Abstract
Fundus albipunctatus (FA) is a rare, congenital form of night blindness with rod system impairment, characterised by the presence of numerous small, white-yellow retinal lesions. FA belongs to a heterogenous group of so-called flecked retina syndromes. This disorder shows autosomal recessive inheritance and is caused mostly by mutations in the RDH5 gene. This gene encodes the enzyme that is a part of the visual cycle, the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase. This study is a brief review of the literature on FA and a report of the first molecular evidence for RDH5 gene mutation in a Polish patient with this rare disorder. We present a novel pathogenic RDH5 gene mutation in a 16-year-old female patient with symptoms of night blindness. The patient underwent ophthalmological examinations, including colour vision testing, fundus photography, automated visual field testing, full-field electroretinography (ERG) and spectral optical coherent tomography (SOCT). The patient showed typical FA ERG records, the visual field was constricted and fundus examination revealed numerous characteristic, small, white-yellowish retinal lesions. DNA sequencing of the RDH5 gene coding sequence (exons 2–5) enabled the detection of the homozygous missense substitution c.524A > T (p.Tyr175Phe) in exon 3. This is the first report of RDH5 gene mutation that affects the invariant tyrosine, one of the most conserved amino acid residues in short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases/reductases (SDRs), crucial for these enzymes’ activity. The location of this substitution, together with its predicted influence on the protein function, indicate that the p.Tyr175Phe mutation is the cause of FA in our patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Clinical characterisation of fundus albipunctatus
Fundus albipunctatus (FA; MIM 136880) is a rare, hereditary, in most cases stationary, retinal disease, which is characterised by impaired night vision and numerous small, white-yellowish retinal lesions placed throughout the retina, except the fovea (Sergouniotis et al. 2011). FA belongs to a heterogenous group of genetically determined flecked retina syndromes. The symptoms of these disorders include conditions characterised by multiple retinal yellowish-white lesions of various sizes and configuration, without vascular or optic nerve abnormalities. The group of flecked retina syndromes encompasses FA, retinitis punctata albescens, fundus flavimaculatus (Stargardt disease), familial drusen and fleck retina of Kandori, but far more diseases correspond to the rather vague definition of fleck retina syndromes (De Laey 1993; Walia et al. 2009). Moreover, there is a collection of diseases called white dots syndromes that can also be misdiagnosed with flecked retina syndromes. White dots syndromes are characterised by white lesions in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) or choroidal layers. The aetiology of these disorders is unknown, but these syndromes are suspected to be inflammatory in nature and can be associated with uveitis (Matsumoto et al. 2007).
FA is a form of congenital stationary night blindness. The symptoms of defective dark adaptation may not be perceptible to the affected person. The optic nerve heads and the retinal vessels show no signs of irregularity. The visual field and visual acuity examinations of patients suffering from FA do not detect any abnormalities unless a dim stimulus is used. Dim stimulus causes a worsening of visual acuity and a constriction of the visual field. The scotopic electroretinography (ERG) responses are reduced after a 30–40-min period of dark adaptation, but typically normalise after prolonged dark adaptation (Yamamoto et al. 1999; Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Wang et al. 2012). The photopic responses are usually normal if FA is not accompanied by macular dystrophy. Although long-term follow-up usually shows no progression in rods dysfunction in patients with this form of night blindness, some patients, especially the elderly, reveal progressive cone dystrophy (Nakamura et al. 2000, 2003; Wada et al. 2001; Niwa et al. 2005). Full-field photopic electroretinograms of these individuals are usually severely reduced, a bull’s eye maculopathy is often identified, and visual fields and acuity are impaired (Nakamura et al. 2000 2003). Recently, it has been estimated that cone dysfunction can affect more than 30 % of patients with FA (Niwa et al. 2005; Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Pras et al. 2012). Lidén and coworkers suggested that cone dystrophy may be either the result of impaired function of the RPE caused by a RDH5 gene mutation or a direct consequence of a decreased supply of 11-cis retinal to the cones (Lidén et al. 2001).
