Abstract
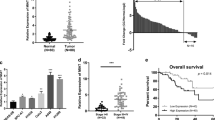
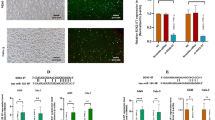
Lung carcinoma is the most common human cancer with poor prognosis and has an increasing incidence in recent years. However, the related mechanism of lung cancer onset has not been completely explored. Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) is a type of noncoding small RNA with established function in germ cells, and interestingly, piRNA has also been shown to be implicated in cancer biology. In this study, piR-55490 was found to be silenced in lung carcinoma specimens and cell lines, compared with normal lung tissues and cells. Intriguingly, the expression level of piR-55490 is negatively associated with patients’ survival. Restoration of piR-55490 can reduce the proliferation rates of lung cancer cells, while piR-55490 suppression led to the gain in the proliferation rates. Animal model study showed that piR-55490 can suppress the growth of lung carcinoma xenograft. Further study revealed that piR-55490 suppressed the activation of Akt/mTOR pathway in lung cancer cells. Surprisingly, piR-55490 was found to bind 3′UTR of mTOR messenger RNA (mRNA) and induce its degradation in a mechanism similar to microRNA (miRNA). The introduction of an mTOR construct resistant to action of piR-55490 was able to abolish the effect of piR-55490 on lung cancer cells. In conclusions, we found that piRNA can contribute to the suppression of cancer cell phenotypes by directly targeting a oncogene mRNA. This finding facilitates our understanding of piRNA’s function and its association with human cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith RA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Brooks D, Doroshenk M, Fedewa S, Saslow D, et al. Cancer screening in the United States, 2015: a review of current American cancer society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):30–54. doi:10.3322/caac.21261.
Hale BJ, Yang CX, Ross JW. Small RNA regulation of reproductive function. Mol Reprod Dev. 2014;81(2):148–59. doi:10.1002/mrd.22272.
Cheng J, Guo JM, Xiao BX, Miao Y, Jiang Z, Zhou H, et al. piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2011;412(17–18):1621–5. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2011.05.015.
Cui L, Lou Y, Zhang X, Zhou H, Deng H, Song H, et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using piRNAs as markers. Clin Biochem. 2011;44(13):1050–7. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.06.004.
Cheng J, Deng H, Xiao B, Zhou H, Zhou F, Shen Z, et al. piR-823, a novel non-coding small RNA, demonstrates in vitro and in vivo tumor suppressive activity in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012;315(1):12–7. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.004.
Yan H, Wu QL, Sun CY, Ai LS, Deng J, Zhang L, et al. piRNA-823 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2015;29(1):196–206. doi:10.1038/leu.2014.135.
Huang G, Hu H, Xue X, Shen S, Gao E, Guo G, et al. Altered expression of piRNAs and their relation with clinicopathologic features of breast cancer. Clin Transl Oncol Off Publ Fed Spanish Oncol Soc Nat Cancer Inst Mexico. 2013;15(7):563–8. doi:10.1007/s12094-012-0966-0.
Law PT, Qin H, Ching AK, Lai KP, Co NN, He M, et al. Deep sequencing of small RNA transcriptome reveals novel non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013;58(6):1165–73. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.032.
Zhang H, Ren Y, Xu H, Pang D, Duan C, Liu C. The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 2013;22(4):217–23. doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2013.07.001.
Chu H, Hui G, Yuan L, Shi D, Wang Y, Du M, et al. Identification of novel piRNAs in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;356(2 Pt B):561–7. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.004.
Li Y, Wu X, Gao H, Jin JM, Li AX, Kim YS, et al. PIWI-interacting RNAs are dysregulated in renal cell carcinoma and associated with tumor metastasis and cancer specific survival. Mol Med. 2015. doi:10.2119/molmed.2014.00203.
Siddiqi S, Matushansky I. Piwis and piwi-interacting RNAs in the epigenetics of cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(2):373–80. doi:10.1002/jcb.23363.
Shan J, Shen J, Liu L, Xia F, Xu C, Duan G, et al. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56(3):1004–14. doi:10.1002/hep.25745.
Yip PY. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-Akt-mTOR) signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4(2):165–76. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.01.04.
Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122(1):6–7. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Song, L., Liu, C. et al. piR-55490 inhibits the growth of lung carcinoma by suppressing mTOR signaling. Tumor Biol. 37, 2749–2756 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4056-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4056-0