Abstract
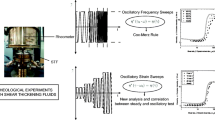
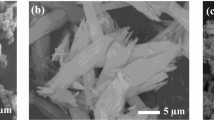
Shear thickening fluids (STFs) of differing compositions were fabricated and characterised in order to observe the effect of varying chemical and material properties on the resultant rheological behavior. Steady shear tests showed that for a given carrier fluid and particle size exists an optimum weight fraction which exhibits optimal shear thickening performance. Testing also showed that increasing particle size resulted in increased shear thickening performance and its onset whilst altering the carrier fluid chemistry has a significant effect on the thickening performance. An explanation is provided connecting the effect of varying particle size, carrier fluid chemistry and weight fraction to the resultant rheological behavior of the STFs. Two STFs were chosen for further testing due to their improved but contrasting rheological behaviors. Both STFs displayed a relationship between steady and dynamic shear conditions via the Modified Cox-Merz rule at high strain amplitudes (γ≥500%). Understanding the effects of particle and liquid polymer chemistry on the shear thickening effect will assist in ‘tailoring’ STFs for certain potential or existing applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird, J.A., R. Olayo-Valles, C. Rinaldi, and L.S. Taylor, 2010, Effect of molecular weight, temperature, and additives on the moisture sorption properties of polyethylene glycol, J. Pharm. Sci. 99, 154–168.
Barnes, H.A., 1989, Shear-thickening (“Dilatancy”) in suspensions of nonaggregating solid particles dispersed in Newtonian liquids, J. Rheol. 33, 329–366.
Bergenholtz, J., J.F. Brady, and M. Vicic, 2002, The non-Newtonian rheology of dilute colloidal suspensions, J. Fluid Mech. 456, 239–275.
Boersma, W.H., J. Laven, and H.N. Stein, 1995, Computer simulations of shear thickening of concentrated dispersions, J. Rheol. 39, 841–860.
Chellamuthu, M., E.M. Arndt, and J.P. Rothstein, 2009, Extensional rheology of shear-thickening nanoparticle suspensions, Soft Matter 5, 2117–2124.
Durlofsky, L., J.F. Brady, and G. Bossis, 1987, Dynamic simulation of hydrodynamically interacting particles, J. Fluid Mech. 180, 21–49.
Fischer, C., C.J.G. Plummer, V. Michaud, P.E. Bourban, and J.A.E. Månson, 2007, Pre- and post-transition behavior of shear-thickening fluids in oscillating shear, Rheol. Acta 46, 1099–1108.
Fischer, C., S.A. Braun, P.-E. Bourban, V. Michaud, C.J.G. Plummer, and J.-A.E. Månson, 2006, Dynamic properties of sandwich structures with integrated shear-thickening fluids, Smart Mater. Struct. 15, 1467–1475.
Galindo-Rosales, F.J., F.J. Rubio-Hernández, and J.F. Velázquez-Navarro, 2009, Shear-thickening behavior of Aerosil® R816 nanoparticles suspensions in polar organic liquids, Rheol. Acta 48, 699–708.
Gong, X., Y. Xu, W. Zhu, S. Xuan, W. Jiang, and W. Jiang, 2014, Study of the knife stab and puncture-resistant performance for shear thickening fluid enhanced fabric, J. Compos Mater. 48, 641–657.
Gun'ko, V.M., I.F. Mironyuk, V.I. Zarko, E.F. Voronin, V.V. Turov, E.M. Pakhlov, E.V. Goncharuk, Y.M. Nychiporuk, N.N. Vlasova, P.P. Gorbik, O.A. Mishchuk, A.A. Chuiko, T.V. Kulik, B.B. Palyanytsya, S.V. Pakhovchishin, J. Skubiszewska-Zieba, W. Janusz, A.V. Turov, and R. Leboda, 2005, Morphology and surface properties of fumed silicas, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 289, 427–445.
Hassan, T.A., V.K. Rangari, and S. Jeelani, 2010, Synthesis, processing and characterization of shear thickening fluid (STF) impregnated fabric composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 527, 2892–2899.
He, Q., X. Gong, S, Xuan, W. Jiang, and Q. Chen, 2015, Shear thickening of suspensions of porous silica nanoparticles, J. Mater. Sci. 50, 6041–6049.
Hoffman, R.L., 1972, Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. I. Observation of a flow instability, J. Rheol. 16, 155–173.