Genetic background
FA shows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. In one family with this retinal disease, autosomal dominant or pseudodominant inheritance was suggested (Kranias et al. 1981). FA is caused almost exclusively by mutations in the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase 5 (RDH5) gene (Yamamoto et al. 1999). However, mutations in two other genes, retinaldehyde binding protein 1 (RLBP1) and RPE-specific protein (RPE65), are also known to be associated with FA (Naz et al. 2011; Schatz et al. 2011). Retinaldehyde binding protein 1 is expressed in the RPE and Müller cells of the neuroretina, where it carries 11-cis retinol and 11-cis retinaldehyde as ligands (Sparkes et al. 1992). Only a few RLBP1 gene mutations in patients with FA have been reported to date (Katsanis et al. 2001; Naz et al. 2011). Katsanis end coworkers (2001) found a p.Arg150Gln mutation in the RLBP1 gene in a consanguineous Saudi Arabian kindred with a retinal dystrophy phenotype that fulfilled the criteria of FA in younger individuals and retinitis punctata albescens in older patients. Two homozygous RLBP1 gene mutations (p.Arg156* and p.Gly116Arg) have also been identified in two unrelated, consanguineous Pakistani families suffering from FA (Naz et al. 2011). RPE-specific protein (RPE65) is the isomerase of the visual cycle, catalysing the conversion of all-trans retinyl ester to 11-cis retinol (Moiseyev et al. 2005). To date, mutations in the RPE65 gene associated with FA have only been reported in one paper. A compound heterozygote of IVS + 5G > A and c.344 T > C mutations in the RPE65 gene was found in a patient with FA (Schatz et al. 2011).
Most cases of FA are caused by mutations in the RDH5 gene (Gonzalez-Fernandez et al. 1999). The RDH5 gene encodes the enzyme that is a part of the visual cycle, the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase (Simon et al. 1995). The retinoid (visual) cycle is an enzyme pathway that occurs to regenerate the visual chromophore following light exposure (Travis et al. 2007). 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase (RDH5) is predominantly expressed in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the RPE of the eye (Simon et al. 1996). RPE cells play multiple roles essential for visual function, such as involvement in the uptake and metabolic processing of retinoids in the visual cycle (Simon et al. 1999). RDH5 has an important role in the molecular background of vision, as it catalyses the final step in the biosynthesis of 11-cis retinaldehyde, the universal chromophore of visual pigments (Simon et al. 1995). Absorption of a photon by an opsin pigment causes isomerisation of the chromophore from 11-cis retinaldehyde to all-trans retinaldehyde. After entering the RPE cell, all-trans retinol is transferred into all-trans retinyl esters, which are isomerised by RPE65 (RPE-specific) protein into 11-cis retinol esters (11-cis retinol). Then, 11-cis retinol is transported through the subretinal space, where it is oxidated by the RDH5 enzyme into 11-cis retinal (Simon et al. 1995; Wang et al. 2012).
Retinol dehydrogenase 5 protein consists of 318 amino acids and is a member of the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) superfamily (Simon et al. 1996). This family encompasses at least 57 varied, well-characterised enzymes (Jörnvall et al. 1995), which catalyse the metabolism of steroids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, amino acids and aromatic compounds (Marchler-Bauer et al. 2015). Although the amino acids sequence identity between the members of this large protein family is only at the 15–30 % level, there are two well-conserved regions within the enzymes’ sequences: the motif Gly-X-X-X-Gly-X-Gly, consisting of three glycines within a cofactor binding site for NAD(H) or NADP(H), and the amino acid motif Tyr-X-X-X-Lys, with an invariant tyrosine residue inside the active site. Like all the classical SDR enzymes, the RDH5 amino acid sequence contains these two conserved domains: the motif Gly-Cys-Asp-Ser-Gly-Phe-Gly at the amino acid residues 35–41 and the sequence encompassing the invariant tyrosine Tyr-Cys-Val-Ser-Lys at the residues 175–179 (Persson et al. 1991; Jörnvall et al. 1995; Simon et al. 1999). Retinol dehydrogenase 5 protein is highly conserved among species (Simon et al. 1996). The amino acid conservation of part of the active site (encompassing three conserved residues: Ser-163, Tyr-175, Lys-179) among RDH5 of several species and three other short-chain dehydrogenases is shown in Fig. 1. RDH5 is an integral membrane protein (Simon et al. 1995). It is composed of the N-terminus (18 amino acids) located within the membrane, the ectodomain encompassing the active site, which is present in the lumen of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) (residues 19–288), the C-terminal membrane-spanning domain (289–310 amino acids) and the C-terminal tail (311–318 amino acids) located in the cytosol of the RPE (Simon et al. 1999; Ajmal et al. 2012). The different localisation of the RDH5 domains within the RPE cell suggests that biosynthesis of 11-cis retinaldehyde is a compartmentalised process (Simon et al. 1999).
The amino acid conservation of part of the active site (residues 157–196 according to the numbering system of the RDH5 protein) among RDH5 of several species and three other short-chain dehydrogenases. The red frame indicates the invariant tyrosine, while the black frame indicates two other highly conserved residues involved in the catalytic mechanism: serine-163 and lysine-179. The abbreviation ‘DH’ in the names of three aligned proteins’ sequences stands for ‘dehydrogenase’
The RDH5 gene is mapped on the chromosome 12q13-q14. The transcript (ENST00000257895) spans 1,269 bp and contains five exons, including four coding exons (2–5). The lengths of the coding exons are as follows: exon 2–342 bp (32 bp of the 5′ untranslated region and 310 bp translated sequence), exon 3–259, exon 4–164 and exon 5–384 bp (the translated part is 221 bp) (Simon et al. 1996).
