Abstract
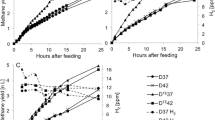
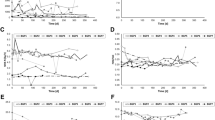
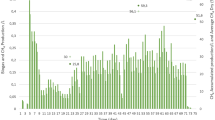
Ammonia is a major environmental factor influencing biomethanation in full-scale anaerobic digesters. In this study, the effect of different ammonia levels on methanogenic pathways and methanogenic community composition of full-scale biogas plants was investigated. Eight full-scale digesters operating under different ammonia levels were sampled, and the residual biogas production was followed in fed-batch reactors. Acetate, labelled in the methyl group, was used to determine the methanogenic pathway by following the 14CH4 and 14CO2 production. Fluorescence in situ hybridisation was used to determine the methanogenic communities’ composition. Results obtained clearly demonstrated that syntrophic acetate oxidation coupled with hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis was the dominant pathway in all digesters with high ammonia levels (2.8–4.57 g NH4 +-N L−1), while acetoclastic methanogenic pathway dominated at low ammonia (<1.21 g NH4 +-N L−1). Thermophilic Methanomicrobiales spp. and mesophilic Methanobacteriales spp. were the most abundant methanogens at free ammonia concentrations above 0.44 g NH3-N L−1 and total ammonia concentrations above 2.8 g NH4 +-N L−1, respectively. Meanwhile, in anaerobic digesters with low ammonia (<1.21 g NH4 +-N L−1) and free ammonia (<0.07 g NH3-N L−1) levels, mesophilic and thermophilic Methanosaetaceae spp. were the most abundant methanogens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahring B (1995) Methanogenesis in thermophilic biogas reactors. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Int J G 67:91–102
Angelidaki I, Ellegaard L, Ahring BK (1993) A mathematical model for dynamic simulation of anaerobic digestion of complex substrates: focusing on ammonia inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:159–166
Angelidaki I, Boe K, Ellegaard L (2005) Effect of operating conditions and reactor configuration on efficiency of full-scale biogas plants. Water Sci Technol 52:189–194
Angelidaki I, Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Plugge CM, Stams AJM (2011) Biomethanation and its potential. In: Amy CR, Stephen WR (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 494. Academic, New York, pp 327–351
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Banu JR, Kaliappan S, Yeom IT (2007) Treatment of domestic wastewater using upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:363–370
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99:4044–4064
de Baere LA, Devocht M, Van Assche P, Verstraete W (1984) Influence of high NaCl and NH4Cl salt levels on methanogenic associations. Water Res 18:543–548
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:173–190
Fotidis IA, Karakashev D, Angelidaki I (2013a) Bioaugmentation with an acetate-oxidising consortium as a tool to tackle ammonia inhibition of anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 146:57–62
Fotidis IA, Karakashev D, Kotsopoulos TA, Martzopoulos GG, Angelidaki I (2013b) Effect of ammonium and acetate on methanogenic pathway and methanogenic community composition. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83:38–48
Gong W-J, Liang H, Li W-Z, Wang Z–Z (2011) Selection and evaluation of biofilm carrier in anaerobic digestion treatment of cattle manure. Energy 36:3572–3578
Gray N, Sherry A, Larter S, Erdmann M, Leyris J, Liengen T, Beeder J, Head I (2009) Biogenic methane production in formation waters from a large gas field in the North Sea. Extremophiles 13:511–519
Hafner SD, Bisogni JJ, Jewell WJ (2006) Measurement of un-ionized ammonia in complex mixtures. Environ Sci Technol 40:1597–1602
Hansen KH, Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1998) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure: inhibition by ammonia. Water Res 32:5–12
Hao L-P, Lü F, Li L, Shao L-M, He P-J (2012) Shift of pathways during initiation of thermophilic methanogenesis at different initial pH. Bioresour Technol 126:418–424
Hejnfelt A, Angelidaki I (2009) Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse by-products. Biomass Bioenerg 33:1046–1054
Hugenholtz P (2002) Design and evaluation of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. In: Aquino de Muro M, Rapley R (eds) Gene probes: principles and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 29–42
Jarrell KF, Saulnier M, Ley A (1987) Inhibition of methanogenesis in pure cultures by ammonia, fatty acids, and heavy metals, and protection against heavy metal toxicity by sewage sludge. Can J Microbiol 33:551–554
Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Angelidaki I (2005) Influence of environmental conditions on methanogenic compositions in anaerobic biogas reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:331–338
Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Trably E, Angelidaki I (2006) Acetate oxidation is the dominant methanogenic pathway from acetate in the absence of methanosaetaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5138–5141
