatica 35(1):63–81
Mozaffar S, Petr D (2002) Artifact extraction from EEG data using independent component analysis. Information Telecommunication and Technology Center, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, Technical Report ITTC-FY2003-TR-03050-02
Chai R, Naik GR, Nugyen TN, Ling SH, Tran Y, Craig A, Nuguyen HT (2015) Driver fatigue classification with independent component by entropy rate bound minimization analysis in an EEG-based system. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, pp (99):1–1
Christian J, Jeanny H (1991) Blind separation of sources, part I: an adaptive algorithm based on neuromimetic architecture. Sig Process 24(1):1–10
Al-Ani A, Naik GR, Abbass HA (2015) A methodology for synthesizing interdependent multichannel EEG data with a comparison among three blind source separation techniques. International conference on neural information processing. Springer, Berlin, pp 154–161
Müller KR, Krauledat M, Dornhege G, Curio G, Blankertz B (2004) Machine learning techniques for brain-computer interfaces. Bio. Tech. 49:11–12
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Gunn SR (1998) Support vector machines for classification and regression. University of Southampton, Technical Report
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Burges CJC (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc 2(2):121–167
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (2001) Optimal control by least squares support vector machines. Neural Netw 14(1):23–35
Gestel TV, Suykens JAK, Baesens B, Viaene S, Vanthienen J, Dedene G, De Moor B, Vandewalle J (2004) Benchmarking least squares support vector machine classifiers. Mach Learn 54:5–32
Kohonen T. (1990) Improved versions of learning vector quantization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international joint conference on neural networks, New York, pp 545–550
Temurtas F (2009) A comparative study on thyroid disease diagnosis using neural networks. Exp Sys App 36:944–949
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning internal representations by error propagation. In: Rumelhart DE, McClelland J (eds) Parallel distributed processing. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 318–362
Hagan MT, Menhaj M (1994) Training feed forward networks with the Marquardt algorithm, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw 5:989–993
Bascil MS, Temurtas F (2011) A study on hepatitis disease diagnosis using multilayer neural network with Levenberg Marquardt training algorithm. J Med Sys 35(3):433–436
Specht DF (1990) Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Netw 3:109–118
Hazrati MKh, Erfanian A (2010) An online EEG based brain–computer interface for controlling hand grasp using an adaptive probabilistic neural network. Med Eng Phy 32(7):730–739
Bascil MS, Oztekin H (2012) A study on hepatitis disease diagnosis using probabilistic neural network. J Med Sys 36(3):1603–1606
Nasehi S, Pourghassem H (2012) An optimal EEG-based emotion recognition algorithm using Gabor features. WSEAS Trans Sign Proc 3(8):87–99
Chai R, Ling SHO, Hunter GP, Tran Y, Nguyen HT (2014) Brain–computer interface classifier for wheelchair commands using neural network with fuzzy particle swarm optimization. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 18(5):1614–1624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bascil, M.S., Tesneli, A.Y. & Temurtas, F. Spectral feature extraction of EEG signals and pattern recognition during mental tasks of 2-D cursor movements for BCI using SVM and ANN. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 39, 665–676 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0462-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-016-0462-x