Materials and methods
This study was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. A 16-year-old female patient of Polish origin with clinical signs of night blindness was examined. The patient underwent colour vision testing, fundus photography, automated visual field testing (Humphrey–Zeiss), full-field ERG and spectral optical coherent tomography (SOCT). The electrophysiological examinations included a full-field ERG protocol with the standard scotopic 20 min dark adaptation and extended protocol with prolonged 120 min of dark adaptation. The standard photopic ERG (30 Hz white flicker stimulation) was performed after 10 min of light adaptation.
Voluntary informed consent for genetic examination was obtained not only from the mother of the patient (as the patient was underaged), but also from both parents and two sisters, who had their blood taken for segregation analysis for the presence of the novel mutation. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using the conventional salting-out procedure. The coding regions of the RDH5 gene (exons 2–5) were amplified and sequenced to screen for disease-causing mutations in the patient. Eight primer pairs (including three pairs for amplifying exon 2, two for exons 3 and 5, and one pair for exon 4) were used following a previous report (Yamamoto et al. 1999). A fragment of exon 3 (primer pair designed 3b) was also amplified in both parents and two sisters of the proband. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were purified with the use of ExoSAP-IT (Exonuclease I and Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase Cleanup for PCR products, Affymetrix) and directly sequenced using Dye Terminator chemistry (v3.1 BigDye® Terminator, Life Technologies). The sequencing products were separated on an ABI 3130xl capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems). The obtained sequences were verified by comparing them to the reference sequence of the RDH5 gene (GenBank NM_001199771.1) and screened for mutations. The in silico analysis using PROVEAN (Choi et al. 2012), SIFT (Kumar et al. 2009) and PolyPhen-2 (Adzhubei et al. 2010) software was performed to assess the possible functional effect of the novel missense mutation.
Results
Family history
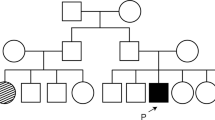
The patient has three sisters. The younger sister suffers from astigmatism, while the mother and the two older sisters had no ophthalmologic problems. In both the proband’s father’s eyes, presenile cataract was revealed at the age of 38 years. He suffered from retinal detachment in the right eye later on. The first pregnancy of the patient’s mother ended with a stillbirth (pedigree, Fig. 2).
Clinical status
Visual acuity and colour vision in the patient were normal. The examination of the anterior segment and the pupillary reflexes showed no abnormalities. An eye fundus examination revealed numerous small white-yellowish retinal lesions mainly in the upper quadrants of the retina (Fig. 3). Examination of the visual field revealed its peripheral constriction to approximately 10–20°. A full-field electroretinogram showed significantly reduced scotopic responses after the standard period of 20–30 min dark adaptation (Fig. 4a). However, after a prolonged 120 min of dark adaptation, rod responses normalised (Fig. 4b). Photopic responses in all examinations were normal. The high-definition SOCT showed no abnormalities of the central macular thickness in either eye, but local modulations of the RPE and IS/OS (inner segment–outer segment) junctions corresponding with retinal flecks were identified.
Comparison of scotopic responses after 30 and 120 min of dark adaptation: RE, right eye; LE, left eye. a The reduction of scotopic responses (DA 0.009 cdxs/m2) (b-wave amplitude RE: 26.68 μV, LE: 26.53 μV, normal 260 ± 151.4 μV), standard electroretinography (ERG) response (3 cdxs/m2) on the borderline after 30 min of dark adaptation. b The normalisation of scotopic responses after 120 min of scotopic adaptation (b-wave amplitude RE: 259.1 μV, LE: 378.2 μV)
Genetic analysis
As the clinical findings, especially characteristic eye fundus appearance, indicated a suspicion of FA, searching for a mutation in the RDH5 gene seemed to be the most appropriate strategy. Bidirectional sequencing of the RDH5 gene coding region (exons 2–5) revealed a homozygous mutation c.524A > T in exon 3. This transversion changes codon UAC to UUC, which results in the substitution of polar tyrosine to non-polar phenylalanine at amino acid position 175 (p.Tyr175Phe) (Fig. 5). The in silico analysis of the predicted influence of the p.Tyr175Phe substitution on protein function with the use of PROVEAN software (the tolerance index score was −3.900), as well as SIFT software (tolerance index score 0.00), revealed that this amino acid change is deleterious. The in silico analysis using PolyPhen-2 software predicted the mutation to be probably damaging (score of 1). The c.524A > T variant was not found in a control cohort annotated in the Exome Variant Server (EVS) database (Exome Variant Server 2015) nor in the 1000 Genomes Project database (1000 Genomes Project Consortium 2012). The segregation analysis of the mutation in the proband’s family revealed that both parents and one of the proband’s sisters are heterozygous carriers of the c.524A > T substitution (pedigree, Fig. 2).