Kayhanian M (1994) Performance of a high-solids anaerobic digestion process under various ammonia concentrations. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 59:349–352
Koster IW, Koomen E (1988) Ammonia inhibition of the maximum growth rate (μm) of hydrogenotrophic methanogens at various pH-levels and temperatures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:500–505
Kotsopoulos TA, Fotidis IA, Tsolakis N, Martzopoulos GG (2009) Biohydrogen production from pig slurry in a CSTR reactor system with mixed cultures under hyper-thermophilic temperature (70°C). Biomass Bioenerg 33:1168–1174
Kougias PG, Fotidis IA, Zaganas ID, Kotsopoulos TA, Martzopoulos GG (2013) Zeolite and swine inoculum effect on poultry manure biomethanation. Int Agrophys 27:169–173
Lu F, Hao L, Guan D, Qi Y, Shao L, He P (2013) Synergetic stress of acids and ammonium on the shift in the methanogenic pathways during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of organics. Water Res 47:2297–2306
Minale M, Worku T (2013) Anaerobic co-digestion of sanitary wastewater and kitchen solid waste for biogas and fertilizer production under ambient temperature: waste generated from condominium house. Int J Environ Sci Technol. doi: 10.1007/s13762-013-0255-7
Nakashimada Y, Ohshima Y, Minami H, Yabu H, Namba Y, Nishio N (2008) Ammonia-methane two-stage anaerobic digestion of dehydrated waste-activated sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:1061–1069
Nielsen HB, Angelidaki I (2008a) Codigestion of manure and industrial organic waste at centralized biogas plants: process imbalances and limitations. Water Sci Technol 58:1521–1528
Nielsen HB, Angelidaki I (2008b) Strategies for optimizing recovery of the biogas process following ammonia inhibition. Bioresour Technol 99:7995–8001
Rajagopal R, Massé DI, Singh G (2013) A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour Technol 0. (in press) doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.030
Raskin L, Stromley JM, Rittmann BE, Stahl DA (1994) Group-specific 16S rRNA hybridization probes to describe natural communities of methanogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1232–1240
Sarmiento FB, Leigh JA, Whitman WB (2011) Genetic systems for hydrogenotrophic methanogens. In: Amy CR, Stephen WR (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 494. Academic, New York, pp 43–73. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-385112-3.00003-2
Schauer-Gimenez AE, Zitomer DH, Maki JS, Struble CA (2010) Bioaugmentation for improved recovery of anaerobic digesters after toxicant exposure. Water Res 44:3555–3564
Sekiguchi Y, Kamagata Y, Nakamura K, Ohashi A, Harada H (1999) Fluorescence in situ hybridization using 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides reveals localization of methanogens and selected uncultured bacteria in mesophilic and thermophilic sludge granules. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1280–1288
Shima S, Hérault DA, Berkessel A, Thauer RK (1998) Activation and thermostabilization effects of cyclic 2,3-diphosphoglycerate on enzymes from the hyperthermophilic Methanopyrus kandleri. Arch Microbiol 170:469–472
Stahl DA, Amann R (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, United Kingdom, pp 205–248
Stams AJM, De Bok FAM, Plugge CM, Van Eekert MHA, Dolfing J, Schraa G (2006) Exocellular electron transfer in anaerobic microbial communities. Environ Microbiol 8:371–382
Tabatabaei M, Rahim RA, Abdullah N, Wright A-DG, Shirai Y, Sakai K, Sulaiman A, Hassan MA (2010) Importance of the methanogenic archaea populations in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Process Biochem 45:1214–1225
Tumbula DL, Whitman WB (1999) Genetics of Methanococcus: possibilities for functional genomics in Archaea. Mol Microbiol 33:1–7
Westerholm M, Dolfing J, Sherry A, Gray ND, Head IM, Schnürer A (2011) Quantification of syntrophic acetate-oxidizing microbial communities in biogas processes. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:500–505
Yenigün O, Demirel B (2013) Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: a review. Process Biochem 48:901–911
Acknowledgments
We thank Hector Garcia for technical assistance with the experiments and Mike Podevin for editing support. This work was supported by Energinet.dk under the project framework ForskEL “Innovative process for digesting high ammonia wastes” (programme no. 2010-10537) and by the Bioref-Øresund project under EU INTERREG IVA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fotidis, I.A., Karakashev, D. & Angelidaki, I. The dominant acetate degradation pathway/methanogenic composition in full-scale anaerobic digesters operating under different ammonia levels. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 2087–2094 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0407-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0407-9