Hoffman, R.L., 1974, Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. II. Theory and experimental tests, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 46, 491–506.
Jiang, J., Y. Liu, L. Shan, X. Zhang, Y. Meng, H.J. Choi, and Y. Tian, 2014, Shear thinning and shear thickening characteristics in electrorheological fluids, Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 015003.
Lee, B.W. and C.G. Kim, 2012, Computational analysis of shear thickening fluid impregnated fabrics subjected to ballistic impacts, Adv. Compos. Mater. 21, 177–192.
Lee, J.D., J.H. So, and S.M. Yang, 1999, Rheological behavior and stability of concentrated silica suspensions, J. Rheol. 43, 1117–1140.
Lee, Y.S., E.D. Wetzel, and N.J. Wagner, 2003, The ballistic impact characteristics of Kevlar® woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fluid, J. Mater. Sci. 38, 2825–2833.
Li, X., H.L. Cao, S. Gao, F.Y. Pan, L.Q. Weng, S.H. Song, and Y.D. Huang, 2013, Preparation of body armour material of Kevlar fabric treated with colloidal silica nanocomposite, Plast. Rubber Compos. 37, 223–226.
Liu, X.-Q., R.-Y. Bao, X.-J. Wu, W. Yang, B.-H. Xie, and M.-B. Yang, 2015, Temperature induced gelation transition of a fumed silica/PEG shear thickening fluid, RSC Adv. 5, 18367–18374.
Neagu, R.C., P.E. Bourban, and J.A.E. Månson, 2009, Micromechanics and damping properties of composites integrating shear thickening fluids, Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 515–522.
Peng, G.R., W. Li, T.F. Tian, J. Ding, and M. Nakano, 2014, Experimental and modeling study of viscoelastic behaviors of magneto-rheological shear thickening fluids, Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 26, 149–158.
Petel, O.E., S. Ouellet, J. Loiseau, B.J. Marr, D.L. Frost, and A.J. Higgins, 2013, The effect of particle strength on the ballistic resistance of shear thickening fluids, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 064103.
Raghavan, S.R. and S.A. Khan, 1997, Shear-thickening response of fumed silica suspensions under steady and oscillatory shear, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 185, 57–67.
Raghavan, S.R., H.J. Walls, and S.A. Khan, 2000, Rheology of silica dispersions in organic liquids: new evidence for solvation forces dictated by hydrogen bonding, Langmuir 16, 7920–7930.
Shan, L., Y. Tian, Y.G. Meng, and X.J. Zhang, 2015, Influences of medium and temperature on the shear thickening behavior of nano fumed silica colloids, Acta Phys. Sin. 64, 068301.
Srivastava, A., A. Majumdar, and B.S. Butola, 2012, Improving the impact resistance of textile structures by using shear thickening fluids: a review, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mat. Sci. 37, 115–129.
Wang, R. and S.L. Wunder, 2000, Effects of silanol density, distribution, and hydration state of fumed silica on the formation of self-assembled monolayers of n-octadecyltrichlorosilane, Langmuir 16, 5008–5016.
Wetzel, E.D., Y.S. Lee, R.G. Egres, K.M. Kirkwood, J.E. Kirkwood, and N.J. Wagner, 2004, The effect of rheological parameters on the ballistic properties of shear thickening fluid (STF)-Kevlar composites, Materials Processing and Design: Modeling, Simulation and Applications NUMIFORM 2004, Columbus, USA, 288–293.
Xu, Y.L., X.L Gong, C. Penga, Y.Q. Sun, W.Q Jiang, and Z. Zhang, 2010, Shear thickening fluids based on additives with different concentrations and molecular chain lengths, Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 23, 342–346.
Zhang, X., W. Li, and X. Gong, 2010, Thixotropy of MR shearthickening fluids, Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 125012.
Zhao, J., H. Cao, X. Li, J. Wan, K. Wang, and J. Zhang, 2012a, Effect of SiO2 particle size on stab resistant properties of STF/Kevlar composites, Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 29, 54–61.
Zhao, J., H. Cao, X. Li, J. Wan, K. Wang, and J. Zhang, 2012b, The stab resistant properties of Kevlar/STF composites, Third International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Shenzhen, China, 84091L-84091L-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moriana, A.D., Tian, T., Sencadas, V. et al. Comparison of rheological behaviors with fumed silica-based shear thickening fluids. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 28, 197–205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0020-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0020-9