A chromatogram showing the c.524A > T mutation in the RDH5 gene. a The wild-type nucleotide sequence and the wild-type protein sequence. The orange frame indicates the most conservative element between short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases, located within the active site of the enzyme. Invariant tyrosine is labelled blue and indicated with the red frame. b The nucleotide sequence of the heterozygous parent. c The sequence of the patient with c.524A > T mutation and truncated protein sequence
Mutations in the RDH5 gene: review of the literature
Since 1999, when Yamamoto et al. described the mutations in the RDH5 gene in two unrelated patients suffering from FA (Yamamoto et al. 1999), there have been reports of missense, in-frame and frameshift mutations (Sergouniotis et al. 2011). To date, more than 40 mutations in the RDH5 gene have been reported, and most of them are missense variants (Nakamura et al. 2000; Driessen et al. 2001; Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Ajmal et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2012; Waldron and Medefindt 2014; Stenson et al. 2014). The list of RDH5 gene mutations identified in patients with FA together with the regions of the protein affected by these changes is shown in Table 1. The RDH5 gene mutations have been identified mostly in homozygotic or compound heterozygotic forms, but a few variants (p.Arg19Gly, p.Arg191Gln and p.Arg278Gln) have been found as single heterozygous mutations (Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Pras et al. 2012). There seems to be no hot spot in the gene, as the reported mutations are distributed across the entire RDH5 coding sequence. The mutations identified affect the entire protein, except the N-terminus, with most mutations located in the longest domain: lumenal ectodomain (see Table 1). The analyses of biochemical defects in RDH5 mutants associated with FA revealed that all the mutations tested (marked with ‘+’ in Table 1) affect the stability and expression level of the protein and result in subcellular mislocalisation. Moreover, loss of enzymatic activity in vitro and in vivo has been observed for almost all the constructed mutants (except the mutant with amino acid change p.Ala294Pro located in the C-terminal domain) (Yamamoto et al. 1999; Cideciyan et al. 2000; Lidén et al. 2001). Even in the absence of the enzyme activity caused by many RDH5 mutations, night vision regenerates after prolonged dark adaptation in patients with FA. This fact can be explained by the results of the studies on Rdh knockout mice models (Driessen et al. 2000; Kim et al. 2005). Driessen and coworkers revealed that transgenic mice missing the RDH5 gene display delayed dark adaptation, but only at a very high bleach level. The studies on Rdh5 and Rdh11 knockout mice revealed that one more enzyme, RDH11, appeared to have an important role in regenerating the chromophore. These results indicate that both RDH5 and RDH11 contribute to 11-cis retinal production (Driessen et al. 2000).
High variability of the disease’s phenotype is observed among patients with FA carrying RDH5 mutations. They show a variable visual acuity and variation in the density of white flecks (from minimal white dots or even normal fundus to numerous larger coalescent spots) (Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Ajmal et al. 2012). Despite the observed phenotypic variability, the presence of white dots appeared to be a common feature in patients with FA. These retinal flecks are hypothesised to be the effect of an accumulation of toxic retinyl esters in the RPE as the result of 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase disruption (Driessen et al. 2000). However, it is known that, with increasing age in the patients with FA or after uveitis, the dots may fade and become smaller and discrete, especially in the far periphery of the fundus (Yamamoto et al. 2003; Imaizumi et al. 2005; Sergouniotis et al. 2011). Patients with mutations in the RDH5 gene can manifest a non-progressive or progressive form of the disease. It has been reported that individuals with or without cone dystrophy also presented varying degrees of severity of FA (Nakamura et al. 2000, 2003; Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Ajmal et al. 2012). Moreover, different phenotypes have been observed in patients with the same mutation, for example, c.928delCinsGAAG (p.Leu310GluVal), which is the most commonly identified RDH5 gene mutation (Nakamura et al. 2000, 2003; Nakamura and Miyake 2002; Sato et al. 2004; Pras et al. 2012; Ajmal et al. 2012).
Therefore, based on the complete review of the literature, it is difficult to establish any valid correlation between the RDH5 variants and the disease. There is no significant association between the localisation or the type of RDH5 mutation with the severity of the disease phenotype (including electrophysiological observations or the presence/absence of cone dystrophy) (Sato et al. 2004; Niwa et al. 2005; Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Pras et al. 2012).
Discussion
The differential diagnosis of flecked retina/white dots syndromes can be difficult using routine ophthalmological examination. In cases of FA with progressive cone dystrophy, signs and symptoms may be non-specific and lead to misdiagnosis. Small white-yellow retinal lesions could indicate the diagnosis of fundus flavimaculatus, familial dominant drusen or retinitis punctata albescens (De Laey 1993; Walia et al. 2009). Moreover, phenotypic variability in the fundus appearance of patients with FA has been described (Sergouniotis et al. 2011; Ajmal et al. 2012). Electrophysiological findings, together with the appropriate genetic analysis, appear to be crucial tools in the differential diagnosis of FA (Pras et al. 2012). Although decreased scotopic ERG responses could appear in many different conditions (retinitis punctata albescens, FA, FA with progressive cone dystrophy and Stargardt disease), their normalisation after 120 min of dark adaptation is observed mostly in FA (Table 2) (Yamamoto et al. 1999; Kanski 2003). However, retinitis punctata albescens due to RLBP1 mutation (Bothnia dystrophy) may be more difficult to distinguish, as in the early stages, there is phenotypic overlap with FA. Some patients with Bothnia dystrophy show a dramatic improvement in electroretinograms after prolonged dark adaptation (Burstedt et al. 2008; Gränse et al. 2001), while some patients with FA may present a minimal change, even after several hours of dark adaptation (Sergouniotis et al. 2011).
Optimistically, recent studies provide hope for the successful treatment of patients diagnosed with FA. Studies on mouse models of FA demonstrated a significant improvement in rod and cone visual function after treatment with 9-cis retinal (Maeda et al. 2006). Moreover, the latest pilot clinical testing on a group of patients with FA revealed that treatment with 9-cis-β-carotene as a food supplement led to a considerable visual improvement. It is very promising, as there has been no reported treatment resulting in a significant improvement in the visual functions in patients with retinal dystrophy to date and, what is more, this approach will also be helpful for some patients with retinitis pigmentosa (Rotenstreich et al. 2010, 2013).
Genetic analysis of the RDH5 gene (exons 2–5) in our patient revealed a novel, homozygous mutation c.524A > T in exon 3. The change of the chemical properties of the substituted amino acids and the mutation’s predicted influence on the protein function indicate that the p.Tyr175Phe mutation is probably pathogenic. Moreover, tyrosine at position 175 of the RDH5 protein is localised within the active site of the enzyme, and was described as invariant tyrosine (Simon et al. 1996). It is known that invariant tyrosines are found in all short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases. The Tyr-X-X-X-Lys sequence motif, a part of the substrate binding (active) site, is the most conserved element in SDRs (Persson et al. 1991; Jörnvall et al. 1995). To date, only one mutation in this highly conserved motif of the human RDH5 enzyme (Tyr-Cys-Val-Ser-Lys) has been identified. It was a substitution of valine to glycine at amino acid position 177. This variant was found in a boy with FA, who was a compound heterozygote of p.Val177Gly and p.Arg280His (Kuroiwa et al. 2000), but also in a boy diagnosed with familial fleck retina with night blindness (a heterozygote of p.Val177Gly and p.Leu310GluVal) (Hayashi et al. 2006).
The invariant tyrosine, together with the lysine at position 179 (of the human RDH5) within the conserved motif and serine-163 (shown in Fig. 1), are involved in the catalytic mechanism (as putative active site residues), but only tyrosine located within this sequence is rigidly conserved in the SDR superfamily (Jörnvall et al. 1995; Filling et al. 2001; Oppermann et al. 2003). The role of the invariant tyrosine was analysed in the most studied member of the SDR superfamily: Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). Albalat and González-Duarte (1992) constructed a Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase, in which the invariant tyrosine (at amino acid position 152) was substituted by phenylalanine. Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase-phenylalanine-152 revealed no enzymatic activity. Therefore, it is very likely that substitution of the invariant tyrosine to phenylalanine in human retinol dehydrogenase (RDH5) protein would have a similarly damaging effect to that reported in Drosophila ADH.
The segregation analysis of the presence of the c.524A > T mutation in the family studied was found to be consistent with the autosomal recessive mode of inheritance. It revealed that both the proband’s parents are heterozygous carriers of this novel substitution. Therefore, it is highly probable that they are related. We did not confirm this assumption based on the exact pedigree data, but the parents’ families come from villages located in very close proximity.
To conclude, we have presented a brief but complete review of the literature on FA, focusing on the genetic background of the disease. Our study expands the spectrum of RDH5 mutations, as we also report the novel mutation in the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase 5 gene. This study is the first report of a RDH5 gene mutation that affects the invariant tyrosine, one of the most conserved amino acid residues in SDRs, crucial for these enzymes’ activity. The location of the substitution, together with the mutation’s predicted influence on protein function, indicate that the p.Tyr175Phe mutation is probably pathogenic and can be recognised as the cause of FA. Moreover, we have presented the first molecular evidence for 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase 5 (RDH5) gene mutation in a Polish patient with this rare retinal disease. This study may also help clinicians to improve the difficult process of FA differential diagnosis, in which genetic analysis is an indispensable element, which would enable the correct treatment of patients.
References
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491:56–65. http://www.1000genomes.org. Accessed 11 February 2015
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7:248–249. http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/. Accessed 25 September 2014
Ajmal M, Khan MI, Neveling K, Khan YM, Ali SH, Ahmed W, Iqbal MS, Azam M, den Hollander AI, Collin RW, Qamar R, Cremers FP (2012) Novel mutations in RDH5 cause fundus albipunctatus in two consanguineous Pakistani families. Mol Vis 18:1558–1571
Albalat R, González-Duarte AS (1992) Protein engineering of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase. The hydroxyl group of Tyr152 is involved in the active site of the enzyme. FEBS Lett 308:235–239
Burstedt MS, Sandgren O, Golovleva I, Wachtmeister L (2008) Effects of prolonged dark adaptation in patients with retinitis pigmentosa of Bothnia type: an electrophysiological study. Doc Ophthalmol 116:193–205
Choi Y, Sims GE, Murphy S, Miller JR, Chan AP (2012) Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS One 7:e46688 http://provean.jcvi.org/index.php. Accessed 25 September 2014
Cideciyan AV, Haeseleer F, Fariss RN, Aleman TS, Jang GF, Verlinde CL, Marmor MF, Jacobson SG, Palczewski K (2000) Rod and cone visual cycle consequences of a null mutation in the 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase gene in man. Vis Neurosci 17:667–678
De Laey JJ (1993) Flecked retina disorders. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol 249:11–22
Driessen CA, Winkens HJ, Hoffmann K, Kuhlmann LD, Janssen BP, Van Vugt AH, Van Hooser JP, Wieringa BE, Deutman AF, Palczewski K, Ruether K, Janssen JJ (2000) Disruption of the 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase gene leads to accumulation of cis-retinols and cis-retinyl esters. Mol Cell Biol 20:4275–4287
Driessen CA, Janssen BP, Winkens HJ, Kuhlmann LD, Van Vugt AH, Pinckers AJ, Deutman AF, Janssen JJ (2001) Null mutation in the human 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase gene associated with fundus albipunctatus. Ophthalmology 108:1479–1484
Exome Variant Server, NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project (ESP), Seattle, WA. Home page at: http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/. Accessed 11 February 2015
Filling C, Nordling E, Benach J, Berndt KD, Ladenstein R, Jörnvall H, Oppermann U (2001) Structural role of conserved Asn179 in the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase scaffold. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:712–717
Gonzalez-Fernandez F, Kurz D, Bao Y, Newman S, Conway BP, Young JE, Han DP, Khani SC (1999) 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase mutations as a major cause of the congenital night-blindness disorder known as fundus albipunctatus. Mol Vis 5:41
Gränse L, Abrahamson M, Ponjavic V, Andréasson S (2001) Electrophysiological findings in two young patients with Bothnia dystrophy and a mutation in the RLBP1 gene. Ophthalmic Genet 22:97–105
Hajali M, Fishman GA, Dryja TP, Sweeney MO, Lindeman M (2009) Diagnosis in a patient with fundus albipunctatus and atypical fundus changes. Doc Ophthalmol 118:233–238
Hayashi T, Goto-Omoto S, Takeuchi T, Gekka T, Ueoka Y, Kitahara K (2006) Compound heterozygous RDH5 mutations in familial fleck retina with night blindness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 84:254–258
Hirose E, Inoue Y, Morimura H, Okamoto N, Fukuda M, Yamamoto S, Fujikado T, Tano Y (2000) Mutations in the 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase gene in Japanese patients with Fundus albipunctatus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3933–3935
Hotta K, Nakamura M, Kondo M, Ito S, Terasaki H, Miyake Y, Hida T (2003) Macular dystrophy in a Japanese family with fundus albipunctatus. Am J Ophthalmol 135:917–919
Iannaccone A, Tedesco SA, Gallaher KT, Yamamoto H, Charles S, Dryja TP (2007) Fundus albipunctatus in a 6-year old girl due to compound heterozygous mutations in the RDH5 gene. Doc Ophthalmol 115:111–116
Imaizumi M, Tatewaki SY, Kimoto K, Takaki Y, Nakatsuka K, Furushima M, Matsumoto CS, Choshi T (2005) Disappearance of puncta after uveitis in an eye with fundus albipunctatus. Retina 25:1096–1098
Jörnvall H, Persson B, Krook M, Atrian S, Gonzàlez-Duarte R, Jeffery J, Ghosh D (1995) Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR). Biochemistry 34:6003–6013
Kanski JJ (2003) Clinical ophthalmology: a systematic approach, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Katsanis N, Shroyer NF, Lewis RA, Cavender JC, Al-Rajhi AA, Jabak M, Lupski JR (2001) Fundus albipunctatus and retinitis punctata albescens in a pedigree with an R150Q mutation in RLBP1. Clin Genet 59:424–429
Kim TS, Maeda A, Maeda T, Heinlein C, Kedishvili N, Palczewski K, Nelson PS (2005) Delayed dark adaptation in 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase-deficient mice: a role of RDH11 in visual processes in vivo. J Biol Chem 280:8694–8704
Kranias G, Augsburger JJ, Raymond LA (1981) Resolution of night blindness in fundus albipunctatus. Ann Ophthalmol 13:871–874
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC (2009) Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 4:1073–1081. http://sift.jcvi.org/. Accessed 25 September 2014
Kuroiwa S, Kikuchi T, Yoshimura N (2000) A novel compound heterozygous mutation in the RDH5 gene in a patient with fundus albipunctatus. Am J Ophthalmol 130:672–675
Lidén M, Romert A, Tryggvason K, Persson B, Eriksson U (2001) Biochemical defects in 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase mutants associated with fundus albipunctatus. J Biol Chem 276:49251–49257
Liu X, Liu L, Li H, Xu F, Jiang R, Sui R (2015) RDH5 retinopathy (fundus albipunctatus) with preserved rod function. Retina 35:582–589
Maeda A, Maeda T, Palczewski K (2006) Improvement in rod and cone function in mouse model of Fundus albipunctatus after pharmacologic treatment with 9-cis-retinal. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:4540–4546
Makiyama Y, Ooto S, Hangai M, Ogino K, Gotoh N, Oishi A, Yoshimura N (2014) Cone abnormalities in fundus albipunctatus associated with RDH5 mutations assessed using adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Am J Ophthalmol 157:558–570
Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Geer LY, Geer RC, He J, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lanczycki CJ, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Wang Z, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zheng C, Bryant SH (2015) CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D222–D226. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml. Accessed 11 February 2015
Matsumoto Y, Haen SP, Spaide RF (2007) The white dot syndromes. Compr Ophthalmol Update 8:179–200
Moiseyev G, Chen Y, Takahashi Y, Wu BX, Ma JX (2005) RPE65 is the isomerohydrolase in the retinoid visual cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12413–12418
Nakamura M, Miyake Y (2002) Macular dystrophy in a 9-year-old boy with fundus albipunctatus. Am J Ophthalmol 133:278–280
Nakamura M, Hotta Y, Tanikawa A, Terasaki H, Miyake Y (2000) A high association with cone dystrophy in Fundus albipunctatus caused by mutations of the RDH5 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3925–3932
Nakamura M, Skalet J, Miyake Y (2003) RDH5 gene mutations and electroretinogram in fundus albipunctatus with or without macular dystrophy: RDH5 mutations and ERG in fundus albipunctatus. Doc Ophthalmol 107:3–11
Naz S, Ali S, Riazuddin SA, Farooq T, Butt NH, Zafar AU, Khan SN, Husnain T, Macdonald IM, Sieving PA, Hejtmancik JF, Riazuddin S (2011) Mutations in RLBP1 associated with fundus albipunctatus in consanguineous Pakistani families. Br J Ophthalmol 95:1019–1024
Niwa Y, Kondo M, Ueno S, Nakamura M, Terasaki H, Miyake Y (2005) Cone and rod dysfunction in fundus albipunctatus with RDH5 mutation: an electrophysiological study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:1480–1485
Oppermann U, Filling C, Hult M, Shafqat N, Wu X, Lindh M, Shafqat J, Nordling E, Kallberg Y, Persson B, Jörnvall H (2003) Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR): the 2002 update. Chem Biol Interact 143–144:247–253
Persson B, Krook M, Jörnvall H (1991) Characteristics of short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases and related enzymes. Eur J Biochem 200:537–543
Pras E, Pras E, Reznik-Wolf H, Sharon D, Raivech S, Barkana Y, Abu-Horowitz A, Ygal R, Banin E (2012) Fundus albipunctatus: novel mutations and phenotypic description of Israeli patients. Mol Vis 18:1712–1718
Rotenstreich Y, Harats D, Shaish A, Pras E, Belkin M (2010) Treatment of a retinal dystrophy, fundus albipunctatus, with oral 9-cis-{beta}-carotene. Br J Ophthalmol 94:616–621
Rotenstreich Y, Belkin M, Sadetzki S, Chetrit A, Ferman-Attar G, Sher I, Harari A, Shaish A, Harats D (2013) Treatment with 9-cis β-carotene-rich powder in patients with retinitis pigmentosa: a randomized crossover trial. JAMA Ophthalmol 131:985–992
Rüther K, Janssen BP, Kellner U, Janssen JJ, Bohne M, Reimann J, Driessen CA (2004) Clinical and genetic findings in a patient with fundus albipunctatus. Ophthalmologe 101:177–185
Sato M, Oshika T, Kaji Y, Nose H (2004) A novel homozygous Gly107Arg mutation in the RDH5 gene in a Japanese patient with fundus albipunctatus with sectorial retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Res 36:43–50
Schatz P, Preising M, Lorenz B, Sander B, Larsen M, Eckstein C, Rosenberg T (2010) Lack of autofluorescence in fundus albipunctatus associated with mutations in RDH5. Retina 30:1704–1713
Schatz P, Preising M, Lorenz B, Sander B, Larsen M, Rosenberg T (2011) Fundus albipunctatus associated with compound heterozygous mutations in RPE65. Ophthalmology 118:888–894
Sekiya K, Nakazawa M, Ohguro H, Usui T, Tanimoto N, Abe H (2003) Long-term fundus changes due to Fundus albipunctatus associated with mutations in the RDH5 gene. Arch Ophthalmol 121:1057–1059
Sergouniotis PI, Sohn EH, Li Z, McBain VA, Wright GA, Moore AT, Robson AG, Holder GE, Webster AR (2011) Phenotypic variability in RDH5 retinopathy (fundus albipunctatus). Ophthalmology 118:1661–1670
Simon A, Hellman U, Wernstedt C, Eriksson U (1995) The retinal pigment epithelial-specific 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase belongs to the family of short chain alcohol dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem 270:1107–1112
Simon A, Lagercrantz J, Bajalica-Lagercrantz S, Eriksson U (1996) Primary structure of human 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase and organization and chromosomal localization of the corresponding gene. Genomics 36:424–430
Simon A, Romert A, Gustafson AL, McCaffery JM, Eriksson U (1999) Intracellular localization and membrane topology of 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase in the retinal pigment epithelium suggest a compartmentalized synthesis of 11-cis retinaldehyde. J Cell Sci 112:549–558
Sparkes RS, Heinzmann C, Goldflam S, Kojis T, Saari JC, Mohandas T, Klisak I, Bateman JB, Crabb JW (1992) Assignment of the gene (RLBP1) for cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein (CRALBP) to human chromosome 15q26 and mouse chromosome 7. Genomics 12:58–62
Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, Shaw K, Phillips A, Cooper DN (2014) The Human Gene Mutation Database: building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic medicine. Hum Genet 133:1–9 http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php. Accessed 25 September 2014
Travis GH, Golczak M, Moise AR, Palczewski K (2007) Diseases caused by defects in the visual cycle: retinoids as potential therapeutic agents. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:469–512
Wada Y, Abe T, Sato H, Tamai M (2001) A novel Gly35Ser mutation in the RDH5 gene in a Japanese family with fundus albipunctatus associated with cone dystrophy. Arch Ophthalmol 119:1059–1063
Waldron D, Medefindt C (2014) Retina International. Home page at: http://www.retina-international.org. Accessed 25 September 2014
Walia S, Fishman GA, Kapur R (2009) Flecked-retina syndromes. Ophthalmic Genet 30:69–75
Wang C, Nakanishi N, Ohishi K, Hikoya A, Koide K, Sato M, Nakamura M, Hotta Y, Minoshima S (2008) Novel RDH5 mutation in family with mother having fundus albipunctatus and three children with retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmic Genet 29:29–32
Wang NK, Chuang LH, Lai CC, Chou CL, Chu HY, Yeung L, Chen YP, Chen KJ, Wu WC, Chen TL, Chao AN, Hwang YS (2012) Multimodal fundus imaging in fundus albipunctatus with RDH5 mutation: a newly identified compound heterozygous mutation and review of the literature. Doc Ophthalmol 125:51–62
Yamamoto H, Simon A, Eriksson U, Harris E, Berson EL, Dryja TP (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase cause delayed dark adaptation and fundus albipunctatus. Nat Genet 22:188–191
Yamamoto H, Yakushijin K, Kusuhara S, Escaño MF, Nagai A, Negi A (2003) A novel RDH5 gene mutation in a patient with fundus albipunctatus presenting with macular atrophy and fading white dots. Am J Ophthalmol 136:572–574
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (806/N-NIEMCY/2010/0).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Michal Witt
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Skorczyk-Werner, A., Pawłowski, P., Michalczuk, M. et al. Fundus albipunctatus: review of the literature and report of a novel RDH5 gene mutation affecting the invariant tyrosine (p.Tyr175Phe). J Appl Genetics 56, 317–327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-015-0281-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-015-0281-x